kube-scheduler 及 Scheduler 扩展功能推荐方式: 调度框架(scheduling framework)
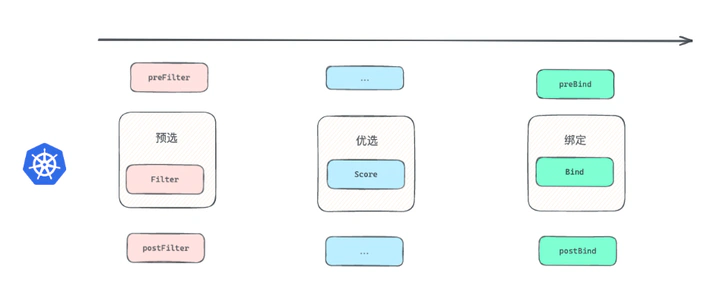
Scheduler是Kubernetes组件中功能&逻辑相对单一&简单的模块,它主要的作用是:watch kube-apiserver,监听PodSpec.NodeName为空的pod,并利用预选和优选算法为该pod选择一个最佳的调度节点,最终将pod与该节点进行绑定,使pod调度在该节点上运行。
scheduler 扩展方案
目前Kubernetes支持四种方式实现客户自定义的调度算法(预选&优选):
- default-scheduler recoding: 直接在Kubernetes默认scheduler基础上进行添加,然后重新编译kube-scheduler
- standalone: 实现一个与kube-scheduler平行的custom scheduler,单独或者和默认kube-scheduler一起运行在集群中
- scheduler extender: 实现一个"scheduler extender",kube-scheduler会调用它(http/https)作为默认调度算法(预选&优选&bind)的补充
- scheduler framework: 实现scheduler framework plugins,重新编译kube-scheduler,类似于第一种方案,但是更加标准化,插件化
scheduler extender
scheduler extender类似于webhook,kube-scheduler会在默认调度算法执行完成后以http/https的方式调用extender,extender server完成自定义的预选&优选逻辑,并返回规定字段给scheduler,scheduler结合这些信息进行最终的调度裁决,从而完成基于extender实现扩展的逻辑。
优点:
- 可以扩展现有调度器的功能,而无需重新编译二进制文件。
- 扩展器可以用任何语言编写。
- 实现后,可用于扩展不同版本的 kube-scheduler
scheduler framework 调度框架
extender提供了非侵入scheduler core的方式扩展scheduler,但是有如下缺点:
- 缺少灵活性:extender提供的接口只能由scheduler core在固定点调用,比如:“Filter” extenders只能在默认预选结束后进行调用;而"Prioritize" extenders只能在默认优选执行后调用
- 性能差:相比原生调用func来说,走http/https + 加解JSON包开销较大
- 错误处理困难:scheduler core在调用extender后,如果出现错误,需要中断调用,很难将错误信息传递给extender,终止extender逻辑
- 无法共享cache:extender是webhook,以单独的server形式与scheduler一起运行,如果scheduler core提供的参数无法满足extender处理需求,同时由于无法共享scheduler core cache,那么extender需要自行与kube-apiserver进行通信,并建立cache
为了解决scheduler extender存在的问题,scheduler framework在scheduler core基础上进行了改造和提取,在scheduler几乎所有关键路径上设置了plugins扩展点,用户可以在不修改scheduler core代码的前提下开发plugins,最后与core一起编译打包成二进制包实现扩展.
Kubernetes v1.15版本中引入了可插拔架构的调度框架,使得定制调度器这个任务变得更加的容易。
调度框架(Schedule Framework)定义了一组扩展点,用户可以实现扩展点定义的接口来定义自己的调度逻辑(我们称之为扩展),并将扩展注册到扩展点上,调度框架在执行调度工作流时,遇到对应的扩展点时,将调用用户注册的扩展。 调度框架在预留扩展点时,都是有特定的目的,有些扩展点上的扩展可以改变调度程序的决策方法,有些扩展点上的扩展只是发送一个通知。
Extension Points 扩展点

type Framework interface {
// framework.Handle 提供与插件的生存期有关的API
Handle
// 扩展用于对 Pod 的待调度队列进行排序,以决定先调度哪个 Pod
QueueSortFunc() LessFunc
// 用于对 Pod 的信息进行预处理,或者检查一些集群或 Pod 必须满足的前提条件,如果 pre-filter 返回了 error,则调度过程终止
RunPreFilterPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) (*PreFilterResult, *Status)
// 是一个通知类型的扩展点,调用该扩展的参数是 filter 阶段结束后被筛选为可选节点的节点列表,可以在扩展中使用这些信息更新内部状态,或者产生日志或 metrics 信息
RunPostFilterPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, filteredNodeStatusMap NodeToStatusMap) (*PostFilterResult, *Status)
// 用于在 Pod 绑定之前执行某些逻辑。例如,pre-bind 扩展可以将一个基于网络的数据卷挂载到节点上,以便 Pod 可以使用
RunPreBindPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// 通知性质的扩展
RunPostBindPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string)
// 一个通知性质的扩展点,有状态的插件可以使用该扩展点来获得节点上为 Pod 预留的资源,该事件发生在调度器将 Pod 绑定到节点之前,目的是避免调度器在等待 Pod 与节点绑定的过程中调度新的 Pod 到节点上时,发生实际使用资源超出可用资源的情况。(因为绑定 Pod 到节点上是异步发生的)。
RunReservePluginsReserve(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// 是一个通知性质的扩展,如果为 Pod 预留了资源,Pod 又在被绑定过程中被拒绝绑定,则 unreserve 扩展将被调用。Unreserve 扩展应该释放已经为 Pod 预留的节点上的计算资源。
RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string)
// 这些插件用于防止或延迟Pod的绑定
RunPermitPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
WaitOnPermit(ctx context.Context, pod *v1.Pod) *Status
RunBindPlugins(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *Status
// ..
}
Framework 是一个接口,需要实现的方法大部分为 RunXXXPlugins(),也就是运行某个扩展点的插件,那么只要实现这个 Framework 接口就可以对 Pod 进行调度。kube-scheduler 目前已有接口实现 frameworkImpl
核心数据结构

type CycleState struct {
// storage is keyed with StateKey, and valued with StateData.
storage sync.Map
// if recordPluginMetrics is true, metrics.PluginExecutionDuration will be recorded for this cycle.
recordPluginMetrics bool
// SkipFilterPlugins are plugins that will be skipped in the Filter extension point.
SkipFilterPlugins sets.Set[string]
// SkipScorePlugins are plugins that will be skipped in the Score extension point.
SkipScorePlugins sets.Set[string]
}
在Framework的实现中,每个插件扩展阶段调用都会传递context和CycleState两个对象, 其中context与我们在大多数go编程中的用法类似,这里主要是用于多阶段并行处理的时候的统一退出操作,而CycleState则存储当前这一个调度周期内的所有数据,这是一个并发安全的结构
scheduler framework 调度框架第三方应用
- github.com/koordinator-sh/koordinator
- github.com/kubernetes-sigs/scheduler-plugins
插件分类
根据是否维护在 k8s 代码仓库本身,分为两类。
默认插件 in-tree plugins
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/231849a90853363900391aaa3f406867c8421489/pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/registry.go
func NewInTreeRegistry() runtime.Registry {
// ...
registry := runtime.Registry{
dynamicresources.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, dynamicresources.New),
selectorspread.Name: selectorspread.New,
imagelocality.Name: imagelocality.New, // 优先考虑已经拥有 Pod 运行的容器镜像的节点
tainttoleration.Name: tainttoleration.New, // 实现污点和容忍
nodename.Name: nodename.New, // 检查Pod规格节点名称是否与当前节点匹配
nodeports.Name: nodeports.New, // 检查节点是否有Pod请求的端口的空闲端口
nodeaffinity.Name: nodeaffinity.New, // 实现节点选择器和节点亲和性
podtopologyspread.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, podtopologyspread.New), // 实现Pod拓扑扩展
nodeunschedulable.Name: nodeunschedulable.New, // 过滤出spec.unschedulable设置为true的节点
noderesources.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, noderesources.NewFit), // 检查节点是否具有Pod请求的所有资源
noderesources.BalancedAllocationName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, noderesources.NewBalancedAllocation), // 偏向于如果Pod在那里调度,将获得更平衡资源使用的节点
volumebinding.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, volumebinding.New), / 检查节点是否有或是否可以绑定请求的卷
volumerestrictions.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, volumerestrictions.New), // 检查节点中安装的卷是否满足特定于卷提供程序的限制
volumezone.Name: volumezone.New, // 检查请求的卷是否满足它们可能具有的任何区域需求
nodevolumelimits.CSIName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewCSI),
nodevolumelimits.EBSName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewEBS),
nodevolumelimits.GCEPDName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewGCEPD),
nodevolumelimits.AzureDiskName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewAzureDisk),
nodevolumelimits.CinderName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewCinder),
interpodaffinity.Name: interpodaffinity.New,
queuesort.Name: queuesort.New,
defaultbinder.Name: defaultbinder.New, // 提供默认的绑定机制
defaultpreemption.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, defaultpreemption.New), // 提供默认的抢占机制
schedulinggates.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, schedulinggates.New),
}
return registry
}
- node selectors 和 node affinity 用到了 NodeAffinity plugin;
- taint/toleration 用到了 TaintToleration plugin
第三方插件 out-of-tree plugins
- github.com/kubernetes-sigs/scheduler-plugins: 基于scheduler framework编写的插件,用户只需要引用这个包,编写自己的调度器插件,然后以普通 pod 方式部署就行.
