SR-IOV(Single Root I/O Virtualization)
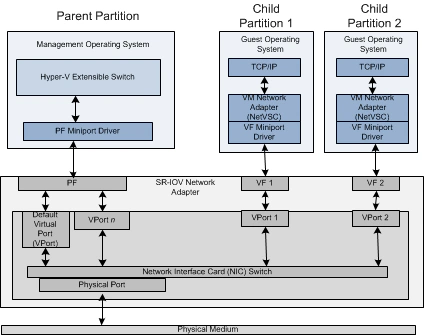
SR-IOV(Single Root I/O Virtualization)是一个将 PCIe(Peripheral Component Interconnect Express 快速外设组件互连)共享给虚拟机的标准,通过为虚拟机提供独立的内存空间、中断、DMA流,来绕过VMM实现数据访问。 SR-IOV基于两种PCIe functions.
- PF (Physical Function):包含完整的PCIe功能,包括SR-IOV的扩张能力,该功能用于SR-IOV的配置和管理。
- VF (Virtual Function):包含轻量级的PCIe功能。每一个VF有它自己独享的PCI配置区域,并且可能与其他VF共享着同一个物理资源. 以Intel 10GE网卡82599为例,PF驱动是标准的ixgbe,VF驱动是ixgbevf。 尽管单个PF理论上可以生成65536个VF,但实际数量受到硬件资源限制,例如82599支持64个VF。
基本知识
linux收包的方式
Linux 内核在收包时有两种方式可供选择,一种是中断方式,另外一种是轮询方式。
一次中断处理需要:
- 将 CPU 的状态寄存器保存到堆栈;
- 运行中断服务程序;
- 再将保存的状态寄存器信息从堆栈中恢复
整个过程需要至少 300 个处理器时钟周期.网络中大量数据包到来时,会频繁产生中断请求,频繁的中断会造成上下文的切换产生时延,产生较高的性能开销。
PMD(Poll Mode Drivers)
一种在用户态基于轮询的驱动程序.
PMD 包含 PMD 应用程序(DPDK程序) + PMD KMOD(pmd kmod: 比如:igb_uio/uio_pci_generic/vfio_pci)
PMD Driver 从网卡上接收到数据包后,会直接通过 DMA 方式传输到预分配的内存中,同时更新无锁环形队列中的数据包指针,不断轮询的应用程序很快就能感知收到数据包,并在预分配的内存地址上直接处理数据包(减少内存拷贝),这个过程非常简洁。
uio_pci_generic 和 igb_uio对比
- uio_pci_generic 是不支持VF设备创建的, igb_uio 支持. igb_uio可以用于宿主机上来创建VF设备。适用性比内核原生的uio_pci_generic更强一些,
- igb_uio.ko是由 dpdk 代码库编译出来的,uio_pci_generic 是原生的,内核自带的
用户态驱动框架
现代系统大多提供DMA和中断重映射功能来确保I/O设备在有限的范围内运行,比如x86平台的AMD-Vi和Intel VT-d。
实现用户态驱动最关键的问题在于如何安全可控的将设备的DMA能力暴露到用户空间,IOMMU的出现可以限制设备对内存的访问,恶意的设备不能直接读写物理内存,经过IOMMU映射之后才能使用IOVA或者虚拟地址进行访存,由IOMMU来保证访存的安全性。
UIO (Userspace I/O)


UIO (Userspace IO) 是 Linux 提供的一款供用户态驱动框架。相比于传统的驱动程序,UIO 仅需安装一个处理硬中断的内核模块,其主要逻辑运行在用户态,通过 read 系统调用感知中断,通过 mmap 系统调用读取设备内存。 但UIO有它的不足之处,如不支持DMA、中断等;
VFIO (Virtual Function I/O)
Virtual Function I/O (VFIO)是一种用户态驱动框架,VFIO是一个可以安全的把设备I/O、中断、DMA等暴露到用户空间(userspace),从而可以在用户空间完成设备驱动的框架。用户空间直接设备访问,虚拟机设备分配可以获得更高的IO性能。
在VFIO驱动框架中,有几个核心概念需要理解。包括:IOMMU,device , group ,container。

- IOMMU是一个硬件单元,它可以把设备的IO地址映射成虚拟地址,为设备提供页表映射,设备通过IOMMU将数据直接DMA写到用户空间。
- Device 是指要操作的硬件设备
- Group 是IOMMU 能进行DMA隔离的最小单元。一个group 可以有一个或者多个device。
IOMMU作用:
- 屏蔽物理地址,起到保护作用。典型应用包括两个:一是实现用户态驱动,由于IOMMU的映射功能,使HPA对用户空间不可见,在vfio部分还会举例。二是将设备透传给虚机,使HPA对虚机不可见,并将GPA映射为HPA.
