Descheduler 集群均衡器
为什么需要集群均衡器
从 kube-scheduler 的角度来看,它通过各种算法计算出最佳节点去运行 Pod 是非常完美的,当出现新的 Pod 进行调度时,调度程序会根据其当时对 Kubernetes 集群的资源描述做出最佳调度决定。 但是 Kubernetes 集群是非常动态的,由于整个集群范围内的变化,比如一个节点为了维护,我们先执行了驱逐操作,这个节点上的所有 Pod 会被驱逐到其他节点去, 但是当我们维护完成后,之前的 Pod 并不会自动回到该节点上来,因为 Pod 一旦被绑定了节点是不会触发重新调度的,由于这些变化,Kubernetes 集群在一段时间内就出现了不均衡的状态,所以需要均衡器来重新平衡集群
- 一些节点过度使用
- 节点添加污点或则labels后,节点上的pod 不不符合要求
- 当新节点被添加到集群
github.com/kubernetes-sigs/descheduler
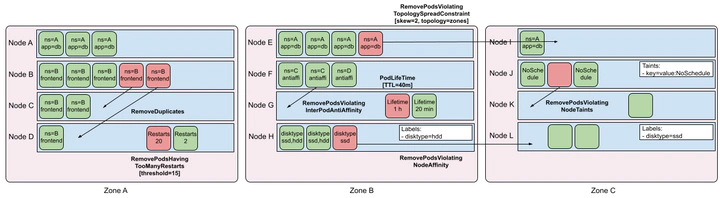
descheduler 目前支持的策略
| 策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| RemoveDuplicates | 将节点上同类型的Pod进行迁移,确保只有一个Pod与同一节点上运行的ReplicaSet、Replication Controller、StatefulSet或者Job关联 |
| LowNodeUtilization | 将 requests 比率较高节点上的Pod进行迁移,该策略主要用于查找未充分利用的节点,并从其他节点驱逐 Pod,以便 kube-scheudler 重新将它们调度到未充分利用的节点上。 |
| HighNodeUtilization | 将 requests 比率较低节点上的Pod进行迁移 |
| RemovePodsViolatingInterPodAntiAffinity | 将不满足反亲和性的Pod进行迁移 |
| RemovePodsViolatingNodeAffinity | 将不满足节点节点亲和性策略的Pod进行迁移 |
| RemovePodsViolatingNodeTaints | 将不满足节点污点策略的Pod进行迁移 |
| RemovePodsViolatingTopologySpreadConstraint | 该策略确保从节点驱逐违反拓扑分布约束的 Pods,具体来说,它试图驱逐将拓扑域平衡到每个约束的 maxSkew 内所需的最小 Pod 数,不过该策略需要 k8s 版本高于1.18才能使用 |
| RemovePodsHavingTooManyRestarts | 将重启次数过多的Pod进行迁移 |
| PodLifeTime | 该策略用于驱逐比 maxPodLifeTimeSeconds 更旧的 Pods,可以通过 podStatusPhases 来配置哪类状态的 Pods 会被驱逐 |
| RemoveFailedPods | 将运行失败的Pod进行迁移 |
LowNodeUtilization
该策略主要用于查找未充分利用资源的节点,并从其他节点驱逐 Pod 将它们重新调度到这些未充分利用的节点上。
apiVersion: "descheduler/v1alpha2"
kind: "DeschedulerPolicy"
profiles:
- name: default
pluginConfig:
- args:
evictLocalStoragePods: true
ignorePvcPods: true
name: DefaultEvictor
# ...
- args:
targetThresholds:
cpu: 50
memory: 50
pods: 50
thresholds:
cpu: 20
memory: 20
pods: 20
name: LowNodeUtilization
- targetThresholds: 大于它,被认为需要被驱逐
- thresholds: 小于它,被认为需要调度到这
- numberOfNodes: 针对大集群,需要重调度节点数量大于它,才需要考虑
- evictionLimits: 驱逐限制
注意点: descheduler 默认基于 requests 和 limits,并未基于节点真实负载, 目的是保持与 kube-scheduler 一致 。
支持以下三种资源类型:cpu、memory、pods, 其他(包括GPU).
