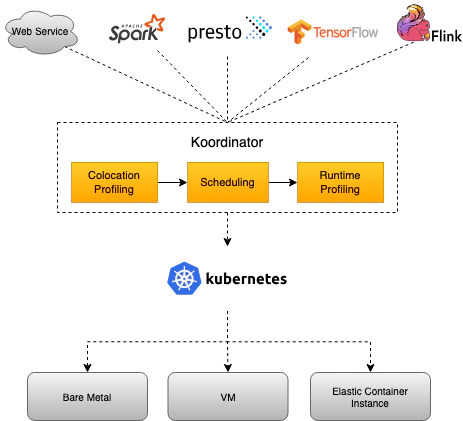
Koodinator 混合工作负载调度系统
基本知识
RDT(Resource Director Technology)

RDT技术提供了LLC(Last Level Cache)以及MB(Memory Bandwidth)内存带宽的分配和监控能力.
RDT的主要功能有以下几个:
- CAT(Cache Allocation Technology):分配和隔离LLC资源
- CMT(Cache Monitor Technology):监控LLC的使用情况
- MBA(Memory Bandwidth Allocation):内存带宽分配和隔离
- MBM(Memory Bandwidth Monitor):内存带宽监控
- CDP(Code & Data Prioritization):细化的Code-Cache和Data-Cache的分配
在混合部署场景下,cgroup提供了粗粒度的CPU、内存、IO等资源的隔离和分配,但是从软件层面无法对LLC(last level cache)缓存和内存带宽等共享资源进行隔离,离线业务可以通过争抢LLC和内存带宽来干扰在线业务。 RDT从硬件层面提供了细粒度的LLC资源的分配和监控能力,在混部场景运用广泛。
Resctrl文件系统是Linux内核在4.10提供的对RDT技术的支持,作为一个伪文件系统在使用方式上与cgroup是类似,通过提供一系列的文件为用户态提供查询和修改接口。
组成

Koordinator 由两个控制面(Koordinator Scheduler/Koordinator Manager)和一个 DaemonSet 组件(Koordlet)组成。
Koord-Scheduler
Koord-Scheduler 以 Deployment 的形式部署在集群中,用于增强 Kubernetes 在 QoS-aware,差异化 SLO 以及任务调度场景的资源调度能力
- QoS-aware 调度,包括负载感知调度让节点间负载更佳平衡,资源超卖的方式支持运行更多的低优先级工作负载。
- 差异化 SLO,包括 CPU 精细化编排,为不同的工作负载提供不同的 QoS 隔离策略(cfs,LLC,memory 带宽,网络带宽,磁盘io)。
- 任务调度,包括弹性额度管理,Gang 调度,异构资源调度等,以支持更好的运行大数据和 AI 工作负载。
Koord-Descheduler
Koord-Decheduler 以 Deployment 的形式部署在集群中,它是 kubernetes 上游社区的增强版本,当前包含:
- 重调度框架, Koord-Decheduler 重新设计了全新重调度框架,在可扩展性、资源确定性以及安全性上增加了诸多的加强,更多的细节.
- 负载感知重调度,基于新框架实现的一个负载感知重调度插件,支持用户配置节点的安全水位,以驱动重调度器持续优化集群编排,从而规避集群中出现局部节点热点.