- IOMMU可以将连续的虚拟地址映射到不连续的多个物理内存片段,这部分功能于MMU类似,对于没有IOMMU的情况,设备访问的物理空间必须是连续的,IOMMU可有效的解决这个问题
DPDK(Intel Data Plane Development Kit)
intel提供的数据平面开发工具集,为Intel architecture(IA)处理器架构下用户空间高效的数据包处理提供库函数和驱动的支持,它不同于Linux系统以通用性设计为目的,而是专注于网络应用中数据包的高性能处理。DPDK应用程序是运行在用户空间上利用自身提供的数据平面库来收发数据包,绕过了Linux内核协议栈对数据包处理过程。
Modalias
Modalias 是 Linux 内核用来识别硬件设备的一种机制。在 Linux 内核中,硬件设备驱动程序需要能够识别并与之交互的硬件设备。 Modalias 字符串包含了设备的基本信息,如设备类型、制造商 ID、设备 ID 等,这些信息被内核用来匹配相应的驱动程
# pci 表示设备遵循 PCI 总线标准,后面的键值对分别表示供应商 ID(vender ID)、设备 ID、子供应商 ID(sub-vendor ID)、子设备 ID(sub-device ID)和设备序列号。
[root@master-01 ~]# cat /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:00.0/modalias
pci:v00008086d00007190sv000015ADsd00001976bc06sc00i00
Modalias 的主要作用是在内核初始化过程中,帮助内核识别新检测到的硬件设备,并找到与之匹配的驱动程序。 当内核发现一个新设备时,它会尝试读取设备的 Modalias 属性,然后通过内核的驱动模型来查找匹配的驱动程序。如果找到了匹配的驱动程序,内核将加载该驱动程序,并允许它管理新检测到的设备。
/sys/bus/pci/devices 目录介绍
# /sys/class目录下 net/scsi_host/fc_host/infiband_host 等 是/sys/bus/pci/devices/*/class下面pci设备的映射,映射到它们指定的类型中
[root@master-01 ~]# ls /sys/class/
ata_device block dmi hidraw iommu msr power_supply scsi_device thermal usbmon
ata_link bsg drm hmm_device leds net ppdev scsi_disk tpm vc
ata_port cpuid drm_dp_aux_dev hwmon mdio_bus pci_bus pwm scsi_generic tpmrm vtconsole
backlight devcoredump gpio i2c-adapter mem pcmcia_socket raw scsi_host tty watchdog
bdi dma graphics input misc powercap rtc spi_master typec
- /sys/class/net/< device name >/device/sriov_numvfs 参数设置了 SR-IOV 网络设备VF数量
/etc/sysconfig/netwrok-scripts/ 目录介绍
与网络接口配置相关的文件,以及控制网络接口状态的脚本文件,全都位于 /etc/sysconfig/netwrok-scripts/ 目录下。 网络接口配置文件用于控制系统中的软件网络接口,并通过这些接口实现对网络设备的控制。 当系统启动时,系统通过这些接口配置文件决定启动哪些接口,以及如何对这些接口进行配置。接口配置文件的名称通常类似于 ifcfg-,其中 与配置文件所控制的设备的名称相关。 在所有的网络接口中,最常用的就是以太网接口ifcfg-eth0,它是系统中第一块网卡的配置文件。
QoS(Quality of Service 服务质量)
三种服务模型:
Best-Effort service 尽力而为服务模型: 不提供任何保证
Integrated service 综合服务模型:
Differentiated service 差分服务模型: 将网络流量分成多个类,不同类按不同优先级处理
VLAN 优先级 priority
802.1P优先级,也叫CoS(Class of Service,服务等级)
SR-IOV 优点
性能提升: SR-IOV通过硬件辅助实现虚拟化,VF可以绕过宿主机直接与硬件交互,减少了数据包处理的延迟,提供了接近原生的性能。
资源利用率: SR-IOV设备能够高效利用物理设备资源,每个VF都有自己的硬件资源,提高了整体资源利用率。
隔离性: 每个VF都是独立的,互不干扰,提高了系统的安全性和稳定性。
可扩展性: 支持更多的虚拟机同时运行,而不会显著降低性能,使其适用于大型虚拟化环境。
SR-IOV 缺点
- VF 数量有限
- ring 结构对于每个 vendor 的 NIC 来说都是独有的。同时,不同 NIC 的配置和控制各不相同,以及对每个 VF 缺少统一的配置、可选项。正是因为这些限制,VFs 需要部署在特定的裸金属服务器上,也就意味着 VNFs 在 host 之间的迁移不是那么容易的。
SR-IOV 基本操作
# 根据domain bus号等信息,查看指定pcie设备的信息,可搭配表1任意参数使用
$ lspci -s 0000:7d:00.0 -vv
7d:00.0 Ethernet controller: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. HNS GE/10GE/25GE RDMA Network Controller (rev 21)
Subsystem: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. Device 0454
Control: I/O- Mem+ BusMaster+ SpecCycle- MemWINV- VGASnoop- ParErr- Stepping- SERR- FastB2B- DisINTx-
Status: Cap+ 66MHz- UDF- FastB2B- ParErr- DEVSEL=fast >TAbort- <TAbort- <MAbort- >SERR- <PERR- INTx-
Latency: 0
NUMA node: 0
Region 0: Memory at 128c00000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=64K]
