List-Watch 机制和 Informer 模块
List-Watch 机制和 Informer 模块
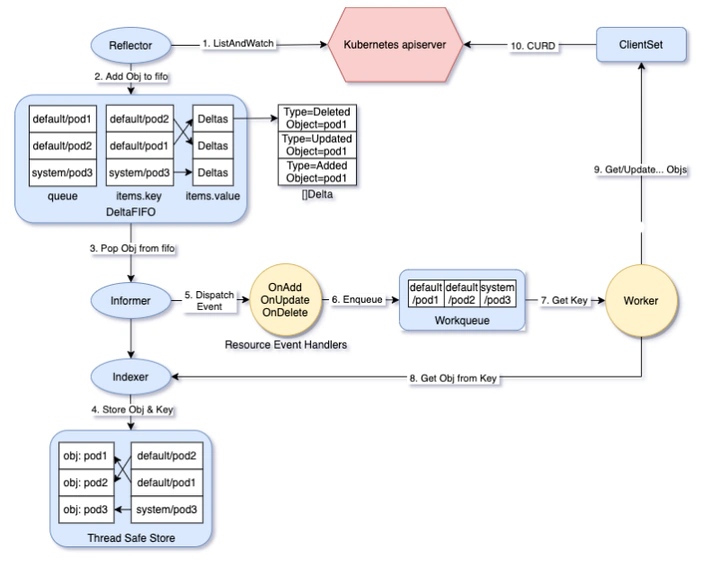
Etcd存储集群的数据信息,apiserver 作为统一入口,任何对数据的操作都必须经过apiserver。
客户端(kubelet/scheduler/controller-manager)通过list-watch监听apiserver中资源(pod/rs/rc等等)的create,update和delete事件,并针对事件类型调用相应的事件处理函数.
那么list-watch具体是什么呢,顾名思义,list-watch有两部分组成,分别是list和watch。list非常好理解,就是调用资源的list API罗列资源,基于HTTP短链接实现;watch则是调用资源的watch API监听资源变更事件,基于HTTP 长链接实现

Informer 中的 Reflector 通过 List/watch 从 apiserver 中获取到集群中所有资源对象的变化事件(event),将其放入 Delta FIFO 队列中(以 Key、Value 的形式保存),触发 onAdd、onUpdate、onDelete 回调将 Key 放入 WorkQueue 中。 同时将 Key 更新 Indexer 本地缓存。 Control Loop 从 WorkQueue 中取到 Key,从 Indexer 中获取到该 Key 的 Value,进行相应的处理.
基本概念
reflector 反射器 :通过 list/watch 监听 apiserver, 后面把增量的数据推到 deltaFIFO 增量事件队列里
deltaFIFO 增量队列: 对资源对象的的操作类型进行队列的基本操作
- FIFO:先进先出队列,提供资源对象的增删改查等操作
- Delta:资源对象存储,可以保存资源对象的操作类型。如:添加操作类型、更新操作类型、删除操作类型、同步操作类型
storeIndex 索引: 存储了索引, 其目的就是为了加速数据的检索. 通过索引值只是拿到资源的 name, 获取对象还是存储在
threadSafeMap里.threadSafeMap 对象缓存: 本地缓存, storeIndex 是索引, threadSafeMap 是存储资源对象的缓存.
controller 控制器: 实例化并启动 reflector 反射器, 并调用 processLoop 来消费 deltaFIFO 队列.
informer: 把上面的这几个模块组合起来就实现的 informer 的功能.
内部依赖 controller 实现 informer 的功能. controller 又会关联 reflector, deltaFIFO, Store (indexer, threadSafeMap ) 组件之间的协调联动.
List-Watch 的设计理念
对消息机制有至少如下四点要求:
- 消息可靠性: list + watch
- 消息实时性: watch
- 消息顺序性: resourceVersion
- 高性能: cache,对应我们的Store组件
使用案例
func main() {
var kubeconfig string
var master string
flag.StringVar(&kubeconfig, "kubeconfig", "", "absolute path to the kubeconfig file")
flag.StringVar(&master, "master", "", "master url")
flag.Parse()
// creates the connection
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags(master, kubeconfig)
if err != nil {
klog.Fatal(err)
}
// 通过kubernetes.NewForConfig创建clientset对象。informer需要通过clientset与apiserver进行交互
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
if err != nil {
klog.Fatal(err)
}
// create the pod watcher
podListWatcher := cache.NewListWatchFromClient(clientset.CoreV1().RESTClient(), "pods", v1.NamespaceDefault, fields.Everything())
// create the workqueue
queue := workqueue.NewRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter())
// Bind the workqueue to a cache with the help of an informer. This way we make sure that
// whenever the cache is updated, the pod key is added to the workqueue.