// https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/scheduler-plugins/blob/588b8ecdf54fc4d5d7a43dca50c76e2bbfaf7e4e/cmd/scheduler/main.go
func main() {
// Register custom plugins to the scheduler framework.
// Later they can consist of scheduler profile(s) and hence
// used by various kinds of workloads.
command := app.NewSchedulerCommand(
app.WithPlugin(capacityscheduling.Name, capacityscheduling.New),
app.WithPlugin(coscheduling.Name, coscheduling.New),
app.WithPlugin(loadvariationriskbalancing.Name, loadvariationriskbalancing.New), // LoadVariationRiskBalancing:负载均衡器插件,用于给节点排序,实现优先选择负载低的节点,使整个集群的负载达到动态均衡
app.WithPlugin(networkoverhead.Name, networkoverhead.New),
app.WithPlugin(topologicalsort.Name, topologicalsort.New),
app.WithPlugin(noderesources.AllocatableName, noderesources.NewAllocatable),
app.WithPlugin(noderesourcetopology.Name, noderesourcetopology.New),
app.WithPlugin(preemptiontoleration.Name, preemptiontoleration.New),
app.WithPlugin(targetloadpacking.Name, targetloadpacking.New), // TargetLoadPacking 目标负载调度器,用于控制节点的CPU利用率不超过目标值x%(例如65%),通过打分让所有cpu利用率超过x%的都不被选中
app.WithPlugin(lowriskovercommitment.Name, lowriskovercommitment.New), // LowRiskOverCommitment:目标是想让limits也能均衡分布,通过跨节点“分散”或“平衡”Pod 的资源limits来缓解可突发Pod导致的资源过度订阅问题
app.WithPlugin(sysched.Name, sysched.New),
app.WithPlugin(peaks.Name, peaks.New),
// Sample plugins below.
// app.WithPlugin(crossnodepreemption.Name, crossnodepreemption.New),
app.WithPlugin(podstate.Name, podstate.New),
app.WithPlugin(qos.Name, qos.New),
)
code := cli.Run(command)
os.Exit(code)
}
插件注册
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/66974670620142271755e165e72fe03ec404dc6e/pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go
func New(client clientset.Interface,
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory,
dynInformerFactory dynamicinformer.DynamicSharedInformerFactory,
recorderFactory profile.RecorderFactory,
stopCh <-chan struct{},
opts ...Option) (*Scheduler, error) {
// ...
if options.applyDefaultProfile {
// 默认插件
var versionedCfg configv1.KubeSchedulerConfiguration
scheme.Scheme.Default(&versionedCfg)
cfg := schedulerapi.KubeSchedulerConfiguration{}
if err := scheme.Scheme.Convert(&versionedCfg, &cfg, nil); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
options.profiles = cfg.Profiles
}
// ...
}
结构体 KubeSchedulerConfiguration
type KubeSchedulerConfiguration struct {
// ...
// Profiles是kube-scheduler支持的调度配置,每个KubeSchedulerProfile对应一个独立的调度器,并有一个唯一的名字。
Profiles []KubeSchedulerProfile `json:"profiles,omitempty"`
// 调度扩展程序的配置列表
Extenders []Extender `json:"extenders,omitempty"`
}
// 随着群集中的工作负载变得越来越多样化(异构),很自然它们有不同的调度需求。kube-scheduler运行不同的调度框架的插件配置,将其称为Profile,并关联一个调度器名字。通过设置Pod.Spec.SchedulerName可以选择特定配置来调度Pod。如果未指定调度器名字,则采用默认配置进行调度
type KubeSchedulerProfile struct {
// 调度器名字
SchedulerName *string `json:"schedulerName,omitempty"`
// ...
// 每个扩展点指定使能或禁用的插件集合
Plugins *Plugins `json:"plugins,omitempty"`
// PluginConfig是每个插件的一组可选的自定义插件参数
PluginConfig []PluginConfig `json:"pluginConfig,omitempty"`
}
// Plugins包括调度框架的全部扩展点的配置
type Plugins struct {
// PreEnqueue is a list of plugins that should be invoked before adding pods to the scheduling queue.
PreEnqueue PluginSet `json:"preEnqueue,omitempty"`
// QueueSort is a list of plugins that should be invoked when sorting pods in the scheduling queue.
QueueSort PluginSet `json:"queueSort,omitempty"`
// PreFilter is a list of plugins that should be invoked at "PreFilter" extension point of the scheduling framework.
PreFilter PluginSet `json:"preFilter,omitempty"`
// Filter is a list of plugins that should be invoked when filtering out nodes that cannot run the Pod.
Filter PluginSet `json:"filter,omitempty"`
// PostFilter is a list of plugins that are invoked after filtering phase, but only when no feasible nodes were found for the pod.
PostFilter PluginSet `json:"postFilter,omitempty"`
// PreScore is a list of plugins that are invoked before scoring.
PreScore PluginSet `json:"preScore,omitempty"`
// Score is a list of plugins that should be invoked when ranking nodes that have passed the filtering phase.
Score PluginSet `json:"score,omitempty"`
// Reserve is a list of plugins invoked when reserving/unreserving resources
// after a node is assigned to run the pod.
Reserve PluginSet `json:"reserve,omitempty"`
// Permit is a list of plugins that control binding of a Pod. These plugins can prevent or delay binding of a Pod.
Permit PluginSet `json:"permit,omitempty"`
// PreBind is a list of plugins that should be invoked before a pod is bound.
PreBind PluginSet `json:"preBind,omitempty"`
// Bind is a list of plugins that should be invoked at "Bind" extension point of the scheduling framework.
// The scheduler call these plugins in order. Scheduler skips the rest of these plugins as soon as one returns success.
Bind PluginSet `json:"bind,omitempty"`
// PostBind is a list of plugins that should be invoked after a pod is successfully bound.
PostBind PluginSet `json:"postBind,omitempty"`
MultiPoint PluginSet `json:"multiPoint,omitempty"`
}
注册默认函数,API对象的设置默认值的函数是通过code-generator自动生成的。
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/6b34fafdaf5998039c7e01fa33920a641b216d3e/pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1/defaults.go
func RegisterDefaults(scheme *runtime.Scheme) error {
// ...
scheme.AddTypeDefaultingFunc(&v1.KubeSchedulerConfiguration{}, func(obj interface{}) {
SetObjectDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration(obj.(*v1.KubeSchedulerConfiguration))
})
// ...
return nil
}
func SetObjectDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration(in *v1.KubeSchedulerConfiguration) {
SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration(in)
}
// SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration sets additional defaults
func SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration(obj *configv1.KubeSchedulerConfiguration) {
// ...
if len(obj.Profiles) == 0 {
obj.Profiles = append(obj.Profiles, configv1.KubeSchedulerProfile{})
}
// 使用默认default-scheduler
if len(obj.Profiles) == 1 && obj.Profiles[0].SchedulerName == nil {
obj.Profiles[0].SchedulerName = pointer.String(v1.DefaultSchedulerName)
}
// Add the default set of plugins and apply the configuration.
for i := range obj.Profiles {
prof := &obj.Profiles[i]
setDefaults_KubeSchedulerProfile(logger, prof)
}
// ..
}
func setDefaults_KubeSchedulerProfile(logger klog.Logger, prof *configv1.KubeSchedulerProfile) {
// 设置默认插件
prof.Plugins = mergePlugins(logger, getDefaultPlugins(), prof.Plugins)
// Set default plugin configs.
scheme := GetPluginArgConversionScheme()
existingConfigs := sets.NewString()
for j := range prof.PluginConfig {
existingConfigs.Insert(prof.PluginConfig[j].Name)
args := prof.PluginConfig[j].Args.Object
if _, isUnknown := args.(*runtime.Unknown); isUnknown {
continue
}
scheme.Default(args)
}
// Append default configs for plugins that didn't have one explicitly set.
for _, name := range pluginsNames(prof.Plugins) {
if existingConfigs.Has(name) {
continue
}
gvk := configv1.SchemeGroupVersion.WithKind(name + "Args")
args, err := scheme.New(gvk)
if err != nil {
// This plugin is out-of-tree or doesn't require configuration.
continue
}
scheme.Default(args)
args.GetObjectKind().SetGroupVersionKind(gvk)
prof.PluginConfig = append(prof.PluginConfig, configv1.PluginConfig{
Name: name,
Args: runtime.RawExtension{Object: args},
})
}
}
// getDefaultPlugins returns the default set of plugins.
func getDefaultPlugins() *v1.Plugins {
plugins := &v1.Plugins{
MultiPoint: v1.PluginSet{
Enabled: []v1.Plugin{
{Name: names.PrioritySort},
{Name: names.NodeUnschedulable},
{Name: names.NodeName},
{Name: names.TaintToleration, Weight: pointer.Int32(3)},
{Name: names.NodeAffinity, Weight: pointer.Int32(2)},
{Name: names.NodePorts},
{Name: names.NodeResourcesFit, Weight: pointer.Int32(1)},
{Name: names.VolumeRestrictions},
{Name: names.EBSLimits},
{Name: names.GCEPDLimits},
{Name: names.NodeVolumeLimits},
{Name: names.AzureDiskLimits},
{Name: names.VolumeBinding},
{Name: names.VolumeZone},
{Name: names.PodTopologySpread, Weight: pointer.Int32(2)},
{Name: names.InterPodAffinity, Weight: pointer.Int32(2)},
{Name: names.DefaultPreemption},
{Name: names.NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation, Weight: pointer.Int32(1)},
{Name: names.ImageLocality, Weight: pointer.Int32(1)},
{Name: names.DefaultBinder},
},
},
}
applyFeatureGates(plugins)
return plugins
}
kube-scheduler
要职责是为新创建的 pod 寻找一个最合适的 node 节点, 然后进行 bind node 绑定, 后面 kubelet 才会监听到并创建真正的 pod.