Region 2: Memory at 120000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=1M]
Capabilities: [40] Express (v2) Endpoint, MSI 00
DevCap: MaxPayload 128 bytes, PhantFunc 0, Latency L0s <64ns, L1 <1us
ExtTag+ AttnBtn- AttnInd- PwrInd- RBE+ FLReset+ SlotPowerLimit 0.000W
DevCtl: CorrErr- NonFatalErr- FatalErr- UnsupReq-
RlxdOrd+ ExtTag+ PhantFunc- AuxPwr- NoSnoop- FLReset-
MaxPayload 128 bytes, MaxReadReq 512 bytes
DevSta: CorrErr- NonFatalErr- FatalErr- UnsupReq- AuxPwr- TransPend-
LnkCap: Port #0, Speed 2.5GT/s, Width x1, ASPM not supported
ClockPM- Surprise- LLActRep- BwNot- ASPMOptComp+
LnkCtl: ASPM Disabled; RCB 64 bytes Disabled- CommClk-
ExtSynch- ClockPM- AutWidDis- BWInt- AutBWInt-
LnkSta: Speed 2.5GT/s (ok), Width x1 (ok)
TrErr- Train- SlotClk- DLActive- BWMgmt- ABWMgmt-
DevCap2: Completion Timeout: Not Supported, TimeoutDis+, NROPrPrP-, LTR-
10BitTagComp-, 10BitTagReq-, OBFF Not Supported, ExtFmt-, EETLPPrefix-
EmergencyPowerReduction Not Supported, EmergencyPowerReductionInit-
FRS-, TPHComp-, ExtTPHComp-
AtomicOpsCap: 32bit- 64bit- 128bitCAS-
DevCtl2: Completion Timeout: 50us to 50ms, TimeoutDis-, LTR-, OBFF Disabled
AtomicOpsCtl: ReqEn-
LnkCtl2: Target Link Speed: 2.5GT/s, EnterCompliance- SpeedDis-
Transmit Margin: Normal Operating Range, EnterModifiedCompliance- ComplianceSOS-
Compliance De-emphasis: -6dB
LnkSta2: Current De-emphasis Level: -6dB, EqualizationComplete-, EqualizationPhase1-
EqualizationPhase2-, EqualizationPhase3-, LinkEqualizationRequest-
Capabilities: [a0] MSI-X: Enable+ Count=131 Masked-
Vector table: BAR=0 offset=00000000
PBA: BAR=0 offset=00008000
Capabilities: [b0] Power Management version 3
Flags: PMEClk- DSI- D1- D2- AuxCurrent=0mA PME(D0-,D1-,D2-,D3hot-,D3cold-)
Status: D0 NoSoftRst- PME-Enable- DSel=0 DScale=0 PME-
Capabilities: [100 v1] Access Control Services
ACSCap: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-
ACSCtl: SrcValid- TransBlk- ReqRedir- CmpltRedir- UpstreamFwd- EgressCtrl- DirectTrans-
Capabilities: [200 v1] Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
IOVCap: Migration-, Interrupt Message Number: 000
IOVCtl: Enable+ Migration- Interrupt- MSE+ ARIHierarchy+
IOVSta: Migration-
Initial VFs: 127, Total VFs: 127, Number of VFs: 127, Function Dependency Link: 00
VF offset: 8, stride: 1, Device ID: a22f
Supported Page Size: 00000553, System Page Size: 00000010
Region 0: Memory at 0000000128c10000 (64-bit, prefetchable)
Region 2: Memory at 0000000120100000 (64-bit, prefetchable)
VF Migration: offset: 00000000, BIR: 0
Capabilities: [300 v1] Transaction Processing Hints
Device specific mode supported
No steering table available
Capabilities: [450 v1] Alternative Routing-ID Interpretation (ARI)
ARICap: MFVC- ACS-, Next Function: 1
ARICtl: MFVC- ACS-, Function Group: 0
Kernel driver in use: hns3
Kernel modules: hclge, hns3, hns_roce_hw_v2
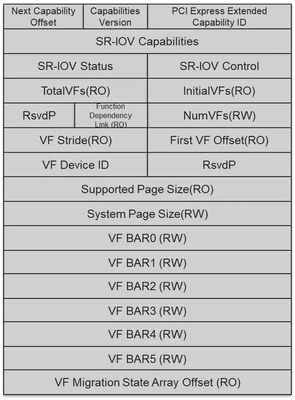
Initial VFs - Indicates to the SR-PCIM the number of VFs that are initially associated with the PF.