// Note that when we finally process the item from the workqueue, we might see a newer version
// of the Pod than the version which was responsible for triggering the update.
indexer, informer := cache.NewIndexerInformer(podListWatcher, &v1.Pod{}, 0, cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
key, err := cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)
if err == nil {
queue.Add(key)
}
},
UpdateFunc: func(old interface{}, new interface{}) {
key, err := cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(new)
if err == nil {
queue.Add(key)
}
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
// IndexerInformer uses a delta queue, therefore for deletes we have to use this
// key function.
key, err := cache.DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)
if err == nil {
queue.Add(key)
}
},
}, cache.Indexers{})
controller := NewController(queue, indexer, informer)
// We can now warm up the cache for initial synchronization.
// Let's suppose that we knew about a pod "mypod" on our last run, therefore add it to the cache.
// If this pod is not there anymore, the controller will be notified about the removal after the
// cache has synchronized.
indexer.Add(&v1.Pod{
ObjectMeta: meta_v1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "mypod",
Namespace: v1.NamespaceDefault,
},
})
// Now let's start the controller
stop := make(chan struct{})
defer close(stop)
go controller.Run(1, stop)
// Wait forever
select {}
}
Reflector 的实现原理
Reflector 的主要职责是从 k8s 的 apiserver 获取全量及监听增量事件, 把获取到的相关资源类型的增删改 Add/Update/Delete 事件写到 DeltaFIFO 递增队列里.
结构体
// Reflector watches a specified resource and causes all changes to be reflected in the given store.
type Reflector struct {
// name identifies this reflector. By default it will be a file:line if possible.
name string
// ...
// 这个 store 指的是 deltaFIFO 队列.
store Store
// 实现了资源的 list 和 watch 接口.
listerWatcher ListerWatcher
// ...
// 从 apiserver 拉取到的最新的修订版号
lastSyncResourceVersion string
}
初始化
func (c *controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// ...
// 创建Reflector
r := NewReflector(
c.config.ListerWatcher,
c.config.ObjectType,
c.config.Queue, // 传入store
c.config.FullResyncPeriod,
)
// ..
// 启动 Reflector
wg.StartWithChannel(stopCh, r.Run)
}
// k8s.io/client-go@v0.26.3/tools/cache/reflector.go:168
func NewReflector(lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
return NewNamedReflector(naming.GetNameFromCallsite(internalPackages...), lw, expectedType, store, resyncPeriod)
}
// NewNamedReflector same as NewReflector, but with a specified name for logging
func NewNamedReflector(name string, lw ListerWatcher, expectedType interface{}, store Store, resyncPeriod time.Duration) *Reflector {
realClock := &clock.RealClock{}
r := &Reflector{
name: name,
listerWatcher: lw,
store: store, // 存储,就是DeltaFIFO
// ...
}
r.setExpectedType(expectedType)
return r
}
启动 reflector,监听处理 listAndWatch
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// ..
wait.BackoffUntil(func() {
if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh); err != nil {
r.watchErrorHandler(r, err)
}
}, r.backoffManager, true, stopCh)
// ..
}
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
// ...
// 首先尝试获取某资源相关条件下的所有对象
err := r.list(stopCh)
if err != nil {
return err
}
resyncerrc := make(chan error, 1)
cancelCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(cancelCh)
go func() {
// 启动一个协程去处理 resync 定时同步逻辑, 默认不开启 resync 的, 也没必要开启该功能.通常 rsyncPeriod 为 0 , 不会触犯 resync 操作
resyncCh, cleanup := r.resyncChan()
// ...
}()
retry := NewRetryWithDeadline(r.MaxInternalErrorRetryDuration, time.Minute, apierrors.IsInternalError, r.clock)
for {
// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errors
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
default:
}
timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))
options := metav1.ListOptions{
// 上次的 resource version, 这样订阅到 apiserver 后, 可以拿到增量的数据.
ResourceVersion: r.LastSyncResourceVersion(),
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any watchers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
}
// start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sent
start := r.clock.Now()
// 创建一个 watcher 监听对象, 监听 apiserver 获取变更事件, 把新增事件扔到 watch.ResultChan 队列中.
