kube-apiserver APF(API Priority and Fairness 优先级和公平性)
对于集群管理员来说,控制 Kubernetes API 服务器在过载情况下的行为是一项关键任务。 kube-apiserver 有一些控件(例如:命令行标志 –max-requests-inflight 和 –max-mutating-requests-inflight), 可以限制将要接受的未处理的请求,从而防止过量请求入站,潜在导致 API 服务器崩溃。 但是这些标志不足以保证在高流量期间,最重要的请求仍能被服务器接受。
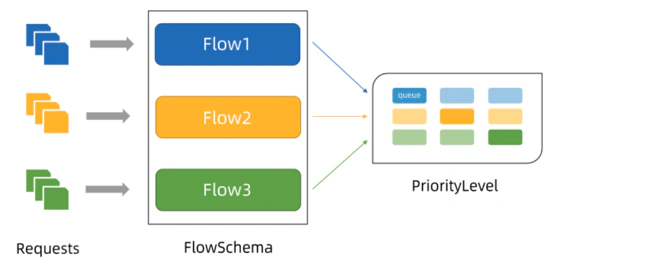
API 优先级和公平性(APF)是一种替代方案,可提升上述最大并发限制。 APF 以更细粒度的方式对请求进行分类和隔离。 它还引入了空间有限的排队机制,因此在非常短暂的突发情况下,API 服务器不会拒绝任何请求。 通过使用公平排队技术从队列中分发请求,这样, 一个行为不佳的控制器就不会饿死其他控制器 (即使优先级相同)
以下代码证基于版本 release-1.27
传统限流方法的缺点
比如突然有一个人发起无数请求,这些请求一个人就可以将apiserver打死,然后它阻塞了其他的所有的请求。 因为是一个共享集群,这个共享集群里面有无数的用户,然后无数的组件,如果有一个组件出现了问题,比如他发了1w个请求到apiserver,这些请求就将apiserver堵死了,请求请求只能在后面排队
开启配置
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/server/options/recommended.go
func (o *RecommendedOptions) ApplyTo(config *server.RecommendedConfig) error {
// ..
// APIPriorityAndFairness判断是否开启
if feature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.APIPriorityAndFairness) {
if config.ClientConfig != nil {
if config.MaxRequestsInFlight+config.MaxMutatingRequestsInFlight <= 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("invalid configuration: MaxRequestsInFlight=%d and MaxMutatingRequestsInFlight=%d; they must add up to something positive", config.MaxRequestsInFlight, config.MaxMutatingRequestsInFlight)
}
config.FlowControl = utilflowcontrol.New(
config.SharedInformerFactory,
kubernetes.NewForConfigOrDie(config.ClientConfig).FlowcontrolV1beta3(), // 1.27 是V1beta3版本,1.29 会是stable v1
config.MaxRequestsInFlight+config.MaxMutatingRequestsInFlight, // 总并发数为 --max-requests-inflight 和 --max-mutating-requests-inflight 两个配置值之和
config.RequestTimeout/4,
)
} else {
klog.Warningf("Neither kubeconfig is provided nor service-account is mounted, so APIPriorityAndFairness will be disabled")
}
}
return nil
}
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/server/config.go
func DefaultBuildHandlerChain(apiHandler http.Handler, c *Config) http.Handler {
handler := filterlatency.TrackCompleted(apiHandler)
// ..
if c.FlowControl != nil {
workEstimatorCfg := flowcontrolrequest.DefaultWorkEstimatorConfig()
requestWorkEstimator := flowcontrolrequest.NewWorkEstimator(
c.StorageObjectCountTracker.Get, c.FlowControl.GetInterestedWatchCount, workEstimatorCfg, c.FlowControl.GetMaxSeats)
handler = filterlatency.TrackCompleted(handler)
handler = genericfilters.WithPriorityAndFairness(handler, c.LongRunningFunc, c.FlowControl, requestWorkEstimator)
handler = filterlatency.TrackStarted(handler, c.TracerProvider, "priorityandfairness")
} else {
// 旧版本: 基于并发连接数的限流
handler = genericfilters.WithMaxInFlightLimit(handler, c.MaxRequestsInFlight, c.MaxMutatingRequestsInFlight, c.LongRunningFunc)
}
}
混洗分片(Shuffle-Sharding)
shuffle sharding用到了虚拟分片(shuffle shard)的概念,这里将不会直接对workers进行分片,而是按照"用户"进行分片,目的是尽量将用户打散分布到不同的worker上
API Priority and Fairness

APF 的核心:
多等级:它将整个集群分为了不同的限流等级FlowSchema,会把相近用户的请求分到不同等级里面,比如和系统相关,那么优先级可能比较高,普通用户的优先级可能比较低。
多队列:对于同一个 FlowSchema,会有多个队列,每个队列单独限流
(⎈|kind-kind:N/A)➜ ~ kubectl api-resources| head -1;kubectl api-resources |grep flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io
NAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
flowschemas flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 false FlowSchema
prioritylevelconfigurations flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3 false PriorityLevelConfiguration
APF限流通过两种资源
// k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/apis/flowcontrol/bootstrap/default.go
// The objects that define the current suggested additional configuration
var (
SuggestedPriorityLevelConfigurations = []*flowcontrol.PriorityLevelConfiguration{
// "system" priority-level is for the system components that affects self-maintenance of the
// cluster and the availability of those running pods in the cluster, including kubelet and
// kube-proxy.