Total VFs - Indicates the maximum number of VFs that can be associated with the PF.
Num VFs - Controls the number of VFs that are visible. Num VFs <= Initial VFs = Total VFs.
# 列出网卡
ls /sys/class/net/
eth0 eth1 bond1 lo calixxx
ethX 是真实的物理网卡,bondX 是网络绑定 (bonding) 接口,lo 是本机的 loopback 网络接口,calixxx 是网络插件 Calico 为容器提供的网络接口.
# ethtool命令用于获取以太网卡的配置信息, -i/--driver 显示网卡驱动的信息,如驱动的名称、版本等
$ ethtool -i eno49
driver: igb # 驱动
version: 5.6.0-k
firmware-version: 1.61, 0x80000daa, 1.949.0
expansion-rom-version:
bus-info: 0000:04:00.0 # PCI 地址
supports-statistics: yes
supports-test: yes
supports-eeprom-access: yes
supports-register-dump: yes
supports-priv-flags: yes
# 查看之前是否已经开启 SR-IOV
cat /sys/class/net/eth0/device/sriov_numvfs
# 开启 SR-IOV: 给网卡创建了 2 个 SR-IOV VF
echo 2 > /sys/class/net/eth0/device/sriov_numvfs
$ lspci | grep Virtual
3d:02.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation Ethernet Virtual Function 700 Series (rev 09)
3d:02.1 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation Ethernet Virtual Function 700 Series (rev 09)
# 查看网卡
ip link show eth0
4: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc noop state DOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 90:f7:b2:4b:dc:3d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
vf 0 link/ether 2e:3a:41:bc:02:cc brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, spoof checking on, link-state auto, trust off
vf 1 link/ether 5a:d4:e4:45:83:7b brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, spoof checking on, link-state auto, trust off
altname enp61s0f0
# 删除 SR-IOV VF
echo 0 > /sys/class/net/eth0/device/sriov_numvfs
# 查看厂商、设备 ID
$ lspci -s 0000:3d:00.0 -n
3d:00.0 0200: 8086:37d1 (rev 09) # 8086 就是厂商 ID,37d1 就是设备 ID。
这里需要注意VF设备是不能增量添加的,如果需要修改启动的VF数量,需要先将sriov_numvfs值重置为0后再重新设置为目标值,所以在使用SR-IOV功能最好能确定最多会使用到几个VF,以防在业务运行过程中需要扩展VF数影响正在使用VF的业务。
Linux Kernel version 3.8.x 及以上版本可以通过上述调整 sriov_numvfs 方法动态调整VF数量。 但是,对于 3.7.x 或更低版本,则不能动态调整,而是要在加载内核模块时传递参数:
开启SR-IOV功能后,在/sys/class/net/eth1/device目录下会多出多个virtfnX的目录,这些目录下分别记录了对应VF的信息,例如可以通过ls /sys/class/net/eth1/device/virtfn*/net显示对应vf设备名称. 如果VF已经被放入了其他网络名字空间,那么net目录下会显示为空,例如上图中的virtfn0。
# 查看 pf 下面的 vf
$ ip -d link show eth4
6: eth4: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,SLAVE,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq master bond0 state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether f0:33:e5:a3:92:81 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff promiscuity 0 minmtu 68 maxmtu 9702
bond_slave state ACTIVE mii_status UP link_failure_count 0 perm_hwaddr f0:33:e5:a3:92:85 queue_id 0 ad_aggregator_id 2 ad_actor_oper_port_state 61 ad_partner_oper_port_state 61 addrgenmode none numtxqueues 2 numrxqueues 2 gso_max_size 65536 gso_max_segs 65535
vf 0 link/ether 00:00:00:00:00:00, spoof checking off, link-state auto, trust off
vf 1 link/ether 00:00:00:00:00:00, spoof checking off, link-state auto, trust off
...
