kube-proxy
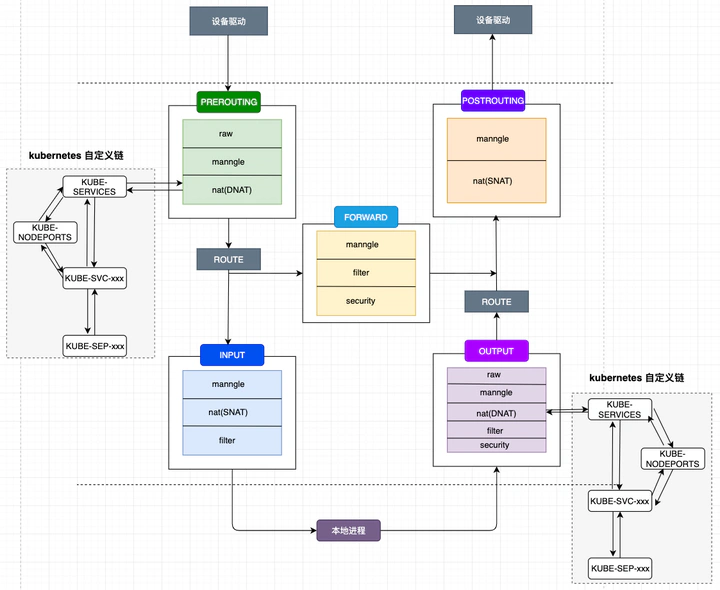
kube-proxy 负责为 Service 实现了一种 VIP(虚拟 IP)的形式。
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/c2bae4dfbd5fb84cbcc53a949231935276a75a51/pkg/proxy/apis/config/types.go
const (
ProxyModeIPTables ProxyMode = "iptables"
ProxyModeIPVS ProxyMode = "ipvs"
ProxyModeKernelspace ProxyMode = "kernelspace"
)
kube-proxy先后出现了三种模式:userspace、iptables、ipvs,其中userspace模式是通过用户态程序实现转发,因性能问题基本被弃用,当前主流的模式是iptables和ipvs。
IPVS vs IPTABLES
- iptables 使用链表,ipvs 使用哈希表;
- iptables 只支持随机、轮询两种负载均衡算法而 ipvs 支持的多达 8 种;
- ipvs 还支持 realserver 运行状况检查、连接重试、端口映射、会话保持等功能。
基本知识
ipvsadm 命令
[root@master-01 ~]# ipvsadm --help
ipvsadm v1.27 2008/5/15 (compiled with popt and IPVS v1.2.1)
Usage:
ipvsadm -A|E -t|u|f service-address [-s scheduler] [-p [timeout]] [-M netmask] [--pe persistence_engine] [-b sched-flags]
ipvsadm -D -t|u|f service-address
ipvsadm -C
ipvsadm -R
ipvsadm -S [-n]
ipvsadm -a|e -t|u|f service-address -r server-address [options]
ipvsadm -d -t|u|f service-address -r server-address
ipvsadm -L|l [options]
ipvsadm -Z [-t|u|f service-address]
ipvsadm --set tcp tcpfin udp
ipvsadm --start-daemon state [--mcast-interface interface] [--syncid sid]
ipvsadm --stop-daemon state
ipvsadm -h
Commands:
Either long or short options are allowed.
--add-service -A add virtual service with options
--edit-service -E edit virtual service with options
--delete-service -D delete virtual service
--clear -C clear the whole table
--restore -R restore rules from stdin
--save -S save rules to stdout
--add-server -a add real server with options
--edit-server -e edit real server with options
--delete-server -d delete real server
--list -L|-l list the table
--zero -Z zero counters in a service or all services
--set tcp tcpfin udp set connection timeout values
--start-daemon start connection sync daemon
--stop-daemon stop connection sync daemon
--help -h display this help message
Options:
--tcp-service -t service-address service-address is host[:port]
--udp-service -u service-address service-address is host[:port]
--fwmark-service -f fwmark fwmark is an integer greater than zero
--ipv6 -6 fwmark entry uses IPv6
--scheduler -s scheduler one of rr|wrr|lc|wlc|lblc|lblcr|dh|sh|sed|nq,
the default scheduler is wlc.