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
// ...
}
// 调用 `watcherHandler` 监听新增的事件, 然后把新增加到 DeltaFIFO 增量队列里.
err = watchHandler(start, w, r.store, r.expectedType, r.expectedGVK, r.name, r.expectedTypeName, r.setLastSyncResourceVersion, r.clock, resyncerrc, stopCh)
retry.After(err)
if err != nil {
// ...
}
}
}
全量拉取
list-watch 中的 list() 并不是每次都拉取全量的数据. 第一次拉取时由于 resourceVersion 为空, 所以拉取的是全量数据. 当 list-watch 出现异常进行重试重连时, list() 拉取的 resourceVersion 为上次最新的版本, 这样 list 会获取比该版本更新的所有数据.
func (r *Reflector) list(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
var resourceVersion string
// 创建一个含有上次的 resourceVersion 版本的 options
options := metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()}
var list runtime.Object
var paginatedResult bool
var err error
listCh := make(chan struct{}, 1)
panicCh := make(chan interface{}, 1)
go func() {
// ...
// Attempt to gather list in chunks, if supported by listerWatcher, if not, the first
// list request will return the full response.
// 使用 tool/pager 组装分页逻辑
pager := pager.New(pager.SimplePageFunc(func(opts metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.listerWatcher.List(opts)
}))
// ...
// 调用 pager.List 获取数据
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), options)
// ...
}()
// ...
// 获取当前最新的版本
listMetaInterface, err := meta.ListAccessor(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v: %v", list, err)
}
resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()
// 转换数据结构
items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v (%v)", list, err)
}
// 把 items 数据同步到 store 里.
if err := r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to sync list result: %v", err)
}
// 更新 resourceVersion
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
return nil
}
// syncWith replaces the store's items with the given list.
func (r *Reflector) syncWith(items []runtime.Object, resourceVersion string) error {
// 做一次slice类型转换
found := make([]interface{}, 0, len(items))
for _, item := range items {
found = append(found, item)
}
// 使用 store replace 写到队列中
return r.store.Replace(found, resourceVersion)
}
增量监听
// watch simply starts a watch request with the server.
func (r *Reflector) watch(w watch.Interface, stopCh <-chan struct{}, resyncerrc chan error) error {
var err error
retry := NewRetryWithDeadline(r.MaxInternalErrorRetryDuration, time.Minute, apierrors.IsInternalError, r.clock)
for {
// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errors
select {
case <-stopCh:
// we can only end up here when the stopCh
// was closed after a successful watchlist or list request
if w != nil {
w.Stop()
}
return nil
default:
}
// start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sent
start := r.clock.Now()
if w == nil {
timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))
options := metav1.ListOptions{
ResourceVersion: r.LastSyncResourceVersion(),
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any watchers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
}
// 监听变更,把变更内容扔到watch.ResultChan中
w, err = r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
if canRetry := isWatchErrorRetriable(err); canRetry {
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v returned %v - backing off", r.name, r.typeDescription, err)
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
case <-r.backoffManager.Backoff().C():
continue
}
}
return err
}
}
err = watchHandler(start, w, r.store, r.expectedType, r.expectedGVK, r.name, r.typeDescription, r.setLastSyncResourceVersion, nil, r.clock, resyncerrc, stopCh)
// Ensure that watch will not be reused across iterations.
w.Stop()
w = nil
retry.After(err)
if err != nil {
// 错误判断 ...
}
}
}
cache.ListWatch 实际调用 Request watch
func (r *Request) Watch(ctx context.Context) (watch.Interface, error) {
// ...
for {
if err := retry.Before(ctx, r); err != nil {
return nil, retry.WrapPreviousError(err)
}
req, err := r.newHTTPRequest(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
resp, err := client.Do(req)
retry.After(ctx, r, resp, err)
if err == nil && resp.StatusCode == http.StatusOK {
return r.newStreamWatcher(resp)
}
// ...
}
}
stream 接收 放入 result
func (sw *StreamWatcher) receive() {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer close(sw.result)
defer sw.Stop()
for {
action, obj, err := sw.source.Decode()
if err != nil {
// ...