# 看 VF 的 net 设备
$ ls /sys/class/net/eth4/device/virtfn*/net
/sys/class/net/eth4/device/virtfn0/net:
/sys/class/net/eth4/device/virtfn100/net:
eth235
/sys/class/net/eth4/device/virtfn101/net:
eth236
/sys/class/net/eth4/device/virtfn102/net:
eth237
/sys/class/net/eth4/device/virtfn103/net:
eth238
...
网卡绑定 bond

网卡bond,即网卡绑定。网卡绑定有多种叫法:Port Trunking, Channel Bonding, Link Aggregation, NIC teaming等等。 主要是将多个物理网卡绑定到一个逻辑网卡上。通过绑定可以达到链路冗余、带宽扩容、负载均衡等目的。 网卡bond一般主要用于网络吞吐量很大,以及对于网络稳定性要求较高的场景,是生产场景中提高性能和可靠性的一种常用技术。
多网卡绑定实际上需要提供一个额外的软件的bond驱动程序实现。通过驱动程序可以将多块网卡屏蔽。 对TCP/IP协议层只存在一个Bond网卡,在Bond程序中实现网络流量的负载均衡,即将一个网络请求重定位到不同的网卡上,来提高总体网络的可用性
怎么看当前bond的mode?
- $ cat /proc/net/bonding/bondX 其中 bondX 是网络绑定接口的名称,其中 X 是数字,表示具体的网络绑定接口编号。
- $ vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0的BONDING_OPTS参数
# 查看 bond 绑定的网卡
$ cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0
Ethernet Channel Bonding Driver: v3.7.1 (April 27, 2011) # 显示网络绑定驱动程序的版本号
Bonding Mode: IEEE 802.3ad Dynamic link aggregation # 显示网络绑定模式,即使用的网络绑定算法
Transmit Hash Policy: layer3+4 (1)
MII Status: up # 显示网络接口的 MII 状态为上线(up)或下线(down)
MII Polling Interval (ms): 100 # 显示 MII 轮询间隔的时间(毫秒)
Up Delay (ms): 0 # 显示网络接口激活时的延迟时间(毫秒)
Down Delay (ms): 0
802.3ad info
LACP rate: slow
Min links: 0
Aggregator selection policy (ad_select): stable
System priority: 65535
System MAC address: --:--:e5:a3:92:81
Active Aggregator Info:
Aggregator ID: 2
Number of ports: 2
Actor Key: 21
Partner Key: 4353
Partner Mac Address: --:--:59:60:10:17
Slave Interface: eth0
MII Status: up
Speed: 25000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 0
Permanent HW addr: --:--:e5:a3:92:81
Slave queue ID: 0
Aggregator ID: 2
Actor Churn State: none
Partner Churn State: none
Actor Churned Count: 0
Partner Churned Count: 0
details actor lacp pdu:
system priority: 65535
system mac address: --:--:e5:a3:92:81
port key: 21
port priority: 255
port number: 1
port state: 61
details partner lacp pdu:
system priority: 17
system mac address: --:--:59:60:10:17
oper key: 4353
port priority: 32768
port number: 4116
port state: 61
Slave Interface: eth4
MII Status: up
Speed: 25000 Mbps
Duplex: full
Link Failure Count: 0
Permanent HW addr: --:--:e5:a3:92:85
Slave queue ID: 0
Aggregator ID: 2
Actor Churn State: none
Partner Churn State: none
Actor Churned Count: 0
Partner Churned Count: 0