--pe engine alternate persistence engine may be sip,
not set by default.
--persistent -p [timeout] persistent service
--netmask -M netmask persistent granularity mask
--real-server -r server-address server-address is host (and port)
--gatewaying -g gatewaying (direct routing) (default)
--ipip -i ipip encapsulation (tunneling)
--masquerading -m masquerading (NAT)
--weight -w weight capacity of real server
--u-threshold -x uthreshold upper threshold of connections
--l-threshold -y lthreshold lower threshold of connections
--mcast-interface interface multicast interface for connection sync
--syncid sid syncid for connection sync (default=255)
--connection -c output of current IPVS connections
--timeout output of timeout (tcp tcpfin udp)
--daemon output of daemon information
--stats output of statistics information
--rate output of rate information
--exact expand numbers (display exact values)
--thresholds output of thresholds information
--persistent-conn output of persistent connection info
--nosort disable sorting output of service/server entries
--sort does nothing, for backwards compatibility
--ops -o one-packet scheduling
--numeric -n numeric output of addresses and ports
--sched-flags -b flags scheduler flags (comma-separated)
[root@master-01 ~]# kubectl get pod -n monitor -l app.kubernetes.io/name=kube-state-metrics -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
prometheus-kube-state-metrics-6ffdc9795c-49sgc 1/1 Running 0 14h 192.168.1.8 worker-01 <none> <none>
[root@master-01 ~]# kubectl get svc -n monitor prometheus-kube-state-metrics -o wide
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE SELECTOR
prometheus-kube-state-metrics ClusterIP 10.68.236.6 <none> 8080/TCP 14h app.kubernetes.io/instance=prometheus,app.kubernetes.io/name=kube-state-metrics
# -S表示输出所保存的规则,-n表示以数字的形式输出ip和端口
[root@master-01 ~]# ipvsadm --save -n |grep 10.68.236.6
-A -t 10.68.236.6:8080 -s rr # ipvs的LB IP为ClusterIP,scheduler 算法为rr
-a -t 10.68.236.6:8080 -r 192.168.1.8:8080 -m -w 1 # real-server为Pod的IP, masquerading (NAT), -w weight 为1
iptables
功能
- 流量转发:DNAT 实现 IP 地址和端口的映射;
- 负载均衡:statistic 模块为每个后端设置权重;
- 会话保持:recent 模块设置会话保持时间;
kube-proxy iptables模式只在nat表和filter表增加了iptables规则
ipset 命令
ipset命令是用于管理内核中IP sets模块的,如iptables之于netfilter
ipset主要是由iptables来使用,用于提高iptables的灵活性,简化iptables的规则。可能你在使用iptables时会感觉到以下不便:
使用iptables命令为一批IP地址或端口应用相同的iptables规则时,不得不为每个IP或端口都新建一条iptables规则。这有时会让iptables某个表特别庞大,但是规则看起来又非常冗余。
当需要给某个iptables规则应用到一个新的IP地址或端口时,我们不得不新建一条iptables规则;当需要给某个iptables规则删除其中某个IP地址或端口时,则需要直接删除那条iptables规则。这会让iptables操作特别繁琐。
ipset可以解决以上问题:
当需要把一批IP地址或端口都应用某个iptables规则时,只需要把一批IP地址和端口放入一个ipset中,把iptables规则应用到这个ipset就可以了。
当需要更新iptables规则的IP地址或端口时,只要更新对应ipset中的IP地址或端口就可以了,不需要修改iptables表。
# 创建名称为test的IP集
$ ipset create test hash:ip
# 添加114.114.114.114到test IP集中
$ ipset add test 114.114.114.114
# 以普通文本格式输出test IP集内容
$ ipset list test -output plain
Name: test
Type: hash:ip
Revision: 4
Header: family inet hashsize 1024 maxelem 65536
Size in memory: 8264
References: 0
Members:
114.114.114.114
问题
kube-proxy 是否可以不用安装,是否有其他替代品?