}
select {
case <-sw.done:
return
case sw.result <- Event{
Type: action,
Object: obj,
}:
}
}
}
监听事件处理
// watchHandler watches w and sets setLastSyncResourceVersion
func watchHandler(start time.Time,
w watch.Interface,
store Store,
expectedType reflect.Type,
expectedGVK *schema.GroupVersionKind,
name string,
expectedTypeName string,
setLastSyncResourceVersion func(string),
clock clock.Clock,
errc chan error,
stopCh <-chan struct{},
) error {
eventCount := 0
// Stopping the watcher should be idempotent and if we return from this function there's no way
// we're coming back in with the same watch interface.
defer w.Stop()
loop:
for {
select {
// ...
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
if !ok {
break loop
}
if event.Type == watch.Error {
return apierrors.FromObject(event.Object)
}
// 。。。
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", name, event))
continue
}
// 获取当前对象的 resourceVersion
resourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added: // 新增事件
err := store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Modified: // 更新事件
err := store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Deleted: // 删除事件
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", name, event))
}
// 更新 resource version 版本, 下次使用该 resourceVersion 来 watch 监听.
setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
if rvu, ok := store.(ResourceVersionUpdater); ok {
rvu.UpdateResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
}
eventCount++
}
}
// ...
return nil
}
// 设置资源版本
func (r *Reflector) setLastSyncResourceVersion(v string) {
r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Lock()
defer r.lastSyncResourceVersionMutex.Unlock()
r.lastSyncResourceVersion = v
}
store –> deltaFIFO 队列
store 初始化
func newInformer(
lw ListerWatcher,
objType runtime.Object,
resyncPeriod time.Duration,
h ResourceEventHandler,
clientState Store,
transformer TransformFunc,
) Controller {
// This will hold incoming changes. Note how we pass clientState in as a
// KeyLister, that way resync operations will result in the correct set
// of update/delete deltas.
fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{
KnownObjects: clientState,
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
Transformer: transformer,
})
cfg := &Config{
Queue: fifo,
ListerWatcher: lw,
ObjectType: objType,
FullResyncPeriod: resyncPeriod,
RetryOnError: false,
// 后期的处理函数
Process: func(obj interface{}, isInInitialList bool) error {
if deltas, ok := obj.(Deltas); ok {
return processDeltas(h, clientState, deltas, isInInitialList)
}
return errors.New("object given as Process argument is not Deltas")
},
}
return New(cfg)
}
func NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(opts DeltaFIFOOptions) *DeltaFIFO {
if opts.KeyFunction == nil {
opts.KeyFunction = MetaNamespaceKeyFunc // 格式为 namespace/name
}
f := &DeltaFIFO{
items: map[string]Deltas{},
queue: []string{},
keyFunc: opts.KeyFunction,
knownObjects: opts.KnownObjects,
emitDeltaTypeReplaced: opts.EmitDeltaTypeReplaced,
}
f.cond.L = &f.lock
return f
}
队列中的事件类型
type DeltaType string
// Change type definition
const (
Added DeltaType = "Added"
Updated DeltaType = "Updated"
Deleted DeltaType = "Deleted"
// Replaced is emitted when we encountered watch errors and had to do a
// relist. We don't know if the replaced object has changed.
//
// NOTE: Previous versions of DeltaFIFO would use Sync for Replace events
// as well. Hence, Replaced is only emitted when the option
// EmitDeltaTypeReplaced is true.
Replaced DeltaType = "Replaced"
// Sync is for synthetic events during a periodic resync.
Sync DeltaType = "Sync"
)
结构体定义
type DeltaFIFO struct {
// lock/cond protects access to 'items' and 'queue'.
lock sync.RWMutex
cond sync.Cond
// `items` maps a key to a Deltas.
// Each such Deltas has at least one Delta.
items map[string]Deltas
// `queue` maintains FIFO order of keys for consumption in Pop().
// There are no duplicates in `queue`.
// A key is in `queue` if and only if it is in `items`.
queue []string
// populated is true if the first batch of items inserted by Replace() has been populated
// or Delete/Add/Update/AddIfNotPresent was called first.
populated bool
// initialPopulationCount is the number of items inserted by the first call of Replace()
initialPopulationCount int
// keyFunc is used to make the key used for queued item
// insertion and retrieval, and should be deterministic.
keyFunc KeyFunc
// ..
}
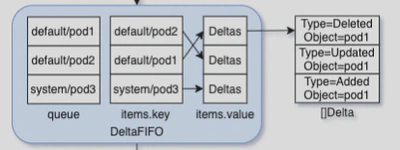
type Delta struct {
Type DeltaType
Object interface{}
}
// Deltas is a list of one or more 'Delta's to an individual object.