details actor lacp pdu:
system priority: 65535
system mac address: --:--:e5:a3:92:81
port key: 21
port priority: 255
port number: 2
port state: 61
details partner lacp pdu:
system priority: 17
system mac address: --:--:59:60:10:17
oper key: 4353
port priority: 32768
port number: 8212
port state: 61
Bond 七种模式
网卡Bond模式总共有7种,最常用的是负载模式(模式0)和主备模式(模式1),在网络流量较大的场景下推荐使用负载模式(Bond0),而在可靠性要求较高的场景下则推荐使用主备模式(Bond1)。
// github.com/vishvananda/netlink/link.go
type BondMode int
// Possible BondMode
const (
BOND_MODE_BALANCE_RR BondMode = iota
BOND_MODE_ACTIVE_BACKUP
BOND_MODE_BALANCE_XOR
BOND_MODE_BROADCAST
BOND_MODE_802_3AD
BOND_MODE_BALANCE_TLB
BOND_MODE_BALANCE_ALB
BOND_MODE_UNKNOWN
)
Mode 0 - Balance-RR(轮询模式 round-robin)
- 描述:链路负载均衡,增加带宽,支持容错,一条链路故障会自动切换正常链路。交换机需要配置聚合口,思科叫port channel。
- 优点:增加网络吞吐量,另外也会增加高可用
- 缺点:不提供冗余性,交换机需要配置trunking。
- 适用场景:报文无冗余,并在存在数据包顺序问题,例如流媒体服务
Mode 1 - Active-Backup(主备模式)
- 原理:主备模式,可以多网卡bond,只有一个网卡传输数据,备网卡均处于就绪状态,在主网卡出故障时接管数据传输任务,接管任务时仍使用原来主网卡的mac,避免切网卡导致网络中断
- 优点:高可用,提供冗余。
- 缺点:端口利用率低,浪费一个网卡的性能。
- 适用场景:需要高可用性的场景。
Mode 2 - Balance-XOR(平衡异或模式)
- 描述:基于源目的mac、传输层协议和端口选择传输的端口,两个口均处于工作中。
- 优点:提供负载均衡。
- 缺点:需要交换机支持链路聚合。
- 适用场景:需要负载均衡且交换机支持链路聚合的环境。
Mode 3 - Broadcast(广播模式)
- 描述:将所有数据包发送到所有接口,所有网卡mac一致。
- 优点:实现广播传输,保证了网络的可靠性。
- 缺点:浪费带宽,可能会导致网络阻塞
- 适用场景:需要高可靠性但不介意带宽浪费的场合,如金融行业。
Mode 4 - 802.3ad(LACP模式)
- 描述:使用LACP协议动态协商,数据传输时使用hash策略,可基于源目的mac,传输层ip端口hash。
- 优点:提供负载均衡和高可用,遵循标准协议。
- 缺点:需要交换机支持LACP。
- 适用场景:交换机支持LACP并且需要高可用和高带宽的场景
Mode 5 - Balance-TLB(自适应传输负载均衡模式)
- 描述:根据网卡当前的负载情况动态调整,使其能够负载均衡
- 优点:提供传输方向的负载均衡,不需要交换机支持。
- 缺点:对于数据接收方不能有负载均衡
Mode 6 - Balance-ALB(自适应负载均衡模式)
- 描述:与mode5类似,不同的是在接收端也支持负载均衡
- 优点:在传输和接收方向上都实现负载均衡,不需要交换机特殊支持。

LACP(Link Aggregation Control Protocol 链路聚合控制协议),链路聚合是一种将设备之间的多个物理链路组合成单个逻辑链路的网络技术。 通过使用链路聚合,可以增加设备之间的通信带宽。 链路聚合技术亦称主干技术(Trunking)或捆绑技术(Bonding)
此外,即使一条物理链路发生故障,也可以使用剩余的物理链路来维护逻辑链路,从而提高容错能力. 链路聚合后来被标准化为 IEEE 802.3ad,它定义了 LACP 的规范。 IEEE 802.3ad 是执行链路聚合的标准方法。 从概念上讲,将多个以太网适配器聚集到单独的虚拟适配器方面与“以太通道(EtherChannel)”的功能相同,能提供更高的带宽防止发生故障。 例如,ent0 和 ent1 可以聚集到称作 ent3 的 IEEE 802.3ad 链路聚合;然后用 IP 地址配置接口 en3。系统将这些聚集的适配器作为一个适配器来考虑。
链路聚合包含两种类型
- 静态 LACP 模式链路聚合: Eth-Trunk 接口的建立,成员接口的加入,都是由手工配置完成的
- 动态 LACP 模式链路: Eth-Trunk 接口的建立,成员接口的加入,活动接口的选择完全由 LACP 协议通过协商完成。
链路聚合控制的相关参数
- Aggregator ID: 在一个设备上,能进行多组聚合,即有多个Aggregator,为了区分这些Aggregator,给每个Aggregator分配了一个聚合ID(Aggregator ID),为一个16位整数