可以,替代品cilium
- https://docs.cilium.io/en/v1.12/gettingstarted/kubeproxy-free/#kubernetes-without-kube-proxy, 对应中文 https://juejin.cn/post/7000021547633098788
ProxyServer 初始化
func NewProxyServer(o *Options) (*ProxyServer, error) {
return newProxyServer(o.config, o.master)
}
func newProxyServer(
config *proxyconfigapi.KubeProxyConfiguration,
master string) (*ProxyServer, error) {
// ...
proxyMode := getProxyMode(config.Mode)
detectLocalMode, err = getDetectLocalMode(config)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot determine detect-local-mode: %v", err)
}
var nodeInfo *v1.Node
podCIDRs := []string{}
if detectLocalMode == proxyconfigapi.LocalModeNodeCIDR {
klog.InfoS("Watching for node, awaiting podCIDR allocation", "hostname", hostname)
nodeInfo, err = waitForPodCIDR(client, hostname)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
podCIDRs = nodeInfo.Spec.PodCIDRs
klog.InfoS("NodeInfo", "podCIDR", nodeInfo.Spec.PodCIDR, "podCIDRs", nodeInfo.Spec.PodCIDRs)
}
klog.V(2).InfoS("DetectLocalMode", "localMode", string(detectLocalMode))
primaryFamily := v1.IPv4Protocol
primaryProtocol := utiliptables.ProtocolIPv4
if netutils.IsIPv6(nodeIP) {
primaryFamily = v1.IPv6Protocol
primaryProtocol = utiliptables.ProtocolIPv6
}
execer := exec.New()
iptInterface := utiliptables.New(execer, primaryProtocol)
var ipt [2]utiliptables.Interface
dualStack := true // While we assume that node supports, we do further checks below
// Create iptables handlers for both families, one is already created
// Always ordered as IPv4, IPv6
if primaryProtocol == utiliptables.ProtocolIPv4 {
ipt[0] = iptInterface
ipt[1] = utiliptables.New(execer, utiliptables.ProtocolIPv6)
} else {
ipt[0] = utiliptables.New(execer, utiliptables.ProtocolIPv4)
ipt[1] = iptInterface
}
nodePortAddresses := config.NodePortAddresses
if !ipt[0].Present() {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("iptables is not supported for primary IP family %q", primaryProtocol)
} else if !ipt[1].Present() {
klog.InfoS("kube-proxy running in single-stack mode: secondary ipFamily is not supported", "ipFamily", ipt[1].Protocol())
dualStack = false
// Validate NodePortAddresses is single-stack
npaByFamily := proxyutil.MapCIDRsByIPFamily(config.NodePortAddresses)
secondaryFamily := proxyutil.OtherIPFamily(primaryFamily)
badAddrs := npaByFamily[secondaryFamily]
if len(badAddrs) > 0 {
klog.InfoS("Ignoring --nodeport-addresses of the wrong family", "ipFamily", secondaryFamily, "addresses", badAddrs)
nodePortAddresses = npaByFamily[primaryFamily]
}
}
if proxyMode == proxyconfigapi.ProxyModeIPTables {
// 实例化 iptables 的 proxy
} else if proxyMode == proxyconfigapi.ProxyModeIPVS {
// 实例化 kernel, ipset,ipvs 管理工具
kernelHandler := ipvs.NewLinuxKernelHandler()
ipsetInterface = utilipset.New(execer)
ipvsInterface = utilipvs.New()
// 实例化 ipvs 的 proxy
}
return &ProxyServer{
Client: client,
EventClient: eventClient,
IptInterface: iptInterface,
IpvsInterface: ipvsInterface,
IpsetInterface: ipsetInterface,
execer: execer,
Proxier: proxier,
Broadcaster: eventBroadcaster,
Recorder: recorder,
ConntrackConfiguration: config.Conntrack,
Conntracker: &realConntracker{},
ProxyMode: proxyMode,
NodeRef: nodeRef,
MetricsBindAddress: config.MetricsBindAddress,
BindAddressHardFail: config.BindAddressHardFail,
EnableProfiling: config.EnableProfiling,
OOMScoreAdj: config.OOMScoreAdj,
ConfigSyncPeriod: config.ConfigSyncPeriod.Duration,
HealthzServer: healthzServer,
localDetectorMode: detectLocalMode,
podCIDRs: podCIDRs,
}, nil
}
启动
func (s *ProxyServer) Run() error {
// To help debugging, immediately log version
klog.InfoS("Version info", "version", version.Get())
// ...