SuggestedPriorityLevelConfigurationSystem,
// "node-high" priority-level is for the node health reporting. It is separated from "system"
// to make sure that nodes are able to report their health even if kube-apiserver is not capable of
// handling load caused by pod startup (fetching secrets, events etc).
// NOTE: In large clusters 50% - 90% of all API calls use this priority-level.
SuggestedPriorityLevelConfigurationNodeHigh,
// "leader-election" is dedicated for controllers' leader-election, which majorly affects the
// availability of any controller runs in the cluster.
SuggestedPriorityLevelConfigurationLeaderElection,
// "workload-high" is used by those workloads with higher priority but their failure won't directly
// impact the existing running pods in the cluster, which includes kube-scheduler, and those well-known
// built-in workloads such as "deployments", "replicasets" and other low-level custom workload which
// is important for the cluster.
SuggestedPriorityLevelConfigurationWorkloadHigh,
// "workload-low" is used by those workloads with lower priority which availability only has a
// minor impact on the cluster.
SuggestedPriorityLevelConfigurationWorkloadLow,
// "global-default" serves the rest traffic not handled by the other suggested flow-schemas above.
SuggestedPriorityLevelConfigurationGlobalDefault,
}
SuggestedFlowSchemas = []*flowcontrol.FlowSchema{
SuggestedFlowSchemaSystemNodes, // references "system" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaSystemNodeHigh, // references "node-high" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaProbes, // (豁免)
SuggestedFlowSchemaSystemLeaderElection, // references "leader-election" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaWorkloadLeaderElection, // references "leader-election" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaEndpointsController, // references "workload-high" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaKubeControllerManager, // references "workload-high" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaKubeScheduler, // references "workload-high" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaKubeSystemServiceAccounts, // references "workload-high" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaServiceAccounts, // references "workload-low" priority-level
SuggestedFlowSchemaGlobalDefault, // references "global-default" priority-level
}
)
- PriorityLevelConfigurations 定义隔离类型和可处理的并发预算量,还可以调整排队行为。
(⎈|kind-kind:N/A)➜ ~ kg prioritylevelconfigurations
NAME TYPE NOMINALCONCURRENCYSHARES QUEUES HANDSIZE QUEUELENGTHLIMIT AGE
catch-all Limited 5 <none> <none> <none> 37h
exempt Exempt <none> <none> <none> <none> 37h
global-default Limited 20 128 6 50 37h
leader-election Limited 10 16 4 50 37h
node-high Limited 40 64 6 50 37h
system Limited 30 64 6 50 37h
workload-high Limited 40 128 6 50 37h
workload-low Limited 100 128 6 50 37h
(⎈|kind-kind:N/A)➜ ~ kg prioritylevelconfigurations global-default -o yaml
apiVersion: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: PriorityLevelConfiguration
metadata:
name: global-default
spec:
limited: #限制策略
lendablePercent: 50
limitResponse:
queuing:
handSize: 6 #队列
queueLengthLimit: 50 #队列长度
queues: 128 #队列数
type: Queue #Queue或者Reject,Reject直接返回429,Queue将请求加入队列
nominalConcurrencyShares: 20