- 操作key : 在动态LACP聚合中,只有操作KEY相同的端口才能属于同一个聚合组,你可以认为操作KEY相同的端口,其属性相
参数介绍
// github.com/vishvananda/netlink/link.go
type Bond struct {
LinkAttrs
Mode BondMode
ActiveSlave int
Miimon int // 指定MII链路监控频率,单位是毫秒(ms)
UpDelay int // 指定当发现一个链路恢复时,在激活该链路之前的等待时间,以毫秒计算。该选项只对miimon链路侦听有效
DownDelay int // 指定一个时间,用于在发现链路故障后,等待一段时间然后禁止一个slave,单位是毫秒(ms)。该选项只对miimon监控有效。
UseCarrier int // 指定miimon是否需要使用MII或者ETHTOOL ioctls还是netif_carrier_ok()来判定链路状态。MII或ETHTOOL ioctls更低效一些,而且使用了内核里废弃的旧调用序列;而netif_carrier_ok()依赖于设备驱动来维护状态(判断载波)
ArpInterval int // 指定ARP链路监控频率,单位是毫秒(ms)。ARP监控不应该和miimon同时使用
ArpIpTargets []net.IP
ArpValidate BondArpValidate
ArpAllTargets BondArpAllTargets
Primary int // 哪个slave成为主设备(primary device),取值为字符串,如eth0,eth1等。只要指定的设备可用,它将一直是激活的slave。只有在主设备(primary device)断线时才会切换设备。primary 选项只对active-backup(mode=1)模式有效。
PrimaryReselect BondPrimaryReselect
FailOverMac BondFailOverMac // 指定 active-backup 模式是否应该将所有从属连接设定为使用同一 MAC 地址作为 enslavement(传统行为),或在启用时根据所选策略执行绑定 MAC 地址的特殊处理。
XmitHashPolicy BondXmitHashPolicy // 分发策略
ResendIgmp int // 指定故障转移事件后要进行的 IGMP 成员报告数。故障转移后会立即提交一个报告,之后会每隔 200 毫秒发送数据包。
NumPeerNotif int
AllSlavesActive int
MinLinks int
LpInterval int
PacketsPerSlave int
LacpRate BondLacpRate
AdSelect BondAdSelect // 指定要使用的 802.3ad(mode=4) 聚合选择逻辑
// looking at iproute tool AdInfo can only be retrived. It can't be set.
AdInfo *BondAdInfo
AdActorSysPrio int
AdUserPortKey int
AdActorSystem net.HardwareAddr
TlbDynamicLb int
}
xmit_hash_policy
layer2: 使用二层帧头作为计算分发出口的参数,这导致通过同一个网关的数据流将完全从一个端口发送,为了更加细化分发策略,必须使用一些三层信息,然而却增加了计算开销。
layer2+3: 在1的基础上增加了三层的ip报头信息,计算量增加了,然而负载却更加均衡了,一个个主机到主机的数据流形成并且同一个流被分发到同一个端口,根据这个思想,如果要使负载更加均衡,我们在继续增加代价的前提下可以拿到4层的信息。
layer3+4: 该策略在可能的时候使用上层协议的信息来生成hash。这将允许特定网络对(network peer)的流量分摊到多个slave上,尽管同一个连接(connection)不会分摊到多个slave上。
bond 创建的一般流程
# 配置逻辑网卡bond0
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-bond0
DEVICE=bond0
BOOTPROTO=static
IPADDR=192.168.10.1
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.10.254
ONBOOT=yes
TYPE=Ethernet
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0
BOOTPROTO=static
ONBOOT=yes
MASTER=bond0
SLAVE=yes # 可以没有此字段,就需要开机执行ifenslave bond0 eth0 eth1命令了
$ cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth1
DEVICE=eth1
BOOTPROTO=static
ONBOOT=yes
MASTER=bond0
SLAVE=yes
# 加载模块,让系统支持bonding
$ cat /etc/ modprobe.conf
...