// Make informers that filter out objects that want a non-default service proxy.
informerFactory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(s.Client, s.ConfigSyncPeriod,
informers.WithTweakListOptions(func(options *metav1.ListOptions) {
options.LabelSelector = labelSelector.String()
}))
// 监听 Services and EndpointSlices
// 初始化阶段时会实例化 ServiceConfig 对象, 并向 serviceConfig 注册 proxier 对象.
//ServiceConfig 实现了对 informer 的监听,并向 informer 注册封装的回调接口. 当有 service 的增删改事件时, 调用 proxier 的 OnServiceAdd, OnServiceUpdate, OnServiceDelete 方法.
serviceConfig := config.NewServiceConfig(informerFactory.Core().V1().Services(), s.ConfigSyncPeriod)
serviceConfig.RegisterEventHandler(s.Proxier)
go serviceConfig.Run(wait.NeverStop)
endpointSliceConfig := config.NewEndpointSliceConfig(informerFactory.Discovery().V1().EndpointSlices(), s.ConfigSyncPeriod)
endpointSliceConfig.RegisterEventHandler(s.Proxier)
go endpointSliceConfig.Run(wait.NeverStop)
// This has to start after the calls to NewServiceConfig because that
// function must configure its shared informer event handlers first.
informerFactory.Start(wait.NeverStop)
// 监听 node 资源更新
// Make an informer that selects for our nodename.
currentNodeInformerFactory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(s.Client, s.ConfigSyncPeriod,
informers.WithTweakListOptions(func(options *metav1.ListOptions) {
options.FieldSelector = fields.OneTermEqualSelector("metadata.name", s.NodeRef.Name).String()
}))
nodeConfig := config.NewNodeConfig(currentNodeInformerFactory.Core().V1().Nodes(), s.ConfigSyncPeriod)
// https://issues.k8s.io/111321
if s.localDetectorMode == kubeproxyconfig.LocalModeNodeCIDR {
nodeConfig.RegisterEventHandler(proxy.NewNodePodCIDRHandler(s.podCIDRs))
}
nodeConfig.RegisterEventHandler(s.Proxier)
go nodeConfig.Run(wait.NeverStop)
// This has to start after the calls to NewNodeConfig because that must
// configure the shared informer event handler first.
currentNodeInformerFactory.Start(wait.NeverStop)
// Birth Cry after the birth is successful
s.birthCry()
go s.Proxier.SyncLoop()
return <-errCh
}
iptables 模式
proxier 初始化
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/46a2ce22293751e4b2817a51ddd093278bf03fbb/pkg/proxy/iptables/proxier.go
func NewProxier(ipFamily v1.IPFamily,
ipt utiliptables.Interface,
sysctl utilsysctl.Interface,
exec utilexec.Interface,
syncPeriod time.Duration,
minSyncPeriod time.Duration,
masqueradeAll bool,
localhostNodePorts bool,
masqueradeBit int,
localDetector proxyutiliptables.LocalTrafficDetector,
hostname string,
nodeIP net.IP,
recorder events.EventRecorder,
healthzServer healthcheck.ProxierHealthUpdater,
nodePortAddressStrings []string,
) (*Proxier, error) {
// ...