type: Limited #类型,Limited或Exempt, Exempt即不限制
- FlowSchemas 用于对每个入站请求进行分类,并与一个 PriorityLevelConfigurations相匹配
(⎈|kind-kind:N/A)➜ ~ kubectl get flowschemas
NAME PRIORITYLEVEL MATCHINGPRECEDENCE DISTINGUISHERMETHOD AGE MISSINGPL
exempt exempt 1 <none> 37h False
probes exempt 2 <none> 37h False
system-leader-election leader-election 100 ByUser 37h False
endpoint-controller workload-high 150 ByUser 37h False
workload-leader-election leader-election 200 ByUser 37h False
system-node-high node-high 400 ByUser 37h False
system-nodes system 500 ByUser 37h False
kube-controller-manager workload-high 800 ByNamespace 37h False
kube-scheduler workload-high 800 ByNamespace 37h False
kube-system-service-accounts workload-high 900 ByNamespace 37h False
service-accounts workload-low 9000 ByUser 37h False
global-default global-default 9900 ByUser 37h False
catch-all catch-all 10000 ByUser 37h False
(⎈|kind-danny-test:N/A)➜ ~ kubectl get flowschema global-default -o yaml
apiVersion: flowcontrol.apiserver.k8s.io/v1beta3
kind: FlowSchema
metadata:
generation: 1
name: global-default
spec:
distinguisherMethod:
type: ByUser
matchingPrecedence: 9900 #匹配优先级,1~1000,越小优先级越高
priorityLevelConfiguration:
name: global-default
rules:
- nonResourceRules:
- nonResourceURLs:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
resourceRules:
- apiGroups:
- '*'
clusterScope: true
namespaces:
- '*'
resources:
- '*'
verbs:
- '*'
subjects:
- group:
name: system:unauthenticated
kind: Group
- group:
name: system:authenticated
kind: Group
每个flowschemas都有其对应的优先级,所以任何请求过来之后它都会从上到下去匹配,优先级数字越小的越优先匹配(第三列),它就通过优先级来决定它的限流策略是什么
prioritylevelconfigurations 配置使用
- 增大 plc 的 queues 参数值,会减少不同 flow 之间冲突的可能性,但是会增加内存负担,如果其值为 1, 则会禁掉 fair-queueing 逻辑,但是请求还是会被排队处理;
- 增大 plc 的 queueLengthLimit 的参数值,可以应对突发的流量,不丢弃相关的请求,但会增大延迟和内存占用;
- 增大 plc 的 handsize 的参数值,可调节不同flow冲突的概率【增加公平度,防止某些 flow 饥饿】,以及总体并发度;但也可能导致某些类型的 flow 霸占住 as,且导致请求处理延迟增大;单 个 flow 上能处理的最大请求的数目可能的值为 handSize * queueLengthLimit
配置初始化
func queueSetCompleterForPL(qsf fq.QueueSetFactory, queues fq.QueueSet, pl *flowcontrol.PriorityLevelConfiguration, requestWaitLimit time.Duration, reqsIntPair metrics.RatioedGaugePair, execSeatsObs metrics.RatioedGauge, seatDemandGauge metrics.Gauge) (fq.QueueSetCompleter, error) {
// ...
qcAPI := pl.Spec.Limited.LimitResponse.Queuing
qcQS := fq.QueuingConfig{Name: pl.Name}
if qcAPI != nil {
qcQS = fq.QueuingConfig{Name: pl.Name,
DesiredNumQueues: int(qcAPI.Queues),
QueueLengthLimit: int(qcAPI.QueueLengthLimit),
HandSize: int(qcAPI.HandSize),
RequestWaitLimit: requestWaitLimit,
}
}
var qsc fq.QueueSetCompleter
var err error
if queues != nil {
qsc, err = queues.BeginConfigChange(qcQS)
} else {
qsc, err = qsf.BeginConstruction(qcQS, reqsIntPair, execSeatsObs, seatDemandGauge)
}
//..
return qsc, err
}
配置创建 dealer
func (qsf *queueSetFactory) BeginConstruction(qCfg fq.QueuingConfig, reqsGaugePair metrics.RatioedGaugePair, execSeatsGauge metrics.RatioedGauge, seatDemandIntegrator metrics.Gauge) (fq.QueueSetCompleter, error) {
// 初始化一个实例
dealer, err := checkConfig(qCfg)
//...
return &queueSetCompleter{
factory: qsf,
reqsGaugePair: reqsGaugePair,
execSeatsGauge: execSeatsGauge,
seatDemandIntegrator: seatDemandIntegrator,
qCfg: qCfg,
dealer: dealer}, nil
}
func checkConfig(qCfg fq.QueuingConfig) (*shufflesharding.Dealer, error) {
// ...