v0.33.0 特性: 可以增加对于节点的监控,基于真实负载进行重调度调整,相关 commit : https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/descheduler/pull/1533
LowNodeUtilization 初始化
func NewLowNodeUtilization(
genericArgs runtime.Object, handle frameworktypes.Handle,
) (frameworktypes.Plugin, error) {
args, ok := genericArgs.(*LowNodeUtilizationArgs)
if !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf(
"want args to be of type LowNodeUtilizationArgs, got %T",
genericArgs,
)
}
// resourceNames holds a list of resources for which the user has
// provided thresholds for. extendedResourceNames holds those as well
// as cpu, memory and pods if no prometheus collection is used.
resourceNames := getResourceNames(args.Thresholds)
extendedResourceNames := resourceNames
// if we are using prometheus we need to validate we have everything we
// need. if we aren't then we need to make sure we are also collecting
// data for cpu, memory and pods.
metrics := args.MetricsUtilization
if metrics != nil && metrics.Source == api.PrometheusMetrics {
// 相关 prometheus 参数校验
if err := validatePrometheusMetricsUtilization(args); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
} else {
extendedResourceNames = uniquifyResourceNames(
append(
resourceNames,
v1.ResourceCPU,
v1.ResourceMemory,
v1.ResourcePods,
),
)
}
// 驱逐 pod 时过滤 pod
podFilter, err := podutil.
NewOptions().
WithFilter(handle.Evictor().Filter).
BuildFilterFunc()
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("error initializing pod filter function: %v", err)
}
// 创建 requestUsage client
var usageClient usageClient = newRequestedUsageClient(
extendedResourceNames, handle.GetPodsAssignedToNodeFunc(),
)
if metrics != nil {
// 使用实际数据client
usageClient, err = usageClientForMetrics(args, handle, extendedResourceNames)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
return &LowNodeUtilization{
handle: handle,
args: args,
underCriteria: thresholdsToKeysAndValues(args.Thresholds),
overCriteria: thresholdsToKeysAndValues(args.TargetThresholds),
resourceNames: resourceNames,
extendedResourceNames: extendedResourceNames,
podFilter: podFilter,
usageClient: usageClient,
}, nil
}
// https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/descheduler/blob/98e6ed65874eb223ba1f6861df87eb9a574e3f2c/pkg/framework/plugins/nodeutilization/lownodeutilization.go
// 平衡
func (l *LowNodeUtilization) Balance(ctx context.Context, nodes []*v1.Node) *frameworktypes.Status {
// 这里用 prometheus 作为案例: 同步节点资源利用率及pod数量
if err := l.usageClient.sync(ctx, nodes); err != nil {
return &frameworktypes.Status{
Err: fmt.Errorf("error getting node usage: %v", err),
}
}
// 获取节点映射, 资源使用,节点pod
nodesMap, nodesUsageMap, podListMap := getNodeUsageSnapshot(nodes, l.usageClient)
capacities := referencedResourceListForNodesCapacity(nodes)
// 转换成百分比
var usage map[string]api.ResourceThresholds
var thresholds map[string][]api.ResourceThresholds
if l.args.UseDeviationThresholds { // 浮动的阈值
// ..
)
} else {
// 静态数值
usage, thresholds = assessNodesUsagesAndStaticThresholds(
nodesUsageMap,
capacities,
l.args.Thresholds,
l.args.TargetThresholds,
)
}
// classify nodes in under and over utilized. we will later try to move
// pods from the overutilized nodes to the underutilized ones.