// 初始化 proxier
proxier := &Proxier{
svcPortMap: make(proxy.ServicePortMap),
serviceChanges: proxy.NewServiceChangeTracker(newServiceInfo, ipFamily, recorder, nil),
endpointsMap: make(proxy.EndpointsMap),
endpointsChanges: proxy.NewEndpointChangeTracker(hostname, newEndpointInfo, ipFamily, recorder, nil),
needFullSync: true,
syncPeriod: syncPeriod,
iptables: ipt,
masqueradeAll: masqueradeAll,
masqueradeMark: masqueradeMark, // 用来标记 k8s 管理的报文,masqueradeBit 默认为 14, 标记 0x4000 的报文(即 POD 发出的报文),在离开 Node 的时候需要进行 SNAT 转换
exec: exec,
localDetector: localDetector,
hostname: hostname,
nodeIP: nodeIP,
recorder: recorder,
serviceHealthServer: serviceHealthServer,
healthzServer: healthzServer,
precomputedProbabilities: make([]string, 0, 1001),
iptablesData: bytes.NewBuffer(nil),
existingFilterChainsData: bytes.NewBuffer(nil),
filterChains: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
filterRules: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
natChains: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
natRules: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
localhostNodePorts: localhostNodePorts,
nodePortAddresses: nodePortAddresses,
networkInterfacer: utilproxy.RealNetwork{},
}
// 初始化 syncRunner,BoundedFrequencyRunner 是一个定时执行器,会定时执行
// proxier.syncProxyRules 方法,syncProxyRules 是每个 proxier 实际刷新iptables 规则的方法
proxier.syncRunner = async.NewBoundedFrequencyRunner("sync-runner", proxier.syncProxyRules, minSyncPeriod, time.Hour, burstSyncs)
// ...
return proxier, nil
}
更新规则 syncProxyRules
更新 proxier.endpointsMap,proxier.servieMap 两个对象
func (proxier *Proxier) syncProxyRules() {
proxier.mu.Lock()
defer proxier.mu.Unlock()
// ...
serviceUpdateResult := proxier.svcPortMap.Update(proxier.serviceChanges)
endpointUpdateResult := proxier.endpointsMap.Update(proxier.endpointsChanges)
}
创建所需要的 iptable 链
if !tryPartialSync {
for _, jump := range append(iptablesJumpChains, iptablesKubeletJumpChains...) {
// 创建自定义链
if _, err := proxier.iptables.EnsureChain(jump.table, jump.dstChain); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to ensure chain exists", "table", jump.table, "chain", jump.dstChain)
return
}
args := jump.extraArgs
if jump.comment != "" {
args = append(args, "-m", "comment", "--comment", jump.comment)
}
args = append(args, "-j", string(jump.dstChain))
// 插入到已有的链
if _, err := proxier.iptables.EnsureRule(utiliptables.Prepend, jump.table, jump.srcChain, args...); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to ensure chain jumps", "table", jump.table, "srcChain", jump.srcChain, "dstChain", jump.dstChain)
return
}
}
}
ipvs 模式
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/8af1ce5863dc520c94baef1699aa1c904f508e2f/pkg/proxy/ipvs/proxier.go
const (
// defaultScheduler is the default ipvs scheduler algorithm - round robin.
defaultScheduler = "rr"
// defaultDummyDevice is the default dummy interface which ipvs service address will bind to it.
