Kubelet
Sep 5, 2024
·
11 min read
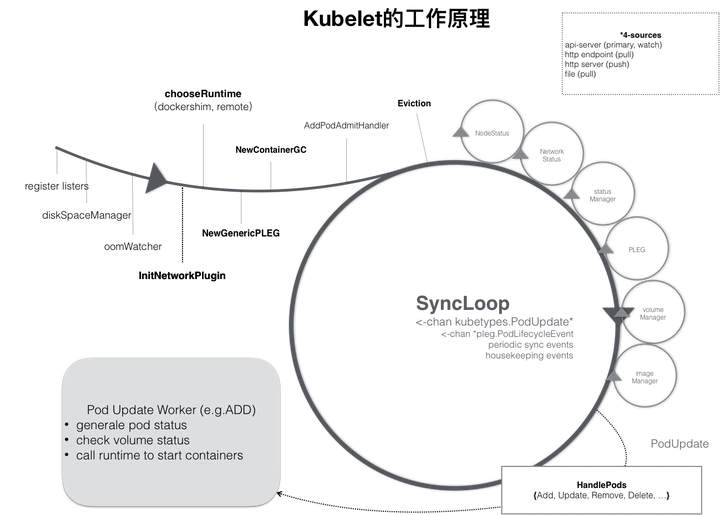
kubelet 的主要功能就是定时从某个地方获取节点上 pod/container 的期望状态(运行什么容器、运行的副本数量、网络或者存储如何配置等等),并调用对应的容器平台接口达到这个状态。
源码:release-1.27
组件说明

type Kubelet struct {
// ...
// podWorkers handle syncing Pods in response to events.
podWorkers PodWorkers
// podManager is a facade that abstracts away the various sources of pods
// this Kubelet services.
podManager kubepod.Manager
// Needed to observe and respond to situations that could impact node stability
evictionManager eviction.Manager
// Volume plugins.
volumePluginMgr *volume.VolumePluginMgr
// Handles container probing.
probeManager prober.Manager
// Manages container health check results.
livenessManager proberesults.Manager
readinessManager proberesults.Manager
startupManager proberesults.Manager
// 负责清理节点上无用的容器
containerGC kubecontainer.GC
// 负责节点节点上的镜像回收
imageManager images.ImageGCManager
// Manager for container logs.
containerLogManager logs.ContainerLogManager
// Secret manager.
secretManager secret.Manager
// ConfigMap manager.
configMapManager configmap.Manager
// Handles certificate rotations.
serverCertificateManager certificate.Manager
// 负责维护状态信息,并把 pod 状态更新到 apiserver; also used as a cache of statuses.
statusManager status.Manager
// VolumeManager runs a set of asynchronous loops that figure out which
// volumes need to be attached/mounted/unmounted/detached based on the pods
// scheduled on this node and makes it so.
volumeManager volumemanager.VolumeManager
// Cloud provider interface.
cloud cloudprovider.Interface
// Handles requests to cloud provider with timeout
cloudResourceSyncManager cloudresource.SyncManager
// Manager of non-Runtime containers.
containerManager cm.ContainerManager
// pluginmanager runs a set of asynchronous loops that figure out which
// plugins need to be registered/unregistered based on this node and makes it so.
pluginManager pluginmanager.PluginManager
// Handles RuntimeClass objects for the Kubelet.
runtimeClassManager *runtimeclass.Manager
// Handles node shutdown events for the Node.
shutdownManager nodeshutdown.Manager
// Manage user namespaces
usernsManager *userns.UsernsManager
// ..
}
- PodWorkers: 处理事件中 Pod 的同步。核心方法 managePodLoop() 间接调用 kubelet.syncPod() 完成 Pod 的同步
- PLEG(pod lifecycle event generator): Pod 生命周期事件(ContainerStarted、ContainerDied、ContainerRemoved、ContainerChanged)生成器.其维护着存储Pod 信息的cache,从运行时获取容器的信息,并根据前后两次信息对比,生成对应的PodLifecycleEvent,通过eventChannel发送到kubelet syncLoop进行消费,最终由kubelet syncPod完成Pod的同步,维护着用户的“期望”。
- VolumeManager: 运行一组异步循环,根据在此节点上调度的 pod 确定需要附加/挂载/卸载/分离哪些卷并执行操作
- EvictionManager : 监控 Node 节点的资源占用情况,根据驱逐规则驱逐 Pod 释放资源,缓解节点的压力
- OOMWatcher: 从系统日志中获取容器的 OOM 日志,将其封装成事件并记录
流程

数据来源
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/90589b8f63d28bcd3db89749950ebc48ed07c190/pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
func makePodSourceConfig(kubeCfg *kubeletconfiginternal.KubeletConfiguration, kubeDeps *Dependencies, nodeName types.NodeName, nodeHasSynced func() bool) (*config.PodConfig, error) {
// ...