nodeGroups := classifier.Classify(
usage, thresholds,
// 未充分利用
func(nodeName string, usage, threshold api.ResourceThresholds) bool {
// 过滤不可调度的
if nodeutil.IsNodeUnschedulable(nodesMap[nodeName]) {
klog.V(2).InfoS(
"Node is unschedulable, thus not considered as underutilized",
"node", klog.KObj(nodesMap[nodeName]),
)
return false
}
return isNodeBelowThreshold(usage, threshold)
},
// 充分利用的
func(nodeName string, usage, threshold api.ResourceThresholds) bool {
return isNodeAboveThreshold(usage, threshold)
},
)
// the nodeutilization package was designed to work with NodeInfo
// structs. these structs holds information about how utilized a node
// is. we need to go through the result of the classification and turn
// it into NodeInfo structs.
nodeInfos := make([][]NodeInfo, 2)
categories := []string{"underutilized", "overutilized"}
classifiedNodes := map[string]bool{}
for i := range nodeGroups {
for nodeName := range nodeGroups[i] {
classifiedNodes[nodeName] = true
klog.InfoS(
"Node has been classified",
"category", categories[i],
"node", klog.KObj(nodesMap[nodeName]),
"usage", nodesUsageMap[nodeName],
"usagePercentage", normalizer.Round(usage[nodeName]),
)
nodeInfos[i] = append(nodeInfos[i], NodeInfo{
NodeUsage: NodeUsage{
node: nodesMap[nodeName],
usage: nodesUsageMap[nodeName],
allPods: podListMap[nodeName],
},
available: capNodeCapacitiesToThreshold(
nodesMap[nodeName],
thresholds[nodeName][1],
l.extendedResourceNames,
),
})
}
}
// 打印充分利用的
for nodeName := range nodesMap {
if !classifiedNodes[nodeName] {
klog.InfoS(
"Node is appropriately utilized",
"node", klog.KObj(nodesMap[nodeName]),
"usage", nodesUsageMap[nodeName],
"usagePercentage", normalizer.Round(usage[nodeName]),
)
}
}
// 分别获取低于标准和高于标准的节点
lowNodes, highNodes := nodeInfos[0], nodeInfos[1]
// log messages for nodes with low and high utilization
klog.V(1).InfoS("Criteria for a node under utilization", l.underCriteria...)
klog.V(1).InfoS("Number of underutilized nodes", "totalNumber", len(lowNodes))
klog.V(1).InfoS("Criteria for a node above target utilization", l.overCriteria...)
klog.V(1).InfoS("Number of overutilized nodes", "totalNumber", len(highNodes))
// 校验逻辑
// 判断是否需要继续驱逐
continueEvictionCond := func(nodeInfo NodeInfo, totalAvailableUsage api.ReferencedResourceList) bool {
if !isNodeAboveTargetUtilization(nodeInfo.NodeUsage, nodeInfo.available) {
return false
}
for name := range totalAvailableUsage {
if totalAvailableUsage[name].CmpInt64(0) < 1 {
return false
}
}
return true
}
// 按照降序排序
sortNodesByUsage(highNodes, false)
var nodeLimit *uint
if l.args.EvictionLimits != nil {
nodeLimit = l.args.EvictionLimits.Node
}
// 基于优先级驱逐 pod
evictPodsFromSourceNodes(
ctx,
l.args.EvictableNamespaces,
highNodes,
lowNodes,
l.handle.Evictor(),
evictions.EvictOptions{StrategyName: LowNodeUtilizationPluginName},
l.podFilter,
l.extendedResourceNames,
continueEvictionCond,
l.usageClient,
nodeLimit,
)
return nil
}
func evictPodsFromSourceNodes(
ctx context.Context,
evictableNamespaces *api.Namespaces,
sourceNodes, destinationNodes []NodeInfo,
podEvictor frameworktypes.Evictor,
evictOptions evictions.EvictOptions,
podFilter func(pod *v1.Pod) bool,
resourceNames []v1.ResourceName,
continueEviction continueEvictionCond,
usageClient usageClient,
maxNoOfPodsToEvictPerNode *uint,
) {
// 计算可用资源
available, err := assessAvailableResourceInNodes(destinationNodes, resourceNames)
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "unable to assess available resources in nodes")
return
}
klog.V(1).InfoS("Total capacity to be moved", usageToKeysAndValues(available)...)