// The oldest delta is at index 0, the newest delta is the last one.
type Deltas []Delta
添加,修改,删除
// Add inserts an item, and puts it in the queue. The item is only enqueued
// if it doesn't already exist in the set.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Add(obj interface{}) error {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
f.populated = true
return f.queueActionLocked(Added, obj)
}
// Update is just like Add, but makes an Updated Delta.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Update(obj interface{}) error {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
f.populated = true
return f.queueActionLocked(Updated, obj)
}
// Delete is just like Add, but makes a Deleted Delta. If the given
// object does not already exist, it will be ignored. (It may have
// already been deleted by a Replace (re-list), for example.) In this
// method `f.knownObjects`, if not nil, provides (via GetByKey)
// _additional_ objects that are considered to already exist.
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Delete(obj interface{}) error {
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
f.populated = true
if f.knownObjects == nil {
if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {
// Presumably, this was deleted when a relist happened.
// Don't provide a second report of the same deletion.
return nil
}
} else {
// We only want to skip the "deletion" action if the object doesn't
// exist in knownObjects and it doesn't have corresponding item in items.
// Note that even if there is a "deletion" action in items, we can ignore it,
// because it will be deduped automatically in "queueActionLocked"
_, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(id)
_, itemsExist := f.items[id]
if err == nil && !exists && !itemsExist {
// Presumably, this was deleted when a relist happened.
// Don't provide a second report of the same deletion.
return nil
}
}
// exist in items and/or KnownObjects
return f.queueActionLocked(Deleted, obj)
}
添加
func (f *DeltaFIFO) queueActionLocked(actionType DeltaType, obj interface{}) error {
// 通过 obj 拼凑 id, 格式为 namespace/name
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
// ...
// 从 items 获取已经存在 deltas 列表
oldDeltas := f.items[id]
// 把新增的事件加入到已存在的 deltas
newDeltas := append(oldDeltas, Delta{actionType, obj})
newDeltas = dedupDeltas(newDeltas)
if len(newDeltas) > 0 {
if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {
f.queue = append(f.queue, id)
}
f.items[id] = newDeltas
// 唤醒其他协程
f.cond.Broadcast()
} else {
// This never happens, because dedupDeltas never returns an empty list
// when given a non-empty list (as it is here).
// If somehow it happens anyway, deal with it but complain.
// ...
}
return nil
}
消费元素
func (c *controller) processLoop() {
for {
// 从 deltaFIFO 队列中获取事件
obj, err := c.config.Queue.Pop(PopProcessFunc(c.config.Process))
// ...
}
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Pop(process PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error) {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
for {
for len(f.queue) == 0 {
// 如果 queue 队列为空, 则使用 cond.Wait 陷入等待.
f.cond.Wait()
}
// 从队列头部获取元素
id := f.queue[0]
// 收缩队列去除头部
f.queue = f.queue[1:]
depth := len(f.queue)
// ...
item, ok := f.items[id]
if !ok {
// This should never happen
klog.Errorf("Inconceivable! %q was in f.queue but not f.items; ignoring.", id)
continue
}
delete(f.items, id)
// ...
// 把上面获取的 deltas 对象交给 process 处理
err := process(item, isInInitialList)
if e, ok := err.(ErrRequeue); ok {
f.addIfNotPresent(id, item)
err = e.Err
}
// Don't need to copyDeltas here, because we're transferring
// ownership to the caller.
return item, err
}
}
调用传入的 process 方法其实就是 controller Process. 按照 deltaType 类型, 选择调用handler.OnAdd OnUpdate OnDelete .
func processDeltas(
// Object which receives event notifications from the given deltas
handler ResourceEventHandler,
clientState Store,
deltas Deltas,
isInInitialList bool,
) error {
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range deltas {
obj := d.Object
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:
if old, exists, err := clientState.Get(obj); err == nil && exists {
// 写入本地缓存
if err := clientState.Update(obj); err != nil {
return err
}
// handler 回调处理
handler.OnUpdate(old, obj)
} else {
if err := clientState.Add(obj); err != nil {
return err
}
handler.OnAdd(obj, isInInitialList)
}
case Deleted:
if err := clientState.Delete(obj); err != nil {
return err
}
handler.OnDelete(obj)
}
}
return nil
}
索引实现原理
初始化
Indexer 的默认实现是 cache
func NewInformer(
lw ListerWatcher,
objType runtime.Object,
resyncPeriod time.Duration,
h ResourceEventHandler,
) (Store, Controller) {
// This will hold the client state, as we know it.