等待调度阶段
PreEnqueue: 只有当所有 PreEnqueue 插件返回Success时,Pod 才允许进入活动队列
QueueSort: 对调度队列(scheduling queue)内的 pod 进行排序,决定先调度哪些 pods
调度阶段(Scheduling cycle)
- findNodesThatFitPod:过滤(或称为预选)–> Filters the nodes to find the ones that fit the pod based on the framework filter plugins and filter extenders.
- prioritizeNodes:打分(或称为优选)–> prioritizeNodes prioritizes the nodes by running the score plugins, which return a score for each node from the call to RunScorePlugins()
过滤阶段会将所有满足 Pod 调度需求的节点选出来。 在打分阶段,调度器会为 Pod 从所有可调度节点中选取一个最合适的节点。
最后,kube-scheduler 会将 Pod 调度到得分最高的节点上。 如果存在多个得分最高的节点,kube-scheduler 会从中随机选取一个.
# 参考 scheduler v=10 日志
I0802 02:51:30.244110 1 eventhandlers.go:149] "Add event for unscheduled pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.244208 1 scheduling_queue.go:635] "Pod moved to an internal scheduling queue" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" event="PodAdd" queue="Active"
I0802 02:51:30.244309 1 schedule_one.go:83] "About to try and schedule pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.244355 1 schedule_one.go:96] "Attempting to schedule pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.247453 1 resource_allocation.go:76] "Listed internal info for allocatable resources, requested resources and score" logger="Score.NodeResourcesFit" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node4" resourceAlloc
ationScorer="LeastAllocated" allocatableResource=[15400,15859908608] requestedResource=[12293,11881957376] resourceScore=22
I0802 02:51:30.247680 1 resource_allocation.go:76] "Listed internal info for allocatable resources, requested resources and score" logger="Score.NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node4
" resourceAllocationScorer="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" allocatableResource=[15400,15859908608] requestedResource=[11393,9429374976] resourceScore=92
I0802 02:51:30.247781 1 resource_allocation.go:76] "Listed internal info for allocatable resources, requested resources and score" logger="Score.NodeResourcesFit" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node5" resourceAlloc
ationScorer="LeastAllocated" allocatableResource=[15400,17072095232] requestedResource=[7267,9854011392] resourceScore=47
I0802 02:51:30.247868 1 resource_allocation.go:76] "Listed internal info for allocatable resources, requested resources and score" logger="Score.NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node5
" resourceAllocationScorer="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" allocatableResource=[15400,17072095232] requestedResource=[6567,8240289792] resourceScore=97
I0802 02:51:30.248010 1 resource_allocation.go:76] "Listed internal info for allocatable resources, requested resources and score" logger="Score.NodeResourcesFit" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node6" resourceAlloc
ationScorer="LeastAllocated" allocatableResource=[15400,15859904512] requestedResource=[3785,6734497792] resourceScore=66
I0802 02:51:30.248091 1 resource_allocation.go:76] "Listed internal info for allocatable resources, requested resources and score" logger="Score.NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node6
" resourceAllocationScorer="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" allocatableResource=[15400,15859904512] requestedResource=[3385,5749921792] resourceScore=92
I0802 02:51:30.248333 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="TaintToleration" node="node4" score=300
I0802 02:51:30.248381 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesFit" node="node4" score=22
I0802 02:51:30.248415 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="PodTopologySpread" node="node4" score=200
I0802 02:51:30.248453 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" node="node4" score=92
I0802 02:51:30.248489 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="ImageLocality" node="node4" score=0
I0802 02:51:30.248528 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="TaintToleration" node="node5" score=300
I0802 02:51:30.248564 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesFit" node="node5" score=47
I0802 02:51:30.248596 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="PodTopologySpread" node="node5" score=100
I0802 02:51:30.248633 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" node="node5" score=97
I0802 02:51:30.248667 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="ImageLocality" node="node5" score=0
I0802 02:51:30.248708 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="TaintToleration" node="node6" score=300
I0802 02:51:30.248744 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesFit" node="node6" score=66
I0802 02:51:30.248793 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="PodTopologySpread" node="node6" score=100
I0802 02:51:30.248826 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" node="node6" score=92
I0802 02:51:30.248859 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="ImageLocality" node="node6" score=0
I0802 02:51:30.248935 1 schedule_one.go:860] "Calculated node's final score for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node4" score=614
I0802 02:51:30.249017 1 schedule_one.go:860] "Calculated node's final score for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node5" score=544
I0802 02:51:30.249053 1 schedule_one.go:860] "Calculated node's final score for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node6" score=558
I0802 02:51:30.249640 1 default_binder.go:53] "Attempting to bind pod to node" logger="Bind.DefaultBinder" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node4"
I0802 02:51:30.249926 1 request.go:1349] Request Body:
00000000 6b 38 73 00 0a 0d 0a 02 76 31 12 07 42 69 6e 64 |k8s.....v1..Bind|
00000010 69 6e 67 12 6c 0a 51 0a 13 61 6c 65 72 74 6d 61 |ing.l.Q..alertma|
00000020 6e 61 67 65 72 2d 6d 61 69 6e 2d 31 12 00 1a 0a |nager-main-1....|
00000030 6d 6f 6e 69 74 6f 72 69 6e 67 22 00 2a 24 35 31 |monitoring".*$51|
00000040 65 32 63 33 30 61 2d 64 36 32 61 2d 34 61 38 32 |e2c30a-d62a-4a82|
00000050 2d 39 38 65 32 2d 30 61 36 36 30 31 61 62 39 31 |-98e2-0a6601ab91|
00000060 61 61 32 00 38 00 42 00 12 17 0a 04 4e 6f 64 65 |aa2.8.B.....Node|
00000070 12 00 1a 05 6e 6f 64 65 34 22 00 2a 00 32 00 3a |....node4".*.2.:|
00000080 00 1a 00 22 00 |...".|
I0802 02:51:30.250204 1 round_trippers.go:466] curl -v -XPOST -H "User-Agent: kube-scheduler/v1.31.4 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/a78aa47/scheduler" -H "Accept: application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf, */*" -H "Content-Type: applicat
ion/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf" 'https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/monitoring/pods/alertmanager-main-1/binding'
I0802 02:51:30.277376 1 eventhandlers.go:201] "Delete event for unscheduled pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.277505 1 eventhandlers.go:231] "Add event for scheduled pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.277931 1 round_trippers.go:553] POST https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/monitoring/pods/alertmanager-main-1/binding 201 Created in 27 milliseconds
I0802 02:51:30.278012 1 round_trippers.go:570] HTTP Statistics: GetConnection 0 ms ServerProcessing 23 ms Duration 27 ms
I0802 02:51:30.278048 1 round_trippers.go:577] Response Headers:
I0802 02:51:30.278085 1 round_trippers.go:580] Content-Length: 48
I0802 02:51:30.278250 1 round_trippers.go:580] Date: Sat, 02 Aug 2025 02:51:30 GMT
I0802 02:51:30.278285 1 round_trippers.go:580] Audit-Id: 97ebb10e-939d-4e21-a794-b796e0a5ee5b
I0802 02:51:30.278402 1 round_trippers.go:580] Cache-Control: no-cache, private
I0802 02:51:30.278431 1 round_trippers.go:580] Content-Type: application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf
I0802 02:51:30.278458 1 round_trippers.go:580] X-Kubernetes-Pf-Flowschema-Uid: 45a530b8-6402-4baf-aa3d-559802f14e3e
I0802 02:51:30.278483 1 round_trippers.go:580] X-Kubernetes-Pf-Prioritylevel-Uid: 67442251-99c9-4bbc-85df-4e552c0ec508
I0802 02:51:30.278589 1 request.go:1349] Response Body:
00000000 6b 38 73 00 0a 0c 0a 02 76 31 12 06 53 74 61 74 |k8s.....v1..Stat|
00000010 75 73 12 18 0a 06 0a 00 12 00 1a 00 12 07 53 75 |us............Su|
I0802 02:51:30.248489 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="ImageLocality" node="node4" score=0
I0802 02:51:30.248528 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="TaintToleration" node="node5" score=300
I0802 02:51:30.248564 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesFit" node="node5" score=47