destinationTaints := make(map[string][]v1.Taint, len(destinationNodes))
for _, node := range destinationNodes {
destinationTaints[node.node.Name] = node.node.Spec.Taints
}
for _, node := range sourceNodes {
klog.V(3).InfoS(
"Evicting pods from node",
"node", klog.KObj(node.node),
"usage", node.usage,
)
nonRemovablePods, removablePods := classifyPods(node.allPods, podFilter)
klog.V(2).InfoS(
"Pods on node",
"node", klog.KObj(node.node),
"allPods", len(node.allPods),
"nonRemovablePods", len(nonRemovablePods),
"removablePods", len(removablePods),
)
if len(removablePods) == 0 {
klog.V(1).InfoS(
"No removable pods on node, try next node",
"node", klog.KObj(node.node),
)
continue
}
klog.V(1).InfoS(
"Evicting pods based on priority, if they have same priority, they'll be evicted based on QoS tiers",
)
// sort the evictable Pods based on priority. This also sorts
// them based on QoS. If there are multiple pods with same
// priority, they are sorted based on QoS tiers.
podutil.SortPodsBasedOnPriorityLowToHigh(removablePods)
// 驱逐直到满足条件
if err := evictPods(
ctx,
evictableNamespaces,
removablePods,
node,
available,
destinationTaints,
podEvictor,
evictOptions,
continueEviction,
usageClient,
maxNoOfPodsToEvictPerNode,
); err != nil {
switch err.(type) {
case *evictions.EvictionTotalLimitError:
return
default:
}
}
}
}
koordinator 负载感知重调度
https://koordinator.sh/zh-Hans/docs/user-manuals/load-aware-descheduling
LowNodeLoad 插件有两个最重要的参数:
- highThresholds 表示负载水位的目标安全阈值,超过该阈值的节点上的 Pod 将参与重调度;
- lowThresholds 表示负载水位的空闲安全水位。低于该阈值的节点上的 Pod 不会被重调度。
lowThresholds 为 45%,highThresholds 为 70%,我们可以把节点归为三类:
- 空闲节点(Idle Node)。资源利用率低于 45% 的节点;
- 正常节点(Normal Node)。资源利用率高于 45% 但低于 70% 的节点,这个负载水位区间是我们期望的合理的区间范围
- 热点节点(Hotspot Node)。如果节点资源利用率高于 70%,这个节点就会被判定为不安全了,属于热点节点,应该驱逐一部分 Pod,降低负载水位,使其不超过 70%。
在迁移前,koord-descheduler 会计算出实际空闲容量,确保要迁移的 Pod 的实际利用率之和不超过集群内空闲总量。 这些实际空闲容量来自于空闲节点,一个空闲节点实际空闲容量 = (highThresholds - 节点当前负载) x 节点总容量。 假设节点 A 的负载水位是 20%,highThreshold 是 70%,节点 A 的 CPU 总量为 96C,那么 (70%-20%) x 96 = 48C,这 48C 就是可以承载的空闲容量了。
在迁移热点节点时,会过滤筛选节点上的 Pod,目前 koord-descheduler 支持多种筛选参数,可以避免迁移驱逐非常重要的 Pod:
- 按 namespace 过滤。可以配置成只筛选某些 namespace 或者过滤掉某些 namespace
- 按 pod selector 过滤。可以通过 label selector 筛选出 Pod,或者排除掉具备某些 Label 的 Pod
- 配置 nodeFit 检查调度规则是否有备选节点。当开启后,koord-descheduler 根据备选 Pod 对应的 Node
筛选 Pod 并完成排序后,开始执行迁移操作。迁移前会检查剩余空闲容量是否满足和当前节点的负载水位是否高于目标安全阈值,如果这两个条件中的一个不能满足,将停止重调度。 每迁移一个 Pod 时,会预扣剩余空闲容量,同时也会调整当前节点的负载水位,直到剩余容量不足或者水位达到安全阈值。