defaultDummyDevice = "kube-ipvs0"
)
当我们创建Service之后,kube-proxy 首先会在宿主机上创建一个虚拟网卡(叫作:kube-ipvs0),并为它分配 Service VIP 作为 IP 地址
[root@master-01 ~]# ip addr show kube-ipvs0
5: kube-ipvs0: <BROADCAST,NOARP> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN group default
link/ether 22:39:ed:93:05:c1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.68.0.1/32 scope global kube-ipvs0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.68.0.2/32 scope global kube-ipvs0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
# ...
初始化
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/8af1ce5863dc520c94baef1699aa1c904f508e2f/pkg/proxy/ipvs/proxier.go
func NewProxier(ipFamily v1.IPFamily,
ipt utiliptables.Interface,
ipvs utilipvs.Interface,
ipset utilipset.Interface,
sysctl utilsysctl.Interface,
exec utilexec.Interface,
syncPeriod time.Duration,
minSyncPeriod time.Duration,
excludeCIDRs []string,
strictARP bool,
tcpTimeout time.Duration,
tcpFinTimeout time.Duration,
udpTimeout time.Duration,
masqueradeAll bool,
masqueradeBit int,
localDetector proxyutiliptables.LocalTrafficDetector,
hostname string,
nodeIP net.IP,
recorder events.EventRecorder,
healthzServer healthcheck.ProxierHealthUpdater,
scheduler string,
nodePortAddressStrings []string,
kernelHandler KernelHandler,
) (*Proxier, error) {
// 一堆校验及sysctl操作
nodePortAddresses := utilproxy.NewNodePortAddresses(nodePortAddressStrings)
serviceHealthServer := healthcheck.NewServiceHealthServer(hostname, recorder, nodePortAddresses, healthzServer)
// excludeCIDRs has been validated before, here we just parse it to IPNet list
parsedExcludeCIDRs, _ := netutils.ParseCIDRs(excludeCIDRs)
proxier := &Proxier{
ipFamily: ipFamily,
svcPortMap: make(proxy.ServicePortMap),
serviceChanges: proxy.NewServiceChangeTracker(newServiceInfo, ipFamily, recorder, nil),
endpointsMap: make(proxy.EndpointsMap),
endpointsChanges: proxy.NewEndpointChangeTracker(hostname, nil, ipFamily, recorder, nil),
initialSync: true,
syncPeriod: syncPeriod,
minSyncPeriod: minSyncPeriod,
excludeCIDRs: parsedExcludeCIDRs,
iptables: ipt,
masqueradeAll: masqueradeAll,
masqueradeMark: masqueradeMark,
exec: exec,
localDetector: localDetector,
hostname: hostname,
nodeIP: nodeIP,
recorder: recorder,
serviceHealthServer: serviceHealthServer,
healthzServer: healthzServer,
ipvs: ipvs,
ipvsScheduler: scheduler,
iptablesData: bytes.NewBuffer(nil),
filterChainsData: bytes.NewBuffer(nil),
natChains: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
natRules: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
filterChains: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
filterRules: utilproxy.LineBuffer{},
netlinkHandle: NewNetLinkHandle(ipFamily == v1.IPv6Protocol),
ipset: ipset,
nodePortAddresses: nodePortAddresses,
networkInterfacer: utilproxy.RealNetwork{},
gracefuldeleteManager: NewGracefulTerminationManager(ipvs),
}
// initialize ipsetList with all sets we needed
proxier.ipsetList = make(map[string]*IPSet)
for _, is := range ipsetInfo {
proxier.ipsetList[is.name] = NewIPSet(ipset, is.name, is.setType, (ipFamily == v1.IPv6Protocol), is.comment)
}
burstSyncs := 2
klog.V(2).InfoS("ipvs sync params", "ipFamily", ipt.Protocol(), "minSyncPeriod", minSyncPeriod, "syncPeriod", syncPeriod, "burstSyncs", burstSyncs)
// 周期执行器
proxier.syncRunner = async.NewBoundedFrequencyRunner("sync-runner", proxier.syncProxyRules, minSyncPeriod, syncPeriod, burstSyncs)
proxier.gracefuldeleteManager.Run()
return proxier, nil
}
func (proxier *Proxier) syncProxyRules() {
proxier.mu.Lock()
defer proxier.mu.Unlock()
// 把从 informer 拿到变更的 servcie 结构,更新到 svcPortMap 里, 每次 Update 还会把 changes 清空.