I0802 02:51:30.248596 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="PodTopologySpread" node="node5" score=100
I0802 02:51:30.248633 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" node="node5" score=97
I0802 02:51:30.248667 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="ImageLocality" node="node5" score=0
I0802 02:51:30.248708 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="TaintToleration" node="node6" score=300
I0802 02:51:30.248744 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesFit" node="node6" score=66
I0802 02:51:30.248793 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="PodTopologySpread" node="node6" score=100
I0802 02:51:30.248826 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation" node="node6" score=92
I0802 02:51:30.248859 1 schedule_one.go:793] "Plugin scored node for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" plugin="ImageLocality" node="node6" score=0
I0802 02:51:30.248935 1 schedule_one.go:860] "Calculated node's final score for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node4" score=614
I0802 02:51:30.249017 1 schedule_one.go:860] "Calculated node's final score for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node5" score=544
I0802 02:51:30.249053 1 schedule_one.go:860] "Calculated node's final score for pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node6" score=558
I0802 02:51:30.249640 1 default_binder.go:53] "Attempting to bind pod to node" logger="Bind.DefaultBinder" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node4"
I0802 02:51:30.249926 1 request.go:1349] Request Body:
00000000 6b 38 73 00 0a 0d 0a 02 76 31 12 07 42 69 6e 64 |k8s.....v1..Bind|
00000010 69 6e 67 12 6c 0a 51 0a 13 61 6c 65 72 74 6d 61 |ing.l.Q..alertma|
00000020 6e 61 67 65 72 2d 6d 61 69 6e 2d 31 12 00 1a 0a |nager-main-1....|
00000030 6d 6f 6e 69 74 6f 72 69 6e 67 22 00 2a 24 35 31 |monitoring".*$51|
00000040 65 32 63 33 30 61 2d 64 36 32 61 2d 34 61 38 32 |e2c30a-d62a-4a82|
00000050 2d 39 38 65 32 2d 30 61 36 36 30 31 61 62 39 31 |-98e2-0a6601ab91|
00000060 61 61 32 00 38 00 42 00 12 17 0a 04 4e 6f 64 65 |aa2.8.B.....Node|
00000070 12 00 1a 05 6e 6f 64 65 34 22 00 2a 00 32 00 3a |....node4".*.2.:|
00000080 00 1a 00 22 00 |...".|
I0802 02:51:30.250204 1 round_trippers.go:466] curl -v -XPOST -H "User-Agent: kube-scheduler/v1.31.4 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/a78aa47/scheduler" -H "Accept: application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf, */*" -H "Content-Type: applicat
ion/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf" 'https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/monitoring/pods/alertmanager-main-1/binding'
I0802 02:51:30.277376 1 eventhandlers.go:201] "Delete event for unscheduled pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.277505 1 eventhandlers.go:231] "Add event for scheduled pod" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.277931 1 round_trippers.go:553] POST https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/monitoring/pods/alertmanager-main-1/binding 201 Created in 27 milliseconds
I0802 02:51:30.278012 1 round_trippers.go:570] HTTP Statistics: GetConnection 0 ms ServerProcessing 23 ms Duration 27 ms
I0802 02:51:30.278048 1 round_trippers.go:577] Response Headers:
I0802 02:51:30.278085 1 round_trippers.go:580] Content-Length: 48
I0802 02:51:30.278250 1 round_trippers.go:580] Date: Sat, 02 Aug 2025 02:51:30 GMT
I0802 02:51:30.278285 1 round_trippers.go:580] Audit-Id: 97ebb10e-939d-4e21-a794-b796e0a5ee5b
I0802 02:51:30.278402 1 round_trippers.go:580] Cache-Control: no-cache, private
I0802 02:51:30.278431 1 round_trippers.go:580] Content-Type: application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf
I0802 02:51:30.278458 1 round_trippers.go:580] X-Kubernetes-Pf-Flowschema-Uid: 45a530b8-6402-4baf-aa3d-559802f14e3e
I0802 02:51:30.278483 1 round_trippers.go:580] X-Kubernetes-Pf-Prioritylevel-Uid: 67442251-99c9-4bbc-85df-4e552c0ec508
I0802 02:51:30.278589 1 request.go:1349] Response Body:
00000000 6b 38 73 00 0a 0c 0a 02 76 31 12 06 53 74 61 74 |k8s.....v1..Stat|
00000010 75 73 12 18 0a 06 0a 00 12 00 1a 00 12 07 53 75 |us............Su|
00000020 63 63 65 73 73 1a 00 22 00 30 c9 01 1a 00 22 00 |ccess..".0....".|
I0802 02:51:30.279067 1 cache.go:389] "Finished binding for pod, can be expired" podKey="51e2c30a-d62a-4a82-98e2-0a6601ab91aa" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1"
I0802 02:51:30.279165 1 schedule_one.go:314] "Successfully bound pod to node" pod="monitoring/alertmanager-main-1" node="node4" evaluatedNodes=6 feasibleNodes=3
调度 monitoring/alertmanager-main-1,总共分析evaluatedNodes=6 个,可用feasibleNodes=3个
涉及的插件(最终 node-4 为例)
- NodeResourcesFit : 22
- NodeResourcesBalancedAllocation: 92
- TaintToleration: 300
- PodTopologySpread: 200
- ImageLocality: 0
计算 node-4 总得分: 614
调度器性能
考虑一个问题, 当 k8s 的 node 节点特别多时, 这些节点都要参与预先的调度过程么 ? 比如大集群有 2500 个节点, 注册的插件有 10 个, 那么 筛选 Filter 和 打分 Score 过程需要进行 2500 * 10 * 2 = 50000 次计算, 最后选定一个最高分值的节点来绑定 pod. k8s scheduler 考虑到了这样的性能开销, 所以加入了百分比参数控制参与预选的节点数.
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/3e34da6e2a6d908922ad28bda84cb021d22e2b1e/pkg/scheduler/schedule_one.go
const (
minFeasibleNodesToFind = 100
minFeasibleNodesPercentageToFind = 5
)
func (sched *Scheduler) numFeasibleNodesToFind(percentageOfNodesToScore *int32, numAllNodes int32) (numNodes int32) {
if numAllNodes < minFeasibleNodesToFind {
// 当集群节点小于 100 时, 集群中的所有节点都参与预选
return numAllNodes
}
// Use profile percentageOfNodesToScore if it's set. Otherwise, use global percentageOfNodesToScore.
var percentage int32
if percentageOfNodesToScore != nil {
percentage = *percentageOfNodesToScore
} else {
// k8s scheduler 的 nodes 百分比默认为 0
percentage = sched.percentageOfNodesToScore
}
if percentage == 0 {
percentage = int32(50) - numAllNodes/125
if percentage < minFeasibleNodesPercentageToFind {
// 不能小于 5
percentage = minFeasibleNodesPercentageToFind
}
}
numNodes = numAllNodes * percentage / 100
if numNodes < minFeasibleNodesToFind {
return minFeasibleNodesToFind
}
return numNodes
}
如果你不指定阈值,Kubernetes 使用线性公式计算出一个比例,在大于 100 节点集群取 50%,在 5000 节点的集群取 10% ,随节点数增加,这个数组不停在减少。这个自动设置的参数的最低值是 5%.
numAllNodes * (50 - numAllNodes/125) / 100
初始化
func Setup(ctx context.Context, opts *options.Options, outOfTreeRegistryOptions ...Option) (*schedulerserverconfig.CompletedConfig, *scheduler.Scheduler, error) {
// 获取默认配置
if cfg, err := latest.Default(); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
} else {
opts.ComponentConfig = cfg
}
// 验证 scheduler 的配置参数
if errs := opts.Validate(); len(errs) > 0 {
return nil, nil, utilerrors.NewAggregate(errs)
}
c, err := opts.Config(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
// 配置中填充和调整
cc := c.Complete()
outOfTreeRegistry := make(runtime.Registry)
for _, option := range outOfTreeRegistryOptions {
if err := option(outOfTreeRegistry); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
}
recorderFactory := getRecorderFactory(&cc)
completedProfiles := make([]kubeschedulerconfig.KubeSchedulerProfile, 0)
// 构建 scheduler 对象
sched, err := scheduler.New(cc.Client,
cc.InformerFactory,
cc.DynInformerFactory,
recorderFactory,
ctx.Done(),
scheduler.WithComponentConfigVersion(cc.ComponentConfig.TypeMeta.APIVersion),
scheduler.WithKubeConfig(cc.KubeConfig),
scheduler.WithProfiles(cc.ComponentConfig.Profiles...),
scheduler.WithPercentageOfNodesToScore(cc.ComponentConfig.PercentageOfNodesToScore),
scheduler.WithFrameworkOutOfTreeRegistry(outOfTreeRegistry),
scheduler.WithPodMaxBackoffSeconds(cc.ComponentConfig.PodMaxBackoffSeconds),
scheduler.WithPodInitialBackoffSeconds(cc.ComponentConfig.PodInitialBackoffSeconds),
scheduler.WithPodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration(cc.PodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration),
scheduler.WithExtenders(cc.ComponentConfig.Extenders...),
scheduler.WithParallelism(cc.ComponentConfig.Parallelism),
scheduler.WithBuildFrameworkCapturer(func(profile kubeschedulerconfig.KubeSchedulerProfile) {
// Profiles are processed during Framework instantiation to set default plugins and configurations. Capturing them for logging
completedProfiles = append(completedProfiles, profile)
}),
)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
if err := options.LogOrWriteConfig(klog.FromContext(ctx), opts.WriteConfigTo, &cc.ComponentConfig, completedProfiles); err != nil {
return nil, nil, err
}
return &cc, sched, nil
}
func New(client clientset.Interface,
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory,
dynInformerFactory dynamicinformer.DynamicSharedInformerFactory,
recorderFactory profile.RecorderFactory,
stopCh <-chan struct{},
opts ...Option) (*Scheduler, error) {
// ..