// define file config source
if kubeCfg.StaticPodPath != "" {
klog.InfoS("Adding static pod path", "path", kubeCfg.StaticPodPath)
config.NewSourceFile(kubeCfg.StaticPodPath, nodeName, kubeCfg.FileCheckFrequency.Duration, cfg.Channel(ctx, kubetypes.FileSource))
}
// define url config source
if kubeCfg.StaticPodURL != "" {
klog.InfoS("Adding pod URL with HTTP header", "URL", kubeCfg.StaticPodURL, "header", manifestURLHeader)
config.NewSourceURL(kubeCfg.StaticPodURL, manifestURLHeader, nodeName, kubeCfg.HTTPCheckFrequency.Duration, cfg.Channel(ctx, kubetypes.HTTPSource))
}
if kubeDeps.KubeClient != nil {
klog.InfoS("Adding apiserver pod source")
config.NewSourceApiserver(kubeDeps.KubeClient, nodeName, nodeHasSynced, cfg.Channel(ctx, kubetypes.ApiserverSource))
}
return cfg, nil
}
3 个不同来源的 pod 信息的变化(file,http,apiserver)
这里 apiserver 为例
// NewSourceApiserver creates a config source that watches and pulls from the apiserver.
func NewSourceApiserver(c clientset.Interface, nodeName types.NodeName, nodeHasSynced func() bool, updates chan<- interface{}) {
lw := cache.NewListWatchFromClient(c.CoreV1().RESTClient(), "pods", metav1.NamespaceAll, fields.OneTermEqualSelector("spec.nodeName", string(nodeName)))
go func() {
// ..
newSourceApiserverFromLW(lw, updates)
}()
}
只监听当前node 的pods 信息
syncLoop 循环监听管道信息
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/90589b8f63d28bcd3db89749950ebc48ed07c190/pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoop(ctx context.Context, updates <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler) {
// 从 pleg 中获取信息
plegCh := kl.pleg.Watch()
// ...
for {
// ...
if !kl.syncLoopIteration(ctx, updates, handler, syncTicker.C, housekeepingTicker.C, plegCh) {
break
}
//...
}
}
syncLoopIteration处理事件循环中的逻辑
func (kl *Kubelet) syncLoopIteration(ctx context.Context, configCh <-chan kubetypes.PodUpdate, handler SyncHandler,
syncCh <-chan time.Time, housekeepingCh <-chan time.Time, plegCh <-chan *pleg.PodLifecycleEvent) bool {
select {
case u, open := <-configCh:
// ..
switch u.Op {
case kubetypes.ADD:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop ADD", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjSlice(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodAdditions(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.UPDATE:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop UPDATE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjSlice(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.REMOVE:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop REMOVE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjSlice(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodRemoves(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.RECONCILE:
klog.V(4).InfoS("SyncLoop RECONCILE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjSlice(u.Pods))
handler.HandlePodReconcile(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.DELETE:
klog.V(2).InfoS("SyncLoop DELETE", "source", u.Source, "pods", klog.KObjSlice(u.Pods))
// DELETE is treated as a UPDATE because of graceful deletion.
handler.HandlePodUpdates(u.Pods)
case kubetypes.SET:
// TODO: Do we want to support this?
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Kubelet does not support snapshot update")
default:
klog.ErrorS(nil, "Invalid operation type received", "operation", u.Op)
}
kl.sourcesReady.AddSource(u.Source)
case e := <-plegCh:
// ..
// ..