Koord-Manager
Koord-Manager 以 Deployment 的形式部署,通常由两个实例组成,一个 leader 实例和一个 backup 实例。Koordinator Manager 由几个控制器和 webhooks 组成,用于协调混部场景下的工作负载,资源超卖(resource overcommitment)和 SLO 管理。
目前,提供了三个组件:
- Colocation Profile,用于支持混部而不需要修改工作负载。用户只需要在集群中做少量的配置,原来的工作负载就可以在混部模式下运行,了解更多关于Colocation Profile。
- SLO 控制器,用于资源超卖(resource overcommitment)管理,根据节点混部时的运行状态,动态调整集群的超发(overcommit)配置比例。该控制器的核心职责是管理混部时的 SLO,如智能识别出集群中的异常节点并降低其权重,动态调整混部时的水位和压力策略,从而保证集群中 pod 的稳定性和吞吐量。
- Recommender(即将推出),它使用 histograms 来统计和预测工作负载的资源使用细节,用来预估工作负载的峰值资源需求
Koordlet
Koordlet 以 DaemonSet 的形式部署在 Kubernetes 集群中,用于支持混部场景下的资源超卖(resource overcommitment)、干扰检测、QoS 保证等。
在Koordlet内部,它主要包括以下模块:
- 资源 Profiling,估算 Pod 资源的实际使用情况,回收已分配但未使用的资源,用于低优先级 Pod 的 overcommit。
- 资源隔离,为不同类型的 Pod 设置资源隔离参数,避免低优先级的 Pod 影响高优先级 Pod 的稳定性和性能。
- 干扰检测,对于运行中的 Pod,动态检测资源争夺,包括 CPU 调度、内存分配延迟、网络、磁盘 IO 延迟等。
- QoS 管理器,根据资源剖析、干扰检测结果和 SLO 配置,动态调整混部节点的水位,抑制影响服务质量的 Pod。
- 资源调优,针对混部场景进行容器资源调优,优化容器的 CPU Throttle、OOM 等,提高服务运行质量。
Koord-RuntimeProxy
Koord-RuntimeProxy 以 systemd service 的形式部署在 Kubernetes 集群的节点上,用于代理 Kubelet 与 containerd/docker 之间的 CRI 请求。这一个代理被设计来支持精细化的资源管理策略,比如为不同 QoS Pod 设置不同的 cgroup 参数,包括内核 cfs quota,resctl 等等技术特性,以改进 Pod 的运行时质量。。
优先级
Koordinator 将不同类型的工作负载匹配到不同的优先级:
- koord-prod,运行典型的延迟敏感型服务,一般是指需要 “实时 “响应的服务类型,比如通过点击移动APP中的按钮调用的典型服务。
- koord-mid,对应于长周期的可用资源,一般用于运行一些实时计算、人工智能训练任务/作业,如 tensorflow/pytorch 等。
- koord-batch,对应于的短周期可用资源,运行典型的离线批处理作业,一般指离线分析类作业,如日级大数据报告、非交互式 SQL 查询。
- koord-free,运行低优先级的离线批处理作业,一般指不做资源预算,利用闲置资源尽量完成,如开发人员为测试目提交的作业。
QOS

- LSE(Latency Sensitive Exclusive): 很少使用,常见于中间件类应用,一般在独立的资源池中使用
- LSR(Latency Sensitive Reserved): 类似于社区的 Guaranteed,CPU 核被绑定
- LS(Latency Sensitive): 微服务工作负载的典型QoS级别,实现更好的资源弹性和更灵活的资源调整能力
- BE(Best Effort): 批量作业的典型 QoS 水平,在一定时期内稳定的计算吞吐量,低成本资源
| Koordinator QoS | Kubernetes QoS |
|---|---|
| LSE(Latency Sensitive Exclusive) | Guaranteed |
| LSR(Latency Sensitive Reserved) | Guaranteed |
| LS(Latency Sensitive) | Guaranteed/Burstable |
| BE(Best Effort) | BestEffort |
自定义 crd
nodemetrics 节点指标
[root@master-01 ~]# kubectl get nodemetrics.slo.koordinator.sh master-01 -o yaml
apiVersion: slo.koordinator.sh/v1alpha1
kind: NodeMetric
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2025-05-24T11:31:54Z"
generation: 1
name: master-01
resourceVersion: "15281512"
uid: 21d81aaf-0338-4e94-bccc-07540fec3575
spec:
metricCollectPolicy:
aggregateDurationSeconds: 300
nodeAggregatePolicy:
durations:
- 5m0s
- 10m0s
- 30m0s
nodeMemoryCollectPolicy: usageWithoutPageCache
reportIntervalSeconds: 60
status:
nodeMetric:
aggregatedNodeUsages:
- duration: 5m0s
usage:
p50:
resources:
cpu: 429m
memory: 5712464Ki
p90:
resources:
cpu: 886m
memory: 5750116Ki
p95:
resources:
cpu: 1097m
memory: 5833412Ki
p99:
resources:
cpu: 1366m
memory: 5938812Ki
# ...
- duration: 30m0s
usage:
p50:
resources:
cpu: 429m
memory: 5723620Ki
p90:
resources:
cpu: 858m
memory: 5823232Ki
p95:
resources:
cpu: 1113m
memory: 5867972Ki
p99:
resources:
cpu: 1467m
memory: 5977372Ki
aggregatedSystemUsages:
- duration: 5m0s
usage:
p50:
resources:
cpu: 153m
memory: 3078852Ki
p90:
resources:
cpu: 407m
memory: 3085764Ki
p95:
resources:
cpu: 539m
memory: 3088652Ki
p99:
resources:
cpu: 795m
memory: 3106312Ki
# ...
- duration: 30m0s
usage:
p50:
resources:
cpu: 156m
memory: 3082092Ki
p90:
resources:
cpu: 424m
memory: 3179492Ki
p95:
resources:
cpu: 569m
memory: 3184832Ki
p99:
resources:
cpu: 853m
memory: 3203756Ki
nodeUsage:
resources:
cpu: 515m
memory: "5862330450"
systemUsage:
resources:
cpu: 196m
memory: "3150994008"
podsMetric:
- name: my-clickhouse-zookeeper-0
namespace: clickhouse
podUsage:
resources:
cpu: 26m
memory: "396051912"
priority: koord-prod
qos: LS
# ....
- name: mysql-7474b86d4f-52p5n
namespace: mysql
podUsage:
resources:
cpu: 21m
memory: "393941019"
priority: koord-prod
qos: LSR
prodReclaimableMetric:
resource:
resources:
cpu: 2380m
memory: "0"
updateTime: "2025-05-25T03:36:38Z"
插件
// https://github.com/koordinator-sh/koordinator/blob/76436ec089110311b8a8a359918e1c7b0942ed67/cmd/koord-scheduler/main.go
var koordinatorPlugins = map[string]frameworkruntime.PluginFactory{
loadaware.Name: loadaware.New, // 负载感知
nodenumaresource.Name: nodenumaresource.New, // numa 感知
reservation.Name: reservation.New, // 资源预留
coscheduling.Name: coscheduling.New,
deviceshare.Name: deviceshare.New,
elasticquota.Name: elasticquota.New,
defaultprebind.Name: defaultprebind.New,
noderesourcesfitplus.Name: noderesourcesfitplus.New,
scarceresourceavoidance.Name: scarceresourceavoidance.New,
schedulinghint.Name: schedulinghint.New,
}
负载感知调度(Load Aware Scheduling)
https://koordinator.sh/zh-Hans/docs/user-manuals/load-aware-scheduling

Koordinator 的调度器提供了一个可配置的调度插件控制集群的利用率。 该调度能力主要依赖于 koordlet 上报的节点指标数据,在调度时会过滤掉负载高于某个阈值的节点,防止 Pod 在这种负载较高的节点上无法获得很好的资源保障,另一方面是避免负载已经较高的节点继续恶化。 在打分阶段选择利用率更低的节点。该插件会基于时间窗口和预估机制规避因瞬间调度太多的 Pod 到冷节点机器出现一段时间后冷节点过热的情况。
过滤
func (p *Plugin) Filter(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *corev1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) *framework.Status {
node := nodeInfo.Node()
// ...