options := defaultSchedulerOptions
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(&options)
}
if options.applyDefaultProfile {
var versionedCfg configv1.KubeSchedulerConfiguration
scheme.Scheme.Default(&versionedCfg)
cfg := schedulerapi.KubeSchedulerConfiguration{}
if err := scheme.Scheme.Convert(&versionedCfg, &cfg, nil); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
options.profiles = cfg.Profiles
}
// 构建 registry 对象, 默认集成了一堆的插件
registry := frameworkplugins.NewInTreeRegistry()
// 第三方插件
if err := registry.Merge(options.frameworkOutOfTreeRegistry); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// extenders 调度
extenders, err := buildExtenders(options.extenders, options.profiles)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("couldn't build extenders: %w", err)
}
podLister := informerFactory.Core().V1().Pods().Lister()
nodeLister := informerFactory.Core().V1().Nodes().Lister()
snapshot := internalcache.NewEmptySnapshot()
clusterEventMap := make(map[framework.ClusterEvent]sets.String)
profiles, err := profile.NewMap(options.profiles, registry, recorderFactory, stopCh,
frameworkruntime.WithComponentConfigVersion(options.componentConfigVersion),
frameworkruntime.WithClientSet(client),
frameworkruntime.WithKubeConfig(options.kubeConfig),
frameworkruntime.WithInformerFactory(informerFactory),
frameworkruntime.WithSnapshotSharedLister(snapshot),
frameworkruntime.WithCaptureProfile(frameworkruntime.CaptureProfile(options.frameworkCapturer)),
frameworkruntime.WithClusterEventMap(clusterEventMap),
frameworkruntime.WithClusterEventMap(clusterEventMap),
frameworkruntime.WithParallelism(int(options.parallelism)),
frameworkruntime.WithExtenders(extenders),
frameworkruntime.WithMetricsRecorder(metricsRecorder),
)
// ...
preEnqueuePluginMap := make(map[string][]framework.PreEnqueuePlugin)
for profileName, profile := range profiles {
preEnqueuePluginMap[profileName] = profile.PreEnqueuePlugins()
}
// 实例化调度队列 queue, 该 queue 为 PriorityQueue
podQueue := internalqueue.NewSchedulingQueue(
profiles[options.profiles[0].SchedulerName].QueueSortFunc(),
informerFactory,
internalqueue.WithPodInitialBackoffDuration(time.Duration(options.podInitialBackoffSeconds)*time.Second),
internalqueue.WithPodMaxBackoffDuration(time.Duration(options.podMaxBackoffSeconds)*time.Second),
internalqueue.WithPodLister(podLister),
internalqueue.WithClusterEventMap(clusterEventMap),
internalqueue.WithPodMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration(options.podMaxInUnschedulablePodsDuration),
internalqueue.WithPreEnqueuePluginMap(preEnqueuePluginMap),
internalqueue.WithPluginMetricsSamplePercent(pluginMetricsSamplePercent),
internalqueue.WithMetricsRecorder(*metricsRecorder),
)
for _, fwk := range profiles {
fwk.SetPodNominator(podQueue)
}
// 实例化 cache 缓存: scheduler Cache 缓存 Pod,Node 等信息,各个扩展点的插件在计算时所需要的 Node 和 Pod 信息都是从 scheduler Cache 获取。
schedulerCache := internalcache.New(durationToExpireAssumedPod, stopEverything)
// Setup cache debugger.
debugger := cachedebugger.New(nodeLister, podLister, schedulerCache, podQueue)
debugger.ListenForSignal(stopEverything)
// 实例化 scheduler 对象
sched := &Scheduler{
// ...
NextPod: internalqueue.MakeNextPodFunc(podQueue), // 获取 pod,调用 queue.Pop()
StopEverything: stopEverything,
SchedulingQueue: podQueue,
Profiles: profiles,
}
sched.applyDefaultHandlers()
// 在 informer 里注册自定义的事件处理方法
addAllEventHandlers(sched, informerFactory, dynInformerFactory, unionedGVKs(clusterEventMap))
return sched, nil
}
func (s *Scheduler) applyDefaultHandlers() {
// 默认 pod 调度
s.SchedulePod = s.schedulePod
// 默认调度失败处理
s.FailureHandler = s.handleSchedulingFailure
}
type SchedulingQueue interface {
framework.PodNominator
Add(pod *v1.Pod) error
// Activate moves the given pods to activeQ iff they're in unschedulablePods or backoffQ.
// The passed-in pods are originally compiled from plugins that want to activate Pods,
// by injecting the pods through a reserved CycleState struct (PodsToActivate).
Activate(pods map[string]*v1.Pod)
// AddUnschedulableIfNotPresent adds an unschedulable pod back to scheduling queue.
// The podSchedulingCycle represents the current scheduling cycle number which can be
// returned by calling SchedulingCycle().
AddUnschedulableIfNotPresent(pod *framework.QueuedPodInfo, podSchedulingCycle int64) error
// SchedulingCycle returns the current number of scheduling cycle which is
// cached by scheduling queue. Normally, incrementing this number whenever
// a pod is popped (e.g. called Pop()) is enough.
SchedulingCycle() int64
// Pop removes the head of the queue and returns it. It blocks if the
// queue is empty and waits until a new item is added to the queue.
Pop() (*framework.QueuedPodInfo, error)
Update(oldPod, newPod *v1.Pod) error
Delete(pod *v1.Pod) error
MoveAllToActiveOrBackoffQueue(event framework.ClusterEvent, preCheck PreEnqueueCheck)
AssignedPodAdded(pod *v1.Pod)
AssignedPodUpdated(pod *v1.Pod)
PendingPods() ([]*v1.Pod, string)
// Close closes the SchedulingQueue so that the goroutine which is
// waiting to pop items can exit gracefully.
Close()
// Run starts the goroutines managing the queue.
Run()
}
func NewSchedulingQueue(
lessFn framework.LessFunc,
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory,
opts ...Option) SchedulingQueue {
return NewPriorityQueue(lessFn, informerFactory, opts...)
}
// 初始化队列
func NewPriorityQueue(
lessFn framework.LessFunc,
informerFactory informers.SharedInformerFactory,
opts ...Option,
) *PriorityQueue {
options := defaultPriorityQueueOptions
if options.podLister == nil {
options.podLister = informerFactory.Core().V1().Pods().Lister()
}
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(&options)
}
comp := func(podInfo1, podInfo2 interface{}) bool {
pInfo1 := podInfo1.(*framework.QueuedPodInfo)
pInfo2 := podInfo2.(*framework.QueuedPodInfo)
return lessFn(pInfo1, pInfo2)
}
pq := &PriorityQueue{
// ...
}
// ...
return pq
}
type PriorityQueue struct {
// ...
// activeQ is heap structure that scheduler actively looks at to find pods to
// schedule. Head of heap is the highest priority pod.
activeQ *heap.Heap
// podBackoffQ is a heap ordered by backoff expiry. Pods which have completed backoff
// are popped from this heap before the scheduler looks at activeQ
podBackoffQ *heap.Heap
// unschedulablePods holds pods that have been tried and determined unschedulable.
unschedulablePods *UnschedulablePods
// ..
}
SchedulingQueue 是一个 internalqueue.SchedulingQueue 接口类型,PriorityQueue 对这个接口进行了实现,创建 Scheduler 的时候 SchedulingQueue 会被 PriorityQueue 类型对象赋值。SchedulerQueue 包含三个队列:activeQ、podBackoffQ、unschedulablePods。
- activeQ 是一个优先队列,基于堆实现,用于存放待调度的 Pod,优先级高的会放在队列头部,优先被调度。该队列存放的 Pod 可能的情况有:刚创建未被调度的Pod;backOffPod 队列中转移过来的Pod;unschedule 队列里转移过来的 Pod;
- podBackoffQ 也是一个优先队列,用于存放那些异常的Pod,这种 Pod 需要等待一定的时间才能够被再次调度,会有协程定期去读取这个队列,然后加入到 activeQ 队列然后重新调度;
- unschedulablePods 严格上来说不属于队列,用于存放调度失败的 Pod。这个队列也会有协程定期(默认30s)去读取,然后判断当前时间距离上次调度时间的差是否超过5min,如果超过这个时间则把 Pod 移动到 activeQ 重新调度
func (p *PriorityQueue) Run() {
// 运行异常的 Pod 等待时间完成后,flushBackoffQCompleted 将该 Pod 移动到 activeQ;
go wait.Until(p.flushBackoffQCompleted, 1.0*time.Second, p.stop)
// 调度失败的 Pod 如果满足一定条件,这个函数会将这种 Pod 移动到 activeQ 或 podBackoffQ;
go wait.Until(p.flushUnschedulablePodsLeftover, 30*time.Second, p.stop)
}
启动
func (sched *Scheduler) Run(ctx context.Context) {
// 队列相关
sched.SchedulingQueue.Run()
// 真正的逻辑
go wait.UntilWithContext(ctx, sched.scheduleOne, 0)
<-ctx.Done()
sched.SchedulingQueue.Close()
}
关注的是整个 kubernetes scheduler 调度器只有一个协程处理主调度循环 scheduleOne, 虽然 kubernetes scheduler 可以启动多个实例, 但启动时需要 leaderelection 选举, 只有 leader 才可以处理调度, 其他节点作为 follower 等待 leader 失效. 也就是说整个 k8s 集群调度核心的并发度为 1 个.
scheduleOne() 核心逻辑:拿出一个 pod 来进行调度
func (sched *Scheduler) scheduleOne(ctx context.Context) {
// 从 activeQ 中获取需要调度的 pod 数据
podInfo := sched.NextPod()
// pod could be nil when schedulerQueue is closed
if podInfo == nil || podInfo.Pod == nil {
return
}
pod := podInfo.Pod
// 根据 SchedulerName 获取调度器
fwk, err := sched.frameworkForPod(pod)
// ...