clientState := NewStore(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc)
return clientState, newInformer(lw, objType, resyncPeriod, h, clientState, nil)
}
func NewStore(keyFunc KeyFunc) Store {
return &cache{
cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(Indexers{}, Indices{}),
keyFunc: keyFunc,
}
}
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
// 存储资源对象
items map[string]interface{}
// index implements the indexing functionality
// 存储资源对象的查询索引
index *storeIndex
}
key 计算
// DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc checks for
// DeletedFinalStateUnknown objects before calling
// MetaNamespaceKeyFunc.
func DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {
if d, ok := obj.(DeletedFinalStateUnknown); ok {
return d.Key, nil
}
return MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)
}
索引的数据结构
// storeIndex implements the indexing functionality for Store interface
type storeIndex struct {
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
// key 为 索引函数的名字, value 为 IndexFunc 类型的索引函数
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
// key 为 索引函数的名字, value 是一个 Index 结构.
// 相当于倒排的逻辑, 比如 annotation 里含有 nginx 字符串的有哪些 names.
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// Indices maps a name to an Index
// key 为索引条件, value 为一个集群, 存储了符合条件的 names 集合.
type Indices map[string]Index
案例
package main
import (
"fmt"
v1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/api/meta"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache"
)
// LabelsIndexFunc 用作给出可检索所有的索引值
func LabelsIndexFunc(obj interface{}) ([]string, error) {
metaD, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
return []string{""}, fmt.Errorf("object has no meta: %v", err)
}
return []string{metaD.GetLabels()["app"]}, nil
}
func main() {
// 建立一个名为 app 的 Indexer, 并使用我们自己编写的 索引方法
idxs := cache.Indexers{"app": LabelsIndexFunc}
// 伪造2个pod资源
pod1 := &v1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "pod1",
Namespace: "ns1",
Labels: map[string]string{
"app": "l1",
}}}
pod2 := &v1.Pod{ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: "pod2",
Namespace: "ns2",
Labels: map[string]string{
"app": "l2",
}}}
// 初始化 Indexer
myIdx := cache.NewIndexer(cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc, idxs)
// 添加pod
myIdx.Add(pod1)
myIdx.Add(pod2)
// 打印通过索引检索的资源
fmt.Println(myIdx.IndexKeys("app", "l1"))
}
// Output
// 结果只返回 app=l1 的 pod
// [ns1/pod1] <nil>
增删改索引
// Add inserts an item into the cache.
func (c *cache) Add(obj interface{}) error {
// 计算 key 一般是资源对象的 namespace/name 值,
key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
c.cacheStorage.Add(key, obj)
return nil
}
// Update sets an item in the cache to its updated state.
func (c *cache) Update(obj interface{}) error {
key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
c.cacheStorage.Update(key, obj)
return nil
}
// Delete removes an item from the cache.
func (c *cache) Delete(obj interface{}) error {
key, err := c.keyFunc(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
c.cacheStorage.Delete(key)
return nil
}
添加
func (c *threadSafeMap) Add(key string, obj interface{}) {
c.Update(key, obj)
}
func (c *threadSafeMap) Update(key string, obj interface{}) {
c.lock.Lock()
defer c.lock.Unlock()
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj
c.index.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key)
}
updateIndices 方法是用来更新索引, 其内部逻辑是这样的, 遍历所有注册的 indexer 索引方法集合, 然后使用 indexFunc 计算出 oldobj 和 newobj 的索引值. 后面删除旧的 obj 的索引值, 接着添加新的 obj 索引值.