// deckSize为队列数,handSize表示为一条流分配的队列数量
dealer, err := shufflesharding.NewDealer(qCfg.DesiredNumQueues, qCfg.HandSize)
if err != nil {
err = fmt.Errorf("the QueueSetConfig implies an invalid shuffle sharding config (DesiredNumQueues is deckSize): %w", err)
}
return dealer, err
}
// 返回为流选择的队列ID
func (d *Dealer) DealIntoHand(hashValue uint64, hand []int) []int {
h := hand[:0]
d.Deal(hashValue, func(card int) { h = append(h, card) })
return h
}
func (d *Dealer) Deal(hashValue uint64, pick func(int)) {
// 15 is the largest possible value of handSize
var remainders [15]int
// 这个for循环用于生成[0,deckSize)范围内的随机数。
for i := 0; i < d.handSize; i++ {
hashValueNext := hashValue / uint64(d.deckSize-i)
remainders[i] = int(hashValue - uint64(d.deckSize-i)*hashValueNext)
hashValue = hashValueNext
}
for i := 0; i < d.handSize; i++ {
card := remainders[i]
for j := i; j > 0; j-- {
if card >= remainders[j-1] {
card++
}
}
pick(card)
}
}
FlowSchemas 配置使用
- matchingPrecedence:定义 FlowSchema 的应用顺序,数字越低,优先级越高。
- rules:定义请求过滤规则,格式与 Kubernetes RBAC 中的格式相同。
- distinguisherMethod:指定一个参数(用户或命名空间),用于在将请求转发到优先级时将请求分离到流中,如果省略该参数,所有请求将分配给同一流(flow)。
查看效果
TOKEN=$(kubectl -n d8-cni-cilium get secrets agent-token-45s7n -o json | jq -r .data.token | base64 -d)
curl https://127.0.0.1:6445/apis/cilium.io/v2/ciliumclusterwidenetworkpolicies?limit=500 -X GET --header "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" -k -I
HTTP/2 200
audit-id: 4f647505-8581-4a99-8e4c-f3f4322f79fe
cache-control: no-cache, private
content-type: application/json
x-kubernetes-pf-flowschema-uid: 7f0afa35-07c3-4601-b92c-dfe7e74780f8
x-kubernetes-pf-prioritylevel-uid: df8f409a-ebe7-4d54-9f21-1f2a6bee2e81
content-length: 173
date: Sun, 26 Mar 2023 17:45:02 GMT
kubectl get flowschemas -o custom-columns="uid:{metadata.uid},name:{metadata.name}" | grep 7f0afa35-07c3-4601-b92c-dfe7e74780f8
7f0afa35-07c3-4601-b92c-dfe7e74780f8 d8-serviceaccounts
kubectl get prioritylevelconfiguration -o custom-columns="uid:{metadata.uid},name:{metadata.name}" | grep df8f409a-ebe7-4d54-9f21-1f2a6bee2e81
df8f409a-ebe7-4d54-9f21-1f2a6bee2e81 d8-serviceaccounts
在响应时,APIServer 会提供特殊的 Header X-Kubernetes-PF-FlowSchema-UID 和X-Kubernetes-PF-PriorityLevel-UID,你可以使用它们来查看请求的去向。
输出显示该请求属于 d8-serviceaccounts 的 FlowSchema 和 d8-serviceaccounts 的 PriorityLevelConfiguration
处理流程
func WithPriorityAndFairness(
handler http.Handler,
longRunningRequestCheck apirequest.LongRunningRequestCheck,
fcIfc utilflowcontrol.Interface,
workEstimator flowcontrolrequest.WorkEstimatorFunc,
) http.Handler {
// ...
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
ctx := r.Context()
requestInfo, ok := apirequest.RequestInfoFrom(ctx)
if !ok {
handleError(w, r, fmt.Errorf("no RequestInfo found in context"))
return
}
user, ok := apirequest.UserFrom(ctx)
if !ok {
handleError(w, r, fmt.Errorf("no User found in context"))
return
}
isWatchRequest := watchVerbs.Has(requestInfo.Verb)
if longRunningRequestCheck != nil && longRunningRequestCheck(r, requestInfo) && !isWatchRequest {
klog.V(6).Infof("Serving RequestInfo=%#+v, user.Info=%#+v as longrunning\n", requestInfo, user)
handler.ServeHTTP(w, r)
return
}
var classification *PriorityAndFairnessClassification
// ...
var served bool
isMutatingRequest := !nonMutatingRequestVerbs.Has(requestInfo.Verb)
noteExecutingDelta := func(delta int32) {
if isMutatingRequest {
watermark.recordMutating(int(atomic.AddInt32(&atomicMutatingExecuting, delta)))
} else {
watermark.recordReadOnly(int(atomic.AddInt32(&atomicReadOnlyExecuting, delta)))
}
}
noteWaitingDelta := func(delta int32) {
if isMutatingRequest {
waitingMark.recordMutating(int(atomic.AddInt32(&atomicMutatingWaiting, delta)))
} else {
waitingMark.recordReadOnly(int(atomic.AddInt32(&atomicReadOnlyWaiting, delta)))
}
}
queueNote := func(inQueue bool) {
if inQueue {
noteWaitingDelta(1)
} else {
noteWaitingDelta(-1)
}
}
digest := utilflowcontrol.RequestDigest{
RequestInfo: requestInfo,
User: user,
}
if isWatchRequest { // watch 请求处理
// ...
} else {
execute := func() {
noteExecutingDelta(1)
defer noteExecutingDelta(-1)
served = true
setResponseHeaders(classification, w)
handler.ServeHTTP(w, r)
}
fcIfc.Handle(ctx, digest, noteFn, estimateWork, queueNote, execute)
}
// ...