// 检查 pod 是否需要跳过调度。1 处于正在被删除状态的 pod 跳过本次调度 2 pod 在 AssumedPod 缓存里面,也跳过调度
if sched.skipPodSchedule(fwk, pod) {
return
}
// Synchronously attempt to find a fit for the pod.
start := time.Now()
state := framework.NewCycleState()
// Initialize an empty podsToActivate struct, which will be filled up by plugins or stay empty.
podsToActivate := framework.NewPodsToActivate()
state.Write(framework.PodsToActivateKey, podsToActivate)
schedulingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
// 为 pod 选择最优的 node 节点
scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, status := sched.schedulingCycle(schedulingCycleCtx, state, fwk, podInfo, start, podsToActivate)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.FailureHandler(schedulingCycleCtx, fwk, assumedPodInfo, status, scheduleResult.nominatingInfo, start)
return
}
// 启动一个协程,开始绑定;
go func() {
//...
// apiserver 发起 pod -> node 绑定
status := sched.bindingCycle(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, start, podsToActivate)
if !status.IsSuccess() {
sched.handleBindingCycleError(bindingCycleCtx, state, fwk, assumedPodInfo, start, scheduleResult, status)
}
}()
}
schedulingCycle 调度阶段
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulingCycle(
ctx context.Context,
state *framework.CycleState,
fwk framework.Framework,
podInfo *framework.QueuedPodInfo,
start time.Time,
podsToActivate *framework.PodsToActivate,
) (ScheduleResult, *framework.QueuedPodInfo, *framework.Status) {
pod := podInfo.Pod
// 调度 pod
scheduleResult, err := sched.SchedulePod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
// ...
assumedPodInfo := podInfo.DeepCopy()
assumedPod := assumedPodInfo.Pod
// 告诉缓存,假设他已经绑定. 需要这个缓存的原因也是为了提升调度效率,将绑定和调度分开,因为绑定需要调用 kube-apiserver,所以 Scheduler 乐观的假设调度已经成功
err = sched.assume(assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
// 预留资源
if sts := fwk.RunReservePluginsReserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !sts.IsSuccess() {
// ...
}
// Run "permit" plugins.
runPermitStatus := fwk.RunPermitPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if !runPermitStatus.IsWait() && !runPermitStatus.IsSuccess() {
// ...
}
// At the end of a successful scheduling cycle, pop and move up Pods if needed.
if len(podsToActivate.Map) != 0 {
sched.SchedulingQueue.Activate(podsToActivate.Map)
// Clear the entries after activation.
podsToActivate.Map = make(map[string]*v1.Pod)
}
return scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, nil
}
调度 pod
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulePod(ctx context.Context, fwk framework.Framework, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) (result ScheduleResult, err error) {
// ..
// 过滤: 选出符合要求的预选节点
feasibleNodes, diagnosis, err := sched.findNodesThatFitPod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
// 优选:为预选出来的节点进行打分 score
priorityList, err := prioritizeNodes(ctx, sched.Extenders, fwk, state, pod, feasibleNodes)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
// 最后选择最合适的 node 节点
host, err := selectHost(priorityList)
return ScheduleResult{
SuggestedHost: host,
EvaluatedNodes: len(feasibleNodes) + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap),
FeasibleNodes: len(feasibleNodes),
}, err
}
findNodesThatFitPod 过滤预选
func (sched *Scheduler) findNodesThatFitPod(ctx context.Context, fwk framework.Framework, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) ([]*v1.Node, framework.Diagnosis, error) {
// ..
// 获取所有的 node 信息
allNodes, err := sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfos().List()
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
// 调用 framework 的 PreFilter 集合里的插件
preRes, s := fwk.RunPreFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod)
// ...
// "NominatedNodeName" can potentially be set in a previous scheduling cycle as a result of preemption.
// This node is likely the only candidate that will fit the pod, and hence we try it first before iterating over all nodes.
if len(pod.Status.NominatedNodeName) > 0 {
feasibleNodes, err := sched.evaluateNominatedNode(ctx, pod, fwk, state, diagnosis)
if err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Evaluation failed on nominated node", "pod", klog.KObj(pod), "node", pod.Status.NominatedNodeName)
}
// Nominated node passes all the filters, scheduler is good to assign this node to the pod.
if len(feasibleNodes) != 0 {
return feasibleNodes, diagnosis, nil
}
}
nodes := allNodes
if !preRes.AllNodes() {
// 根据 prefilter 拿到的 node names 获取 node info 对象.
nodes = make([]*framework.NodeInfo, 0, len(preRes.NodeNames))
for nodeName := range preRes.NodeNames {
if nodeInfo, err := sched.nodeInfoSnapshot.Get(nodeName); err == nil {
nodes = append(nodes, nodeInfo)
}
}
}
// 运行 framework 的 filter 插件判断 node 是否可以运行新 pod.
feasibleNodes, err := sched.findNodesThatPassFilters(ctx, fwk, state, pod, diagnosis, nodes)
// always try to update the sched.nextStartNodeIndex regardless of whether an error has occurred
// this is helpful to make sure that all the nodes have a chance to be searched
processedNodes := len(feasibleNodes) + len(diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
sched.nextStartNodeIndex = (sched.nextStartNodeIndex + processedNodes) % len(allNodes)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
// 调用额外的 extender 调度器来进行预选
feasibleNodesAfterExtender, err := findNodesThatPassExtenders(sched.Extenders, pod, feasibleNodes, diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
if err != nil {
return nil, diagnosis, err
}
if len(feasibleNodesAfterExtender) != len(feasibleNodes) {
// Extenders filtered out some nodes.
//
// Extender doesn't support any kind of requeueing feature like EnqueueExtensions in the scheduling framework.
// When Extenders reject some Nodes and the pod ends up being unschedulable,
// we put framework.ExtenderName to pInfo.UnschedulablePlugins.
// This Pod will be requeued from unschedulable pod pool to activeQ/backoffQ
// by any kind of cluster events.
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/122019
if diagnosis.UnschedulablePlugins == nil {
diagnosis.UnschedulablePlugins = sets.NewString()
}
diagnosis.UnschedulablePlugins.Insert(framework.ExtenderName)
}
return feasibleNodesAfterExtender, diagnosis, nil
}
findNodesThatPassFilters 遍历执行 framework 里 Filter 插件集合的 Filter 方法
为了加快执行效率, 减少预选阶段的时延, framework 内部有个 Parallelizer 并发控制器, 启用 16 个协程并发调用插件的 Filter 方法. 在大集群下 nodes 节点会很多, 为了避免遍历全量的 nodes 执行 Filter 和后续的插件逻辑, 这里通过 numFeasibleNodesToFind 方法来减少扫描计算的 nodes 数量.
// findNodesThatPassFilters finds the nodes that fit the filter plugins.
func (sched *Scheduler) findNodesThatPassFilters(
ctx context.Context,
fwk framework.Framework,
state *framework.CycleState,
pod *v1.Pod,
diagnosis framework.Diagnosis,
nodes []*framework.NodeInfo) ([]*v1.Node, error) {
numAllNodes := len(nodes)
// 计算需要扫描的 nodes 数
numNodesToFind := sched.numFeasibleNodesToFind(fwk.PercentageOfNodesToScore(), int32(numAllNodes))
// Create feasible list with enough space to avoid growing it
// and allow assigning.
feasibleNodes := make([]*v1.Node, numNodesToFind)
if !fwk.HasFilterPlugins() {
for i := range feasibleNodes {
feasibleNodes[i] = nodes[(sched.nextStartNodeIndex+i)%numAllNodes].Node()
}
return feasibleNodes, nil
}
// framework 内置并发控制器, 并发 16 个协程去请求插件的 Filter 方法.
errCh := parallelize.NewErrorChannel()
var statusesLock sync.Mutex
var feasibleNodesLen int32
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
checkNode := func(i int) {
// We check the nodes starting from where we left off in the previous scheduling cycle,
// this is to make sure all nodes have the same chance of being examined across pods.
nodeInfo := nodes[(sched.nextStartNodeIndex+i)%numAllNodes]
status := fwk.RunFilterPluginsWithNominatedPods(ctx, state, pod, nodeInfo)
if status.Code() == framework.Error {
errCh.SendErrorWithCancel(status.AsError(), cancel)
return
}
if status.IsSuccess() {
length := atomic.AddInt32(&feasibleNodesLen, 1)
if length > numNodesToFind {
cancel()
atomic.AddInt32(&feasibleNodesLen, -1)
} else {
feasibleNodes[length-1] = nodeInfo.Node()
}
} else {
statusesLock.Lock()
diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap[nodeInfo.Node().Name] = status
diagnosis.UnschedulablePlugins.Insert(status.FailedPlugin())
statusesLock.Unlock()
}
}
beginCheckNode := time.Now()
statusCode := framework.Success
// 并发调用 framework 的 Filter 插件的 Filter 方法.