serviceUpdateResult := proxier.svcPortMap.Update(proxier.serviceChanges)
// 把从 informer 拿到变更的 endpoint 结构,更新到 endpointsMap 里, 每次 Update 还会把 changes 清空.
endpointUpdateResult := proxier.endpointsMap.Update(proxier.endpointsChanges)
// 创建名为 `kube-ipvs0` 的 dummy 类型网络设备
_, err := proxier.netlinkHandle.EnsureDummyDevice(defaultDummyDevice)
if err != nil {
return
}
// 创建 ipset 规则,调用 ipset create 创建 ipset 时,还需指定 size 和 entry 的格式.
for _, set := range proxier.ipsetList {
if err := ensureIPSet(set); err != nil {
return
}
set.resetEntries()
}
// 遍历当前的 services 对象集合
for svcPortName, svcPort := range proxier.svcPortMap {
// 遍历 endpoints 对象
for _, e := range proxier.endpointsMap[svcPortName] {
// 拿到 endpoints 对象
ep, ok := e.(*proxy.BaseEndpointInfo)
epIP := ep.IP()
epPort, err := ep.Port()
// 定义 endpoint 的 ipset entry 结构
entry := &utilipset.Entry{
IP: epIP,
Port: epPort,
Protocol: protocol,
IP2: epIP,
SetType: utilipset.HashIPPortIP,
}
// 在 kubeLoopBackIPSet 配置集合中加入 entry 配置.
proxier.ipsetList[kubeLoopBackIPSet].activeEntries.Insert(entry.String())
}
// 定义 service 的 ipset entry 结构
entry := &utilipset.Entry{
IP: svcInfo.ClusterIP().String(),
Port: svcInfo.Port(),
}
// 把 service ipset entry 加入到 kubeClusterIPSet 配置集合中
proxier.ipsetList[kubeClusterIPSet].activeEntries.Insert(entry.String())
serv := &utilipvs.VirtualServer{
Address: svcInfo.ClusterIP(),
Port: uint16(svcInfo.Port()),
}
// 创建或更新 lvs virtualServer 配置
if err := proxier.syncService(svcPortNameString, serv, true, bindedAddresses); err == nil {
// 创建或更新 lvs realserver 配置
if err := proxier.syncEndpoint(svcPortName, internalNodeLocal, serv); err != nil {}
}
}
// 篇幅不提, 解决 external ip.
for _, externalIP := range svcInfo.ExternalIPStrings() {
...
}
// 篇幅不提,解决 load balancer
for _, ingress := range svcInfo.LoadBalancerIPStrings() {
...
}
// 同步 ipset 配置.
for _, set := range proxier.ipsetList {
set.syncIPSetEntries()
}
// 同步 iptables 的配置.
proxier.writeIptablesRules()
proxier.iptablesData.Reset()
proxier.iptablesData.Write(proxier.natChains.Bytes())
proxier.iptablesData.Write(proxier.natRules.Bytes())
err = proxier.iptables.RestoreAll(proxier.iptablesData.Bytes(), utiliptables.NoFlushTables, utiliptables.RestoreCounters)
...
// 清理绑定的ip地址
legacyBindAddrs := proxier.getLegacyBindAddr(activeBindAddrs, currentBindAddrs)
// 清理需要删除 service, 逻辑里含有 ipvs vs 和 rs 的清理.
proxier.cleanLegacyService(activeIPVSServices, currentIPVSServices, legacyBindAddrs)
// 遍历不新鲜的 servcies 集合,通过 contrack tool 工具剔除在 contrack 里协议为 UDP 的旧连接.
for _, svcIP := range staleServices.UnsortedList() {
if err := conntrack.ClearEntriesForIP(proxier.exec, svcIP, v1.ProtocolUDP); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to delete stale service IP connections", "IP", svcIP)
}
}
}