})
}
- Long-running 运行的 API 请求(例如,在 pod 中查看日志或执行命令)不受 APF 限制,WATCH 请求也不受限制。
- 还有一个特殊的预定义优先级称为 exempt,该级别的请求会立即得到处理
具体的 handle
func (cfgCtlr *configController) Handle(ctx context.Context, requestDigest RequestDigest,
noteFn func(fs *flowcontrol.FlowSchema, pl *flowcontrol.PriorityLevelConfiguration, flowDistinguisher string),
workEstimator func() fcrequest.WorkEstimate,
queueNoteFn fq.QueueNoteFn,
execFn func()) {
// 对请求进行分类
fs, pl, isExempt, req, startWaitingTime := cfgCtlr.startRequest(ctx, requestDigest, noteFn, workEstimator, queueNoteFn)
// ...
// 执行
idle = req.Finish(func() {
// ...
executed = true
// 请求执行
execFn()
})
/// ...
}
开始请求
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/util/flowcontrol/apf_controller.go
func (cfgCtlr *configController) startRequest(ctx context.Context, rd RequestDigest,
noteFn func(fs *flowcontrol.FlowSchema, pl *flowcontrol.PriorityLevelConfiguration, flowDistinguisher string),
workEstimator func() fcrequest.WorkEstimate,
queueNoteFn fq.QueueNoteFn) (fs *flowcontrol.FlowSchema, pl *flowcontrol.PriorityLevelConfiguration, isExempt bool, req fq.Request, startWaitingTime time.Time) {
klog.V(7).Infof("startRequest(%#+v)", rd)
cfgCtlr.lock.RLock()
defer cfgCtlr.lock.RUnlock()
var selectedFlowSchema, catchAllFlowSchema *flowcontrol.FlowSchema
// 可以根据请求的主体 (User, Group, ServiceAccount)、动作 (Get, List, Create, Delete …)、资源类型 (pod, deployment …)、namespace、url 对请求进行分类
for _, fs := range cfgCtlr.flowSchemas {
// 匹配
if matchesFlowSchema(rd, fs) {
selectedFlowSchema = fs
break
}
if fs.Name == flowcontrol.FlowSchemaNameCatchAll {
catchAllFlowSchema = fs
}
}
// ...
plName := selectedFlowSchema.Spec.PriorityLevelConfiguration.Name
plState := cfgCtlr.priorityLevelStates[plName]
if plState.pl.Spec.Type == flowcontrol.PriorityLevelEnablementExempt { // 豁免的情况
noteFn(selectedFlowSchema, plState.pl, "")
klog.V(7).Infof("startRequest(%#+v) => fsName=%q, distMethod=%#+v, plName=%q, immediate", rd, selectedFlowSchema.Name, selectedFlowSchema.Spec.DistinguisherMethod, plName)
return selectedFlowSchema, plState.pl, true, immediateRequest{}, time.Time{}
}
var numQueues int32
if plState.pl.Spec.Limited.LimitResponse.Type == flowcontrol.LimitResponseTypeQueue {
numQueues = plState.pl.Spec.Limited.LimitResponse.Queuing.Queues
}
var flowDistinguisher string
var hashValue uint64
if numQueues > 1 {
//根据 DistinguisherMethod 判断获取 userName 或 namespace
flowDistinguisher = computeFlowDistinguisher(rd, selectedFlowSchema.Spec.DistinguisherMethod)
// APF 利用 FS 的 name 和 计算一个 hashFlowID 标识 Flow
hashValue = hashFlowID(selectedFlowSchema.Name, flowDistinguisher)
}
noteFn(selectedFlowSchema, plState.pl, flowDistinguisher)
workEstimate := workEstimator()
startWaitingTime = cfgCtlr.clock.Now()
// 使用混洗分片 shuffle-shards 处理请求
req, idle := plState.queues.StartRequest(ctx, &workEstimate, hashValue, flowDistinguisher, selectedFlowSchema.Name, rd.RequestInfo, rd.User, queueNoteFn)
if idle {
cfgCtlr.maybeReapReadLocked(plName, plState)
}
return selectedFlowSchema, plState.pl, false, req, startWaitingTime
}
匹配规则
func matchesPolicyRule(digest RequestDigest, policyRule *flowcontrol.PolicyRulesWithSubjects) bool {
/*
1. 匹配请求主体 subject
2. 对资源的请求,匹配 ResourceRules 中任意一条规则
3. 对非资源的请求, 匹配 NonResourceRules 中任意一条规则
*/
if !matchesASubject(digest.User, policyRule.Subjects) {
return false
}
if digest.RequestInfo.IsResourceRequest {
return matchesAResourceRule(digest.RequestInfo, policyRule.ResourceRules)
}
return matchesANonResourceRule(digest.RequestInfo, policyRule.NonResourceRules)
}
处理请求
// staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/util/flowcontrol/fairqueuing/queueset/queueset.go
func (qs *queueSet) StartRequest(ctx context.Context, workEstimate *fqrequest.WorkEstimate, hashValue uint64, flowDistinguisher, fsName string, descr1, descr2 interface{}, queueNoteFn fq.QueueNoteFn) (fq.Request, bool) {
qs.lockAndSyncTime(ctx)
defer qs.lock.Unlock()
var req *request
// ========================================================================
// 步骤 0:
// Apply only concurrency limit, if zero queues desired
if qs.qCfg.DesiredNumQueues < 1 {
if !qs.canAccommodateSeatsLocked(workEstimate.MaxSeats()) {
klog.V(5).Infof("QS(%s): rejecting request %q %#+v %#+v because %d seats are asked for, %d seats are in use (%d are executing) and the limit is %d",
qs.qCfg.Name, fsName, descr1, descr2, workEstimate, qs.totSeatsInUse, qs.totRequestsExecuting, qs.dCfg.ConcurrencyLimit)
qs.totRequestsRejected++
metrics.AddReject(ctx, qs.qCfg.Name, fsName, "concurrency-limit")
return nil, qs.isIdleLocked()
}
req = qs.dispatchSansQueueLocked(ctx, workEstimate, flowDistinguisher, fsName, descr1, descr2)
return req, false
}
// ========================================================================
// 步骤 1:
// 1) Start with shuffle sharding, to pick a queue.