fwk.Parallelizer().Until(ctx, numAllNodes, checkNode, metrics.Filter)
feasibleNodes = feasibleNodes[:feasibleNodesLen]
return feasibleNodes, nil
}
Predicate有一系列的算法可以使用:
- PodToleratesNodeTaints:检查Pod是否容忍 Node Taint
- CheckNodeMemoryPressure:检查Pod是否可以调度到MemoryPressure的节点
- CheckNodeDiskPressure:检查Pod是否可以调度到DiskPressure的节点
- NoVolumeNodeConflict:检查节点是否满足Pod所引用的Volume的条
- PodFitsPorts:同PodFitsHostPort
- PodFitsHostPorts:检查是否有Host Ports冲
- PodFitsResources:检查Node的资源是否充足,包括允许的Pod数量、CPU、内存、GPU个数以及其他的OpaqueIntResource
- HostName: 检查Pod.Spec.NodeName是否与候选节点一
- MatchNodeSelector:检查候选节点的Pod.Spec.NodeSelector 是否匹
- NoVolumeZoneConflict:检查 volume zone是否冲
- MaxEBSVolumeCount:检查AWS EBS Volume数量是否过多(默认不超过 39)
- MaxGCEPDVolumeCount:检查GCE PD Volume数量是否过多(默认不超过 16)
- MaxAzureDiskVolumeCount:检查Azure Disk Volume数量是否过多(默认不超过 16)
- MatchInterPodAffinity:检查是否匹配Pod的亲和性要求
prioritizeNodes 调度器的优选阶段
func prioritizeNodes(
ctx context.Context,
extenders []framework.Extender,
fwk framework.Framework,
state *framework.CycleState,
pod *v1.Pod,
nodes []*v1.Node,
) ([]framework.NodePluginScores, error) {
// ..
// 在 framework 的 PreScore 插件集合里, 遍历执行插件的 PreScore 方法
preScoreStatus := fwk.RunPreScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !preScoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, preScoreStatus.AsError()
}
// 在 framework 的 Score 插件集合里, 遍历执行插件的 Score 方法
nodesScores, scoreStatus := fwk.RunScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !scoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, scoreStatus.AsError()
}
if len(extenders) != 0 && nodes != nil {
// 当额外 extenders 调度器不为空时, 则需要计算分值.
allNodeExtendersScores := make(map[string]*framework.NodePluginScores, len(nodes))
var mu sync.Mutex
var wg sync.WaitGroup
for i := range extenders {
if !extenders[i].IsInterested(pod) {
continue
}
wg.Add(1)
go func(extIndex int) {
// ...
}(i)
}
// wait for all go routines to finish
wg.Wait()
for i := range nodesScores {
if score, ok := allNodeExtendersScores[nodes[i].Name]; ok {
nodesScores[i].Scores = append(nodesScores[i].Scores, score.Scores...)
nodesScores[i].TotalScore += score.TotalScore
}
}
}
// ..
return nodesScores, nil
}
Score 扩展点分为两个阶段:
- 第一阶段称为“打分”,用于对已通过过滤阶段的节点进行排名。调度程序将为 Score 每个节点调用每个计分插件。
- 第二阶段是“归一化”,用于在调度程序计算节点的最终排名之前修改分数,可以不实现,但是需要保证 Score 插件的输出必须是 [MinNodeScore,MaxNodeScore]([0-100])范围内的整数。如果不是,则调度器会报错,你需要实现 NormalizeScore 来保证最后的得分范围。如果不实现 NormalizeScore,则 Score 的输出必须在此范围内。调度程序将根据配置的插件权重合并所有插件的节点分数。
type ScorePlugin interface {
Plugin
// Score is called on each filtered node. It must return success and an integer
// indicating the rank of the node. All scoring plugins must return success or
// the pod will be rejected.
Score(ctx context.Context, state *CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *Status)
// ScoreExtensions returns a ScoreExtensions interface if it implements one, or nil if does not.
ScoreExtensions() ScoreExtensions
}
Priorities优先级选项包括:
- LeastRequestedPriority:优先调度到请求资源少的节点
- NodePreferAvoidPodsPriority: alpha.kubernetes.io/preferAvoidPods 字段判断, 权重为10000,避免其他优先级策略的影
- NodeAffinityPriority:优先调度到匹配 NodeAffinity 的节点
- TaintTolerationPriority:优先调度到匹配 TaintToleration 的节点
- ServiceSpreadingPriority:尽量将同一个 service 的 Pod 分布到不同节点
- MostRequestedPriority:尽量调度到已经使用过的 Node 上,特别适用
- SelectorSpreadPriority: 优先减少节点上属于同一个Service或Replication Controller的Pod数
- InterPodAffinityPriority:优先将 Pod 调度到相同的拓扑上(如同一个节点、Rack、Zone 等
- BalancedResourceAllocation:优先平衡各节点的资源使用
selectHost 从优选的 nodes 集合里获取分值 score 最高的 node
当相近的两个 node 分值相同时, 则通过随机来选择 node, 目的使 k8s node 的负载更趋于均衡
func selectHost(nodeScores []framework.NodePluginScores) (string, error) {
if len(nodeScores) == 0 {
return "", fmt.Errorf("empty priorityList")
}
maxScore := nodeScores[0].TotalScore
selected := nodeScores[0].Name
cntOfMaxScore := 1
for _, ns := range nodeScores[1:] {
if ns.TotalScore > maxScore {
// 当前的分值更大, 则进行赋值
maxScore = ns.TotalScore
selected = ns.Name
cntOfMaxScore = 1
} else if ns.TotalScore == maxScore {
// 当两个 node 的 分值相同时,
// 使用随机算法来选择当前和上一个 node
cntOfMaxScore++
if rand.Intn(cntOfMaxScore) == 0 {
// Replace the candidate with probability of 1/cntOfMaxScore
selected = ns.Name
}
}
}
return selected, nil
}
bindingCycle 绑定阶段
func (sched *Scheduler) bindingCycle(
ctx context.Context,
state *framework.CycleState,
fwk framework.Framework,
scheduleResult ScheduleResult,
assumedPodInfo *framework.QueuedPodInfo,
start time.Time,
podsToActivate *framework.PodsToActivate) *framework.Status {
assumedPod := assumedPodInfo.Pod
// Run "permit" plugins.
if status := fwk.WaitOnPermit(ctx, assumedPod); !status.IsSuccess() {
return status
}
// // 执行插件的 prebind 逻辑
if status := fwk.RunPreBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !status.IsSuccess() {
return status
}
// 执行 bind 插件逻辑
if status := sched.bind(ctx, fwk, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost, state); !status.IsSuccess() {
return status
}
// Calculating nodeResourceString can be heavy. Avoid it if klog verbosity is below 2.
if assumedPodInfo.InitialAttemptTimestamp != nil {
metrics.PodSchedulingDuration.WithLabelValues(getAttemptsLabel(assumedPodInfo)).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(*assumedPodInfo.InitialAttemptTimestamp))
}
// 在 bind 绑定后执行收尾操作
fwk.RunPostBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
// At the end of a successful binding cycle, move up Pods if needed.
if len(podsToActivate.Map) != 0 {
sched.SchedulingQueue.Activate(podsToActivate.Map)
// Unlike the logic in schedulingCycle(), we don't bother deleting the entries
// as `podsToActivate.Map` is no longer consumed.
}
return nil
}
插件案例
1 NodeResourcesFit
noderesources.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, noderesources.NewFit),
// ScoringStrategyType the type of scoring strategy used in NodeResourcesFit plugin.
type ScoringStrategyType string
const (
// 空闲资源多的分高 --使的node上的负载比较合理一点!
LeastAllocated ScoringStrategyType = "LeastAllocated"
// 空闲资源少的分高 – 可以退回Node资源!
MostAllocated ScoringStrategyType = "MostAllocated"
// RequestedToCapacityRatio strategy allows specifying a custom shape function
// to score nodes based on the request to capacity ratio.
RequestedToCapacityRatio ScoringStrategyType = "RequestedToCapacityRatio"
)
// 下面定义了三个 scorer 打分策略.
var nodeResourceStrategyTypeMap = map[config.ScoringStrategyType]scorer{
config.LeastAllocated: func(args *config.NodeResourcesFitArgs) *resourceAllocationScorer {
resources := args.ScoringStrategy.Resources
return &resourceAllocationScorer{
Name: string(config.LeastAllocated),
scorer: leastResourceScorer(resources),
resources: resources,
}
},
config.MostAllocated: func(args *config.NodeResourcesFitArgs) *resourceAllocationScorer {
resources := args.ScoringStrategy.Resources
return &resourceAllocationScorer{
Name: string(config.MostAllocated),
scorer: mostResourceScorer(resources),
resources: resources,
}
},
config.RequestedToCapacityRatio: func(args *config.NodeResourcesFitArgs) *resourceAllocationScorer {
resources := args.ScoringStrategy.Resources
return &resourceAllocationScorer{
Name: string(config.RequestedToCapacityRatio),
scorer: requestedToCapacityRatioScorer(resources, args.ScoringStrategy.RequestedToCapacityRatio.Shape),
resources: resources,
}
},
}
scheduler 对 resource 打分内置三种不同策略, 分别是 LeastAllocated / MostAllocated / RequestedToCapacityRatio.