}
return true
}
处理 新增
func (kl *Kubelet) HandlePodAdditions(pods []*v1.Pod) {
// ...
for _, pod := range pods {
existingPods := kl.podManager.GetPods()
// 将pod添加到pod管理器中,如果有pod不存在在pod管理器中,那么这个pod表示已经被删除了
kl.podManager.AddPod(pod)
// 把 pod 分配给给 worker 做异步处理,创建pod
kl.dispatchWork(pod, kubetypes.SyncPodCreate, mirrorPod, start)
}
}
HandlePodAdditions主要任务是:
- 按照创建时间给pods进行排序;
- 将pod添加到pod管理器中,如果有pod不存在在pod管理器中,那么这个pod表示已经被删除了;
- 校验pod 是否能在该节点运行,如果不可以直接拒绝;
- 调用dispatchWork把 pod 分配给给 worker 做异步处理,创建pod;
- 将pod添加到probeManager中,如果 pod 中定义了 readiness 和 liveness 健康检查,启动 goroutine 定期进行检测
func (kl *Kubelet) dispatchWork(pod *v1.Pod, syncType kubetypes.SyncPodType, mirrorPod *v1.Pod, start time.Time) {
// Run the sync in an async worker.
kl.podWorkers.UpdatePod(UpdatePodOptions{
Pod: pod,
MirrorPod: mirrorPod,
UpdateType: syncType,
StartTime: start,
})
// ...
}
func (p *podWorkers) UpdatePod(options UpdatePodOptions) {
status, ok := p.podSyncStatuses[uid]
if !ok {
// ...
p.podSyncStatuses[uid] = status
}
podUpdates, exists := p.podUpdates[uid]
if !exists {
// 如果该pod在podUpdates数组里面找不到,那么就创建channel,并启动异步线程
// buffer the channel to avoid blocking this method
podUpdates = make(chan struct{}, 1)
p.podUpdates[uid] = podUpdates
// allow testing of delays in the pod update channel
var outCh <-chan struct{}
if p.workerChannelFn != nil {
outCh = p.workerChannelFn(uid, podUpdates)
} else {
outCh = podUpdates
}
// spawn a pod worker
go func() {
// TODO: this should be a wait.Until with backoff to handle panics, and
// accept a context for shutdown
defer runtime.HandleCrash()
defer klog.V(3).InfoS("Pod worker has stopped", "podUID", uid)
p.podWorkerLoop(uid, outCh)
}()
}
// 下发更新事件
select {
case podUpdates <- struct{}{}:
default:
}
}
func (p *podWorkers) podWorkerLoop(podUID types.UID, podUpdates <-chan struct{}) {
var lastSyncTime time.Time
for range podUpdates {
ctx, update, canStart, canEverStart, ok := p.startPodSync(podUID)
// ..
var isTerminal bool
err := func() error {
var status *kubecontainer.PodStatus
var err error
// Take the appropriate action (illegal phases are prevented by UpdatePod)
switch {
// ...
default:
isTerminal, err = p.podSyncer.SyncPod(ctx, update.Options.UpdateType, update.Options.Pod, update.Options.MirrorPod, status)
}
return err
}()
// ..
}
}
syncPod 同步 pod 状态
func (kl *Kubelet) SyncPod(_ context.Context, updateType kubetypes.SyncPodType, pod, mirrorPod *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus) (isTerminal bool, err error) {
// 判断 pod 能否运行
runnable := kl.canRunPod(pod)
if !runnable.Admit {
}
// 更新状态管理器中的状态
kl.statusManager.SetPodStatus(pod, apiPodStatus)
// 校验网络插件是否已准备好, only start the pod if it uses the host network
if err := kl.runtimeState.networkErrors(); err != nil && !kubecontainer.IsHostNetworkPod(pod) {
// 。。
}
// Create Cgroups for the pod and apply resource parameters
// to them if cgroups-per-qos flag is enabled.