return p.filterNodeUsage(node.Name, pod, usageThresholds, estimated, allocatable, isAgg)
}
func (p *Plugin) filterNodeUsage(nodeName string, pod *corev1.Pod, usageThresholds, estimatedUsed, allocatable ResourceVector, isAgg bool) *framework.Status {
for i, value := range usageThresholds {
if value == 0 {
continue
}
total := allocatable[i]
if total == 0 {
continue
}
// 按利用率阈值过滤节点
estimated := estimatedUsed[i]
usage := int64(math.Round(float64(estimated) / float64(total) * 100))
if usage <= value { // 使用率满足要求
continue
}
// 使用率不满足需求
reason := ErrReasonUsageExceedThreshold
if isAgg {
reason = ErrReasonAggregatedUsageExceedThreshold
}
resourceName := p.vectorizer[i]
if klog.V(5).Enabled() {
klog.InfoS("Node is unschedulable since usage exceeds threshold", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "node", nodeName,
"resource", resourceName, "usage", usage, "threshold", value,
"estimated", getResourceQuantity(resourceName, estimated),
"total", getResourceQuantity(resourceName, total))
}
return framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable, fmt.Sprintf(reason, resourceName))
}
return nil
}
打分
评分算法的核心逻辑是选择资源使用量最小的节点。 但是考虑到资源使用上报的延迟和 Pod 启动时间的延迟,时间窗口内已经调度的 Pod 和当前正在调度的 Pod 的资源请求也会被估算出来,并且估算值将参与计算
func (p *Plugin) Score(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *corev1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *framework.Status) {
// ...
if klog.V(6).Enabled() {
klog.InfoS("Estimate node usage for scoring", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "node", nodeMetric.Name,
"estimated", klog.Format(p.vectorizer.ToList(estimated)),
"estimatedExistingPods", klog.KObjSlice(estimatedPods))
}
score := loadAwareSchedulingScorer(p.args.DominantResourceWeight, p.scoreWeights, estimated, allocatable)
return score, nil
}
func loadAwareSchedulingScorer(dominantWeight int64, resToWeightMap, used, allocatable ResourceVector) int64 {
var nodeScore, dominantScore, weightSum int64
if dominantWeight != 0 {
dominantScore, weightSum = framework.MaxNodeScore, dominantWeight
}
for i, weight := range resToWeightMap {
score := leastUsedScore(used[i], allocatable[i])
nodeScore += score * weight
weightSum += weight
if dominantScore > score {
dominantScore = score
}
}
nodeScore += dominantScore * dominantWeight
if weightSum <= 0 {
return 0
}
return nodeScore / weightSum
}
func leastUsedScore(used, capacity int64) int64 {
if capacity == 0 {
return 0
}
if used > capacity {
return 0
}
// 计算规则
return ((capacity - used) * framework.MaxNodeScore) / capacity
}
还基于主导资源公平性概念添加了一个 dominantResourceWeight 参数,表示主导资源的权重。节点的主导资源是其上利用率最大的资源。
GangScheduling 成组调度
只有当已经完成调度资源数超过前面声明当前最小资源集合数才能触发节点绑定。
资源超发 (Resource Overcommitment)
在使用 K8s 集群时,用户很难准确的评估在线应用的资源使用情况,不知道该怎么更好的设置 Pod 的 Request 和 Limit,因此往往为了保障在线应用的稳定性,都会设置较大的资源规格。 在实际生产中,大部分在线应用的实际 CPU 利用率大多数时候都比较低,高的可能也就百分之十几或者二十几,浪费了大量已经被分配但未使用的资源。
标记为 Reclaimed 的部分就是可被回收的资源,这些可回收的资源就可以超发给低优先级的工作负载使用,例如一些离线任务。为了让这些低优先级工作负载方便使用这些资源,Koordinator 会把这些超发资源更新到 NodeStatus 中
自定义开发插件
https://koordinator.sh/zh-Hans/docs/developer-guide/plugin-development/