// updateIndices modifies the objects location in the managed indexes:
// - for create you must provide only the newObj
// - for update you must provide both the oldObj and the newObj
// - for delete you must provide only the oldObj
// updateIndices must be called from a function that already has a lock on the cache
func (i *storeIndex) updateIndices(oldObj interface{}, newObj interface{}, key string) {
var oldIndexValues, indexValues []string
var err error
for name, indexFunc := range i.indexers {
if oldObj != nil {
oldIndexValues, err = indexFunc(oldObj)
} else {
oldIndexValues = oldIndexValues[:0]
}
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to calculate an index entry for key %q on index %q: %v", key, name, err))
}
if newObj != nil {
indexValues, err = indexFunc(newObj)
} else {
indexValues = indexValues[:0]
}
if err != nil {
panic(fmt.Errorf("unable to calculate an index entry for key %q on index %q: %v", key, name, err))
}
index := i.indices[name]
if index == nil {
index = Index{}
i.indices[name] = index
}
if len(indexValues) == 1 && len(oldIndexValues) == 1 && indexValues[0] == oldIndexValues[0] {
// We optimize for the most common case where indexFunc returns a single value which has not been changed
continue
}
// 在 index 里删除旧的 obj 的索引值列表
for _, value := range oldIndexValues {
i.deleteKeyFromIndex(key, value, index)
}
// 在 index 里添加更新的 obj 的索引值列表
for _, value := range indexValues {
i.addKeyToIndex(key, value, index)
}
}
}
// 添加索引, 直接在 index 关联的 set 集合里添加 key.
func (i *storeIndex) addKeyToIndex(key, indexValue string, index Index) {
set := index[indexValue]
if set == nil {
set = sets.String{}
index[indexValue] = set
}
set.Insert(key)
}
// 删除索引, 直接在 index 关联的 set 集合里删除 key
func (i *storeIndex) deleteKeyFromIndex(key, indexValue string, index Index) {
set := index[indexValue]
if set == nil {
return
}
set.Delete(key)
// If we don't delete the set when zero, indices with high cardinality
// short lived resources can cause memory to increase over time from
// unused empty sets. See `kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/84959`.
if len(set) == 0 {
delete(index, indexValue)
}
}
cache.controller 控制器实现原理
Controller 作为中心的控制器, 连接了 Reflector / DeltaFIFO / Indexer / Store 组件. 其内部逻辑会实例化 reflector, 然后启动 reflector, 接着使用 processLoop 来从 deltaFIFO 队列中获取事件.
type controller struct {
config Config
reflector *Reflector
reflectorMutex sync.RWMutex
clock clock.Clock
}
type Config struct {
// 其实就是 DeltaFIFO 实现
Queue
// 构造 Reflector 需要
ListerWatcher
// Pop 出来的 obj 处理函数
Process ProcessFunc
// 目标对象类型
ObjectType runtime.Object
// Watch 返回 err 的回调函数
WatchErrorHandler WatchErrorHandler
// Watch 分页大小
WatchListPageSize int64
}
Informer 的实现原理
informer 的创建
func NewIndexerInformer(
lw ListerWatcher,
objType runtime.Object,
resyncPeriod time.Duration,
h ResourceEventHandler,
indexers Indexers,
) (Indexer, Controller) {
// 本地缓存
clientState := NewIndexer(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc, indexers)
// 实际就是创建 cache.controller
return clientState, newInformer(lw, objType, resyncPeriod, h, clientState, nil)
}
ResyncDuration 的参数: 多久从 Indexer 缓存中同步一次数据到 Delta FIFO 队列, 为什么需要 Resync 机制呢?因为在处理 Informer 事件回调时,可能存在处理失败的情况,定时的 Resync 让这些处理失败的事件有了重新 onUpdate 处理的机会。 错误理解resync:定时从etcd拉最新的以防出错
// k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache/delta_fifo.go
// 重新同步一次 Indexer 缓存数据到 Delta FIFO 队列中
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Resync() error {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
if f.knownObjects == nil {
return nil
}
// 遍历 indexer 中的 key,传入 syncKeyLocked 中处理
keys := f.knownObjects.ListKeys()
for _, k := range keys {
if err := f.syncKeyLocked(k); err != nil {
return err
}
}
return nil
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) syncKeyLocked(key string) error {
obj, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(key)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Unexpected error %v during lookup of key %v, unable to queue object for sync", err, key)
return nil
} else if !exists {
klog.Infof("Key %v does not exist in known objects store, unable to queue object for sync", key)
return nil
}
// 如果发现 FIFO 队列中已经有相同 key 的 event 进来了,说明该资源对象有了新的 event,
// 在 Indexer 中旧的缓存应该失效,因此不做 Resync 处理直接返回 nil
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
if len(f.items[id]) > 0 {
return nil
}
// 重新放入 FIFO 队列中
if err := f.queueActionLocked(Sync, obj); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("couldn't queue object: %v", err)
}
return nil
}