pcm := kl.containerManager.NewPodContainerManager()
// 校验该pod是否已被Terminate
if !kl.podWorkers.IsPodTerminationRequested(pod.UID) {
// 校验该pod是否首次创建
firstSync := true
for _, containerStatus := range apiPodStatus.ContainerStatuses {
if containerStatus.State.Running != nil {
firstSync = false
break
}
}
podKilled := false
if !pcm.Exists(pod) && !firstSync { // 如果该 pod 的cgroups不存在,并且不是首次启动,那么kill掉
p := kubecontainer.ConvertPodStatusToRunningPod(kl.getRuntime().Type(), podStatus)
if err := kl.killPod(ctx, pod, p, nil); err == nil {
podKilled = true
} else {
klog.ErrorS(err, "KillPod failed", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "podStatus", podStatus)
}
}
if !(podKilled && pod.Spec.RestartPolicy == v1.RestartPolicyNever) { // 如果该pod在上面没有被kill掉,或重启策略不是永不重启
if !pcm.Exists(pod) { // 如果该pod的cgroups不存在,那么就创建cgroups
if err := kl.containerManager.UpdateQOSCgroups(); err != nil {
klog.V(2).InfoS("Failed to update QoS cgroups while syncing pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "err", err)
}
if err := pcm.EnsureExists(pod); err != nil {
kl.recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedToCreatePodContainer, "unable to ensure pod container exists: %v", err)
return false, fmt.Errorf("failed to ensure that the pod: %v cgroups exist and are correctly applied: %v", pod.UID, err)
}
}
}
}
// 创建pod的文件目录
if err := kl.makePodDataDirs(pod); err != nil {
// 。。。
}
// 如果该pod没有被终止,那么需要等待attach/mount volumes
if !kl.podWorkers.IsPodTerminationRequested(pod.UID) {
// Wait for volumes to attach/mount
if err := kl.volumeManager.WaitForAttachAndMount(pod); err != nil {
kl.recorder.Eventf(pod, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedMountVolume, "Unable to attach or mount volumes: %v", err)
klog.ErrorS(err, "Unable to attach or mount volumes for pod; skipping pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return false, err
}
}
// 如果有 image secrets,去 apiserver 获取对应的 secrets 数据
pullSecrets := kl.getPullSecretsForPod(pod)
// 探针检查
kl.probeManager.AddPod(pod)
// 真正的容器创建逻辑
result := kl.containerRuntime.SyncPod(ctx, pod, podStatus, pullSecrets, kl.backOff)
// ...
return false, nil
}
主要准备工作如下:
- 校验该pod能否运行,如果不能运行,那么回写container的等待原因,然后更新状态管理器中的状态;
- 如果校验没通过或pod已被删除或pod跑失败了,那么kill掉pod,然后返回;
- 校验网络插件是否已准备好,如果没有,直接返回;
- 如果该pod的cgroups不存在,那么就创建cgroups;
- 为静态pod创建镜像;
- 创建pod的文件目录,等待volumes attach/mount;
- 拉取这个pod的Secret;
- 调用containerRuntime.SyncPod真正创建pod
syncPod 真正创建pod
// SyncPod syncs the running pod into the desired pod by executing following steps:
//
// 1. 计算 sandbox and container 变化.
// 2. Kill pod sandbox if necessary.
// 3. Kill any containers that should not be running.
// 4. Create sandbox if necessary.
// 5. 创建 ephemeral 容器.
// 6. 创建 init 容器.
// 7. Resize running containers (if InPlacePodVerticalScaling==true)
// 8. Create normal containers.
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) SyncPod(ctx context.Context, pod *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus, pullSecrets []v1.Secret, backOff *flowcontrol.Backoff) (result kubecontainer.PodSyncResult) {
// ...
// Step 4: 新建sandbox, 其实就是 pause 容器
podSandboxID := podContainerChanges.SandboxID
if podContainerChanges.CreateSandbox {
//...
podSandboxID, msg, err = m.createPodSandbox(ctx, pod, podContainerChanges.Attempt)
if err != nil {
// ...
return
}
}
// the start containers routines depend on pod ip(as in primary pod ip)
// instead of trying to figure out if we have 0 < len(podIPs)
// everytime, we short circuit it here
podIP := ""
if len(podIPs) != 0 {
podIP = podIPs[0]
}
// Get podSandboxConfig for containers to start.
configPodSandboxResult := kubecontainer.NewSyncResult(kubecontainer.ConfigPodSandbox, podSandboxID)
result.AddSyncResult(configPodSandboxResult)
podSandboxConfig, err := m.generatePodSandboxConfig(pod, podContainerChanges.Attempt)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("GeneratePodSandboxConfig for pod %q failed: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
klog.ErrorS(err, "GeneratePodSandboxConfig for pod failed", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
configPodSandboxResult.Fail(kubecontainer.ErrConfigPodSandbox, message)
return
}
// Helper containing boilerplate common to starting all types of containers.