// 2) Reject old requests that have been waiting too long
// 3) Reject current request if there is not enough concurrency shares and
// we are at max queue length
// 4) If not rejected, create a request and enqueue
req = qs.timeoutOldRequestsAndRejectOrEnqueueLocked(ctx, workEstimate, hashValue, flowDistinguisher, fsName, descr1, descr2, queueNoteFn)
// req == nil means that the request was rejected - no remaining
// concurrency shares and at max queue length already
if req == nil {
klog.V(5).Infof("QS(%s): rejecting request %q %#+v %#+v due to queue full", qs.qCfg.Name, fsName, descr1, descr2)
// ..
return nil, qs.isIdleLocked()
}
// ========================================================================
// 步骤 2:
// The next step is to invoke the method that dequeues as much
// as possible.
// This method runs a loop, as long as there are non-empty
// queues and the number currently executing is less than the
// assured concurrency value. The body of the loop uses the
// fair queuing technique to pick a queue and dispatch a
// request from that queue.
qs.dispatchAsMuchAsPossibleLocked()
return req, false
}
func (qs *queueSet) dispatchAsMuchAsPossibleLocked() {
// 循环出队
for qs.totRequestsWaiting != 0 && qs.totSeatsInUse < qs.dCfg.ConcurrencyLimit && qs.dispatchLocked() {
}
}
func (qs *queueSet) timeoutOldRequestsAndRejectOrEnqueueLocked(ctx context.Context, workEstimate *fqrequest.WorkEstimate, hashValue uint64, flowDistinguisher, fsName string, descr1, descr2 interface{}, queueNoteFn fq.QueueNoteFn) *request {
// 开始 shuffle sharding 选择队列
queueIdx := qs.shuffleShardLocked(hashValue, descr1, descr2)
queue := qs.queues[queueIdx]
// 针对入队时间超过RequestWaitLimit,设置决定为拒绝
qs.removeTimedOutRequestsFromQueueToBoundLocked(queue, fsName)
defer qs.boundNextDispatchLocked(queue)
// Create a request and enqueue
req := &request{
qs: qs,
fsName: fsName,
flowDistinguisher: flowDistinguisher,
ctx: ctx,
decision: qs.promiseFactory(nil, ctx.Done(), decisionCancel), // 决定
arrivalTime: qs.clock.Now(),
arrivalR: qs.currentR,
queue: queue,
descr1: descr1,
descr2: descr2,
queueNoteFn: queueNoteFn,
workEstimate: qs.completeWorkEstimate(workEstimate),
}
// 达到上限进行拒绝
if ok := qs.rejectOrEnqueueToBoundLocked(req); !ok {
return nil
}
// ...
return req
}
func (qs *queueSet) shuffleShardLocked(hashValue uint64, descr1, descr2 interface{}) int {
var backHand [8]int
// 获取本条流的队列列表
hand := qs.dealer.DealIntoHand(hashValue, backHand[:])
handSize := len(hand)
// qs.enqueues表示队列中的请求总数,这里第一次哈希取模算出队列的起始偏移量
offset := qs.enqueues % handSize
qs.enqueues++
bestQueueIdx := -1
minQueueSeatSeconds := fqrequest.MaxSeatSeconds
for i := 0; i < handSize; i++ {
queueIdx := hand[(offset+i)%handSize]
queue := qs.queues[queueIdx]
queueSum := queue.requests.QueueSum()
// this is the total amount of work in seat-seconds for requests
// waiting in this queue, we will select the queue with the minimum.