- LeastAllocated(最少资源使用): 默认策略, 空闲资源多的分高, 优先调度到空闲资源多的节点上, 各个 node 节点负载均衡.
- MostAllocated(最多资源使用) : 空闲资源少的分高, 优先调度到空闲资源较少的 node 上, 这样 pod 尽量集中起来方便后面资源回收.
- RequestedToCapacityRatio(资源占用比例): 请求 request 和 node 资源总量的比率低的分高.
LeastAllocated 为例
// Details:
// (cpu((capacity-requested)*MaxNodeScore*cpuWeight/capacity) + memory((capacity-requested)*MaxNodeScore*memoryWeight/capacity) + ...)/weightSum
// 计算了每种资源的未使用量(可分配-请求),然后根据每种资源的权重计算出一个加权平均分。
// 最后,它返回一个分数,分数越高表示节点上未使用的资源越多
func leastResourceScorer(resources []config.ResourceSpec) func([]int64, []int64) int64 {
return func(requested, allocable []int64) int64 {
var nodeScore, weightSum int64
for i := range requested {
if allocable[i] == 0 {
continue
}
weight := resources[i].Weight
resourceScore := leastRequestedScore(requested[i], allocable[i])
nodeScore += resourceScore * weight
weightSum += weight
}
if weightSum == 0 {
return 0
}
return nodeScore / weightSum
}
}
- 过滤
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/be080584c632b031583310dd090424b06aa4f498/pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/noderesources/fit.go
func (f *Fit) Filter(ctx context.Context, cycleState *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) *framework.Status {
// 获取在 preFilter 阶段写入的 preFilterState
s, err := getPreFilterState(cycleState)
if err != nil {
return framework.AsStatus(err)
}
// 判断当前的 node 是否满足 pod 的资源请求 request 需求
insufficientResources := fitsRequest(s, nodeInfo, f.ignoredResources, f.ignoredResourceGroups)
if len(insufficientResources) != 0 {// 存在不足资源
// We will keep all failure reasons.
failureReasons := make([]string, 0, len(insufficientResources))
for i := range insufficientResources {
failureReasons = append(failureReasons, insufficientResources[i].Reason)
}
return framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable, failureReasons...)
}
return nil
}
func fitsRequest(podRequest *preFilterState, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo, ignoredExtendedResources, ignoredResourceGroups sets.String) []InsufficientResource {
insufficientResources := make([]InsufficientResource, 0, 4)
// 保证不超过节点最大运行数目
allowedPodNumber := nodeInfo.Allocatable.AllowedPodNumber
if len(nodeInfo.Pods)+1 > allowedPodNumber {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
ResourceName: v1.ResourcePods,
Reason: "Too many pods",
Requested: 1,
Used: int64(len(nodeInfo.Pods)),
Capacity: int64(allowedPodNumber),
})
}
// 保证资源 cpu,memory,EphemeralStorage足够 request
if podRequest.MilliCPU == 0 &&
podRequest.Memory == 0 &&
podRequest.EphemeralStorage == 0 &&
len(podRequest.ScalarResources) == 0 {
return insufficientResources
}
if podRequest.MilliCPU > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.MilliCPU - nodeInfo.Requested.MilliCPU) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
ResourceName: v1.ResourceCPU,
Reason: "Insufficient cpu",
Requested: podRequest.MilliCPU,
Used: nodeInfo.Requested.MilliCPU,
Capacity: nodeInfo.Allocatable.MilliCPU,
})
}
// 内存判断
if podRequest.Memory > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.Memory - nodeInfo.Requested.Memory) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
ResourceName: v1.ResourceMemory,
Reason: "Insufficient memory",
Requested: podRequest.Memory,
Used: nodeInfo.Requested.Memory,
Capacity: nodeInfo.Allocatable.Memory,
})
}
// 临时存储判断
if podRequest.EphemeralStorage > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.EphemeralStorage - nodeInfo.Requested.EphemeralStorage) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
ResourceName: v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage,
Reason: "Insufficient ephemeral-storage",
Requested: podRequest.EphemeralStorage,
Used: nodeInfo.Requested.EphemeralStorage,
Capacity: nodeInfo.Allocatable.EphemeralStorage,
})
}
// 其他资源
for rName, rQuant := range podRequest.ScalarResources {
// Skip in case request quantity is zero
if rQuant == 0 {
continue
}
if v1helper.IsExtendedResourceName(rName) {
// If this resource is one of the extended resources that should be ignored, we will skip checking it.
// rName is guaranteed to have a slash due to API validation.
var rNamePrefix string
if ignoredResourceGroups.Len() > 0 {
rNamePrefix = strings.Split(string(rName), "/")[0]
}
if ignoredExtendedResources.Has(string(rName)) || ignoredResourceGroups.Has(rNamePrefix) {
continue
}
}
if rQuant > (nodeInfo.Allocatable.ScalarResources[rName] - nodeInfo.Requested.ScalarResources[rName]) {
insufficientResources = append(insufficientResources, InsufficientResource{
ResourceName: rName,
Reason: fmt.Sprintf("Insufficient %v", rName),
Requested: podRequest.ScalarResources[rName],
Used: nodeInfo.Requested.ScalarResources[rName],
Capacity: nodeInfo.Allocatable.ScalarResources[rName],
})
}
}
return insufficientResources
}
打分
func (f *Fit) Score(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *framework.Status) {
nodeInfo, err := f.handle.SnapshotSharedLister().NodeInfos().Get(nodeName)
if err != nil {
return 0, framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("getting node %q from Snapshot: %w", nodeName, err))
}
s, err := getPreScoreState(state)
if err != nil {
s = &preScoreState{
podRequests: f.calculatePodResourceRequestList(pod, f.resources),
}
}
return f.score(pod, nodeInfo, s.podRequests)
}
func (r *resourceAllocationScorer) score(
pod *v1.Pod,
nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo,
podRequests []int64) (int64, *framework.Status) {
node := nodeInfo.Node()
// ...
requested := make([]int64, len(r.resources))
allocatable := make([]int64, len(r.resources))
// 遍历 resources 累加计算 allocatable 和 requested.
for i := range r.resources {
// allocatable 是 node 还可以分配的资源
// req 是 pod 所需要的资源
alloc, req := r.calculateResourceAllocatableRequest(nodeInfo, v1.ResourceName(r.resources[i].Name), podRequests[i])
// Only fill the extended resource entry when it's non-zero.
if alloc == 0 {
continue
}
allocatable[i] = alloc
requested[i] = req
}
// 打分
score := r.scorer(requested, allocatable)
// ...
return score, nil
}
问题: 这种调度策略往往也会在单个节点上产生较多资源碎片。

每个节点都有 1 个 GPU 卡空闲,可是又无法被利用,导致资源 GPU 这种昂贵的资源被浪费。 如果使用的资源调度策略是 Binpack,优先将节点资源填满之后,再调度下一个节点,则上图所出现的资源碎片问题得到解决。

申请 2GPU 的作业被正常调度到节点上,提升了集群的资源使用率。
2 ImageLocality
倾向于选择那些已经拥有请求的pod 容器镜像的节点。
// https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/blob/65faa9c6800dfe97462fd0c8229be1c3435f60fb/pkg/scheduler/framework/plugins/imagelocality/image_locality.go
func (pl *ImageLocality) Score(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *framework.Status) {
nodeInfo, err := pl.handle.SnapshotSharedLister().NodeInfos().Get(nodeName)
if err != nil {
return 0, framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("getting node %q from Snapshot: %w", nodeName, err))
}
nodeInfos, err := pl.handle.SnapshotSharedLister().NodeInfos().List()
if err != nil {
return 0, framework.AsStatus(err)
}
totalNumNodes := len(nodeInfos)
imageScores := sumImageScores(nodeInfo, pod, totalNumNodes)
score := calculatePriority(imageScores, len(pod.Spec.InitContainers)+len(pod.Spec.Containers))
return score, nil
}
// 函数 sumImageScores 遍历 pod 中的初始化容器 InitContainers 和其他容器 Containers,
// 对于每一个容器,它都会检查该容器的镜像是否已经存在于目标节点上。
// 如果存在,它会调用 scaledImageScore 函数来计算这个镜像的得分,并将其累加到总分中。
func sumImageScores(nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo, pod *v1.Pod, totalNumNodes int) int64 {
var sum int64
for _, container := range pod.Spec.InitContainers {
if state, ok := nodeInfo.ImageStates[normalizedImageName(container.Image)]; ok {
sum += scaledImageScore(state, totalNumNodes)
}
}
for _, container := range pod.Spec.Containers {
if state, ok := nodeInfo.ImageStates[normalizedImageName(container.Image)]; ok {
sum += scaledImageScore(state, totalNumNodes)
}
}
return sum
}
// 这个得分是基于镜像的大小计算的,并且会根据节点的总数进行缩放。这样一来,镜像的大小和节点的数量都会影响到最终的得分。
// 这有助于在进行 pod 调度时,优先选择那些已经拥有所需镜像的节点,从而可以减少镜像拉取的时间,加快 pod 的启动速度。
func scaledImageScore(imageState *framework.ImageStateSummary, totalNumNodes int) int64 {
spread := float64(imageState.NumNodes) / float64(totalNumNodes)
return int64(float64(imageState.Size) * spread)