// typeName is a description used to describe this type of container in log messages,
// currently: "container", "init container" or "ephemeral container"
// metricLabel is the label used to describe this type of container in monitoring metrics.
// currently: "container", "init_container" or "ephemeral_container"
start := func(ctx context.Context, typeName, metricLabel string, spec *startSpec) error {
// ..
// NOTE (aramase) podIPs are populated for single stack and dual stack clusters. Send only podIPs.
if msg, err := m.startContainer(ctx, podSandboxID, podSandboxConfig, spec, pod, podStatus, pullSecrets, podIP, podIPs); err != nil {
// ...
}
return nil
}
// Step 5: 临时容器相关
for _, idx := range podContainerChanges.EphemeralContainersToStart {
start(ctx, "ephemeral container", metrics.EphemeralContainer, ephemeralContainerStartSpec(&pod.Spec.EphemeralContainers[idx]))
}
// Step 6: 启动 init 容器
if container := podContainerChanges.NextInitContainerToStart; container != nil {
// Start the next init container.
if err := start(ctx, "init container", metrics.InitContainer, containerStartSpec(container)); err != nil {
return
}
// Successfully started the container; clear the entry in the failure
klog.V(4).InfoS("Completed init container for pod", "containerName", container.Name, "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
}
// Step 7: For containers in podContainerChanges.ContainersToUpdate[CPU,Memory] list, invoke UpdateContainerResources
if isInPlacePodVerticalScalingAllowed(pod) {
if len(podContainerChanges.ContainersToUpdate) > 0 || podContainerChanges.UpdatePodResources {
m.doPodResizeAction(pod, podStatus, podContainerChanges, result)
}
}
// Step 8: 启动业务容器
for _, idx := range podContainerChanges.ContainersToStart {
start(ctx, "container", metrics.Container, containerStartSpec(&pod.Spec.Containers[idx]))
}
return
}
启动容器 startContainer
// startContainer starts a container and returns a message indicates why it is failed on error.
// It starts the container through the following steps:
// * pull the image
// * create the container
// * start the container
// * run the post start lifecycle hooks (if applicable)
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) startContainer(ctx context.Context, podSandboxID string, podSandboxConfig *runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig, spec *startSpec, pod *v1.Pod, podStatus *kubecontainer.PodStatus, pullSecrets []v1.Secret, podIP string, podIPs []string) (string, error) {
container := spec.container
// Step 1: 拉取镜像
imageRef, msg, err := m.imagePuller.EnsureImageExists(ctx, pod, container, pullSecrets, podSandboxConfig)
// ...
// Step 2: create the container.
// For a new container, the RestartCount should be 0
// 初始化Container config配置
containerConfig, cleanupAction, err := m.generateContainerConfig(ctx, container, pod, restartCount, podIP, imageRef, podIPs, target)
if cleanupAction != nil {
defer cleanupAction()
}
// ..
// 调用生命周期的钩子,预创建 Pre Create Container
err = m.internalLifecycle.PreCreateContainer(pod, container, containerConfig)
// 调用CRI接口创建Container
containerID, err := m.runtimeService.CreateContainer(ctx, podSandboxID, containerConfig, podSandboxConfig)
// 调用生命周期的钩子,预启动Pre Start Container
err = m.internalLifecycle.PreStartContainer(pod, container, containerID)
// Step 3: 调用CRI接口启动container
err = m.runtimeService.StartContainer(ctx, containerID)
// Step 4: 依然是调用生命周期中设置的钩子 post start
if container.Lifecycle != nil && container.Lifecycle.PostStart != nil {
kubeContainerID := kubecontainer.ContainerID{
Type: m.runtimeName,
ID: containerID,
}
msg, handlerErr := m.runner.Run(ctx, kubeContainerID, pod, container, container.Lifecycle.PostStart)
if handlerErr != nil {
klog.ErrorS(handlerErr, "Failed to execute PostStartHook", "pod", klog.KObj(pod),
"podUID", pod.UID, "containerName", container.Name, "containerID", kubeContainerID.String())
// do not record the message in the event so that secrets won't leak from the server.