thisQueueSeatSeconds := queueSum.TotalWorkSum
klog.V(7).Infof("QS(%s): For request %#+v %#+v considering queue %d with sum: %#v and %d seats in use, nextDispatchR=%v", qs.qCfg.Name, descr1, descr2, queueIdx, queueSum, queue.seatsInUse, queue.nextDispatchR)
if thisQueueSeatSeconds < minQueueSeatSeconds {
minQueueSeatSeconds = thisQueueSeatSeconds
bestQueueIdx = queueIdx
}
}
// ..
return bestQueueIdx
}
// 使用 fair queuing算法: 从所有queue中选择一个合适的queue取出请求,解除请求的阻塞,执行这个请求
func (qs *queueSet) dispatchLocked() bool {
queue, request := qs.findDispatchQueueToBoundLocked()
if queue == nil {
return false
}
if request == nil { // This should never happen. But if it does...
return false
}
qs.totRequestsWaiting--
qs.totSeatsWaiting -= request.MaxSeats()
metrics.AddRequestsInQueues(request.ctx, qs.qCfg.Name, request.fsName, -1)
request.NoteQueued(false)
qs.reqsGaugePair.RequestsWaiting.Add(-1)
defer qs.boundNextDispatchLocked(queue)
if !request.decision.Set(decisionExecute) {
qs.seatDemandIntegrator.Set(float64(qs.totSeatsInUse + qs.totSeatsWaiting))
return true
}
// ...
queue.nextDispatchR += request.totalWork()
return true
}
func (qs *queueSet) findDispatchQueueToBoundLocked() (*queue, *request) {
minVirtualFinish := fqrequest.MaxSeatSeconds
sMin := fqrequest.MaxSeatSeconds
dsMin := fqrequest.MaxSeatSeconds
sMax := fqrequest.MinSeatSeconds
dsMax := fqrequest.MinSeatSeconds
var minQueue *queue
var minIndex int
nq := len(qs.queues)
for range qs.queues {
qs.robinIndex = (qs.robinIndex + 1) % nq
queue := qs.queues[qs.robinIndex]
oldestWaiting, _ := queue.requests.Peek()
if oldestWaiting != nil {
sMin = ssMin(sMin, queue.nextDispatchR)
sMax = ssMax(sMax, queue.nextDispatchR)
estimatedWorkInProgress := fqrequest.SeatsTimesDuration(float64(queue.seatsInUse), qs.estimatedServiceDuration)
dsMin = ssMin(dsMin, queue.nextDispatchR-estimatedWorkInProgress)
dsMax = ssMax(dsMax, queue.nextDispatchR-estimatedWorkInProgress)
currentVirtualFinish := queue.nextDispatchR + oldestWaiting.totalWork()
klog.V(11).InfoS("Considering queue to dispatch", "queueSet", qs.qCfg.Name, "queue", qs.robinIndex, "finishR", currentVirtualFinish)
if currentVirtualFinish < minVirtualFinish {
minVirtualFinish = currentVirtualFinish
minQueue = queue
minIndex = qs.robinIndex
}
}
}
oldestReqFromMinQueue, _ := minQueue.requests.Peek()
if oldestReqFromMinQueue == nil {
// This cannot happen
klog.ErrorS(errors.New("selected queue is empty"), "Impossible", "queueSet", qs.qCfg.Name)
return nil, nil
}
if !qs.canAccommodateSeatsLocked(oldestReqFromMinQueue.MaxSeats()) {
// since we have not picked the queue with the minimum virtual finish
// time, we are not going to advance the round robin index here.
klogV := klog.V(4)
if klogV.Enabled() {
klogV.Infof("QS(%s): request %v %v seats %d cannot be dispatched from queue %d, waiting for currently executing requests to complete, %d requests are occupying %d seats and the limit is %d",
qs.qCfg.Name, oldestReqFromMinQueue.descr1, oldestReqFromMinQueue.descr2, oldestReqFromMinQueue.MaxSeats(), minQueue.index, qs.totRequestsExecuting, qs.totSeatsInUse, qs.dCfg.ConcurrencyLimit)
}
metrics.AddDispatchWithNoAccommodation(qs.qCfg.Name, oldestReqFromMinQueue.fsName)
return nil, nil
}
oldestReqFromMinQueue.removeFromQueueLocked()
// If the requested final seats exceed capacity of that queue,
// we reduce them to current capacity and adjust additional latency
// to preserve the total amount of work.