m.recordContainerEvent(pod, container, kubeContainerID.ID, v1.EventTypeWarning, events.FailedPostStartHook, "PostStartHook failed")
if err := m.killContainer(ctx, pod, kubeContainerID, container.Name, "FailedPostStartHook", reasonFailedPostStartHook, nil); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to kill container", "pod", klog.KObj(pod),
"podUID", pod.UID, "containerName", container.Name, "containerID", kubeContainerID.String())
}
return msg, ErrPostStartHook
}
}
return "", nil
}
Sandbox 沙箱
Sandbox沙箱是一种程序的隔离运行机制,其目的是限制不可信进程的权限。 在 Linux CRI 体系里,Pod Sandbox 其实就是 pause 容器,在Kubernetes中,pause容器作为pod中所有容器的“父容器”。pause容器有两个核心职责。 首先,它是pod中Linux Namespace共享的基础(network、PID、IPC、UTS)。 其次,启用了PID(进程ID)命名空间共享后,它为每个pod充当PID 1,并接收僵尸进程。当前Pod的所有容器都和Pod对应的sandbox共享同一个namespace从而共享一个namespace里面的资源

// createPodSandbox creates a pod sandbox and returns (podSandBoxID, message, error).
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) createPodSandbox(ctx context.Context, pod *v1.Pod, attempt uint32) (string, string, error) {
// 生成pod相关配置数据
podSandboxConfig, err := m.generatePodSandboxConfig(pod, attempt)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("Failed to generate sandbox config for pod %q: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to generate sandbox config for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return "", message, err
}
// 这里会在宿主机上创建pod logs目录,在/var/log/pods/{namespace}_{pod_name}_{uid}目录下
err = m.osInterface.MkdirAll(podSandboxConfig.LogDirectory, 0755)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("Failed to create log directory for pod %q: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to create log directory for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return "", message, err
}
// ...
// 调用容器运行时创建sandbox container
podSandBoxID, err := m.runtimeService.RunPodSandbox(ctx, podSandboxConfig, runtimeHandler)
if err != nil {
message := fmt.Sprintf("Failed to create sandbox for pod %q: %v", format.Pod(pod), err)
klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to create sandbox for pod", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
return "", message, err
}
return podSandBoxID, "", nil
}
配置生成
func (m *kubeGenericRuntimeManager) generatePodSandboxConfig(pod *v1.Pod, attempt uint32) (*runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig, error) {
podUID := string(pod.UID)
podSandboxConfig := &runtimeapi.PodSandboxConfig{
Metadata: &runtimeapi.PodSandboxMetadata{
Name: pod.Name,
Namespace: pod.Namespace,
Uid: podUID,
Attempt: attempt,
},
Labels: newPodLabels(pod),
Annotations: newPodAnnotations(pod),
}
dnsConfig, err := m.runtimeHelper.GetPodDNS(pod)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
podSandboxConfig.DnsConfig = dnsConfig
if !kubecontainer.IsHostNetworkPod(pod) {
// TODO: Add domain support in new runtime interface
podHostname, podDomain, err := m.runtimeHelper.GeneratePodHostNameAndDomain(pod)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
podHostname, err = util.GetNodenameForKernel(podHostname, podDomain, pod.Spec.SetHostnameAsFQDN)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
podSandboxConfig.Hostname = podHostname
}
// 日志目录
logDir := BuildPodLogsDirectory(pod.Namespace, pod.Name, pod.UID)
podSandboxConfig.LogDirectory = logDir
// 端口映射
portMappings := []*runtimeapi.PortMapping{}
for _, c := range pod.Spec.Containers {
containerPortMappings := kubecontainer.MakePortMappings(&c)
for idx := range containerPortMappings {
port := containerPortMappings[idx]
hostPort := int32(port.HostPort)
containerPort := int32(port.ContainerPort)
protocol := toRuntimeProtocol(port.Protocol)
portMappings = append(portMappings, &runtimeapi.PortMapping{
HostIp: port.HostIP,
HostPort: hostPort,
ContainerPort: containerPort,
Protocol: protocol,
})
}
}
if len(portMappings) > 0 {
podSandboxConfig.PortMappings = portMappings
}
lc, err := m.generatePodSandboxLinuxConfig(pod)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
podSandboxConfig.Linux = lc
if runtime.GOOS == "windows" {
// 。。
}
// Update config to include overhead, sandbox level resources
if err := m.applySandboxResources(pod, podSandboxConfig); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return podSandboxConfig, nil
}