if oldestReqFromMinQueue.workEstimate.FinalSeats > uint64(qs.dCfg.ConcurrencyLimit) {
finalSeats := uint64(qs.dCfg.ConcurrencyLimit)
additionalLatency := oldestReqFromMinQueue.workEstimate.finalWork.DurationPerSeat(float64(finalSeats))
oldestReqFromMinQueue.workEstimate.FinalSeats = finalSeats
oldestReqFromMinQueue.workEstimate.AdditionalLatency = additionalLatency
}
// we set the round robin indexing to start at the chose queue
// for the next round. This way the non-selected queues
// win in the case that the virtual finish times are the same
qs.robinIndex = minIndex
if minQueue.nextDispatchR < oldestReqFromMinQueue.arrivalR {
klog.ErrorS(errors.New("dispatch before arrival"), "Inconceivable!", "QS", qs.qCfg.Name, "queue", minQueue.index, "dispatchR", minQueue.nextDispatchR, "request", oldestReqFromMinQueue)
}
metrics.SetDispatchMetrics(qs.qCfg.Name, qs.currentR.ToFloat(), minQueue.nextDispatchR.ToFloat(), sMin.ToFloat(), sMax.ToFloat(), dsMin.ToFloat(), dsMax.ToFloat())
return minQueue, oldestReqFromMinQueue
}
等待请求结束
func (req *request) Finish(execFn func()) bool {
exec, idle := req.wait()
if !exec {
return idle
}
func() {
defer func() {
idle = req.qs.finishRequestAndDispatchAsMuchAsPossible(req)
}()
execFn()
}()
return idle
}
func (req *request) wait() (bool, bool) {
qs := req.qs
// ========================================================================
// 步骤 3:
// The final step is to wait on a decision from
// somewhere and then act on it.
decisionAny := req.decision.Get()
qs.lockAndSyncTime(req.ctx)
defer qs.lock.Unlock()
if req.waitStarted {
// This can not happen, because the client is forbidden to
// call Wait twice on the same request
klog.Errorf("Duplicate call to the Wait method! Immediately returning execute=false. QueueSet=%s, startTime=%s, descr1=%#+v, descr2=%#+v", req.qs.qCfg.Name, req.startTime, req.descr1, req.descr2)
return false, qs.isIdleLocked()
}
req.waitStarted = true
switch decisionAny {
case decisionReject: // 拒绝
klog.V(5).Infof("QS(%s): request %#+v %#+v timed out after being enqueued\n", qs.qCfg.Name, req.descr1, req.descr2)
qs.totRequestsRejected++
qs.totRequestsTimedout++
metrics.AddReject(req.ctx, qs.qCfg.Name, req.fsName, "time-out")
return false, qs.isIdleLocked()
case decisionCancel: // 取消
case decisionExecute:
klog.V(5).Infof("QS(%s): Dispatching request %#+v %#+v from its queue", qs.qCfg.Name, req.descr1, req.descr2)
return true, false
default:
// This can not happen, all possible values are handled above
klog.Errorf("QS(%s): Impossible decision (type %T, value %#+v) for request %#+v %#+v! Treating as cancel", qs.qCfg.Name, decisionAny, decisionAny, req.descr1, req.descr2)
}
// TODO(aaron-prindle) add metrics for this case
klog.V(5).Infof("QS(%s): Ejecting request %#+v %#+v from its queue", qs.qCfg.Name, req.descr1, req.descr2)
// remove the request from the queue as it has timed out
queue := req.queue
if req.removeFromQueueLocked() != nil {
defer qs.boundNextDispatchLocked(queue)
qs.totRequestsWaiting--
qs.totSeatsWaiting -= req.MaxSeats()
qs.totRequestsRejected++
qs.totRequestsCancelled++
metrics.AddReject(req.ctx, qs.qCfg.Name, req.fsName, "cancelled")
metrics.AddRequestsInQueues(req.ctx, qs.qCfg.Name, req.fsName, -1)
req.NoteQueued(false)
qs.reqsGaugePair.RequestsWaiting.Add(-1)
qs.seatDemandIntegrator.Set(float64(qs.totSeatsInUse + qs.totSeatsWaiting))
}
return false, qs.isIdleLocked()
}
指标
| metrics | 解释 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| apiserver_flowcontrol_rejected_requests_total | apf 拒绝的 request 数目 | 按照 pl 的名称以及 fs 的名称以及 rejection 原因进行排序, 拒绝掉的原因可能值有 queue-full【队列中已经有太多的请求在排队】、concurrency-limit【根据 plc 拒掉请求】、 time-out【请求还在队列中排队的时候就超时了】 |
| apiserver_flowcontrol_dispatched_requests_total | 已经处理的请求总数 | - |
| apiserver_flowcontrol_current_inqueue_requests | 还在队列中有待处理的请求总数 | - |
| apiserver_flowcontrol_request_queue_length_after_enqueue | 实时队列中数据数目。这个值是抽样获取到的 | - |
| apiserver_flowcontrol_request_concurrency_limit | 每个 plc 的并行上限 | - |
| apiserver_flowcontrol_request_wait_duration_seconds | 请求处理过程中排队的时长,以及请求处理失败量 | - |
| apiserver_flowcontrol_request_execution_seconds | 请求执行花费时间 | - |