alias bond0 bonding
options bond0 miimon=100 mode=0
$ cat /etc/rc.d/rc.local
...
ifenslave bond0 eth0 eth1
route add -net 172.31.3.254 netmask 255.255.255.0 bond0
$ service network restart
Step 1、创建slave口
Step 2、slave口配置网卡队列、网口启动
Step 3、创建bond口
Step 4、bond口添加slave口
Step 5、bond口配置网卡队列、网口启动
Step 6、通过bond口id进行收发包
// https://github.com/k8snetworkplumbingwg/bond-cni/blob/9f57b80f66ccfcba6167dba560b8b93184177cd4/bond/bond.go
func createBond(bondName string, bondConf *bondingConfig, nspath string, ns ns.NetNS) (*current.Interface, error) {
bond := ¤t.Interface{}
// get the namespace from the CNI_NETNS environment variable
netNs, err := netns.GetFromPath(nspath)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to retrieve netNs from path (%+v), error: %+v", nspath, err)
}
defer netNs.Close()
// get a handle for the namespace above, this handle will be used to interact with existing links and add a new one
netNsHandle, err := netlink.NewHandleAt(netNs)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to create a new handle at netNs (%+v), error: %+v", netNs, err)
}
defer netNsHandle.Close()
if !bondConf.LinksContNs {
if err := setLinksInNetNs(bondConf, nspath, false); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to move the links (%+v) in container network namespace, error: %+v", bondConf.Links, err)
}
}
// 获取需要绑定的网络设备
linkObjectsToBond, err := getLinkObjectsFromConfig(bondConf, netNsHandle, false)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to retrieve link objects from configuration file (%+v), error: %+v", bondConf, err)
}
err = util.ValidateMTU(linkObjectsToBond, bondConf.MTU)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if bondConf.FailOverMac < 0 || bondConf.FailOverMac > 2 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("FailOverMac mode should be 0, 1 or 2 actual: %+v", bondConf.FailOverMac)
}
// 创建 网卡绑定
bondLinkObj, err := createBondedLink(bondName, bondConf.Mode, bondConf.Miimon, bondConf.MTU, bondConf.FailOverMac, netNsHandle)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to create bonded link (%+v), error: %+v", bondName, err)
}
// 网卡绑定添加slave口
err = attachLinksToBond(bondLinkObj, linkObjectsToBond, netNsHandle)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to attached links to bond, error: %+v", err)
}
if err := netNsHandle.LinkSetUp(bondLinkObj); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to set bond link UP, error: %v", err)
}
bond.Name = bondName
// Re-fetch interface to get all properties/attributes
contBond, err := netNsHandle.LinkByName(bond.Name)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to refetch bond %q: %v", bond.Name, err)
}
bond.Mac = contBond.Attrs().HardwareAddr.String()
bond.Sandbox = ns.Path()
return bond, nil
}
func getLinkObjectsFromConfig(bondConf *bondingConfig, netNsHandle *netlink.Handle, releaseLinks bool) ([]netlink.Link, error) {
linkNames := []string{}
for _, linkName := range bondConf.Links {
s, ok := linkName["name"].(string)
if !ok {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to find link name")
}
linkNames = append(linkNames, s)
}
// 保证2个网络设备以上
if len(linkNames) < 2 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Bonding requires at least two links, we have %+v", len(linkNames))
}
linkObjectsToBond := []netlink.Link{}
for _, linkName := range linkNames {
linkObject, err := netNsHandle.LinkByName(linkName)
if err != nil {
// Do not fail if device in container assigned to the bond has been deleted.
// This device might have been deleted by another plugin.
_, ok := err.(netlink.LinkNotFoundError)
if !ok || !releaseLinks {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Failed to confirm that link (%+v) exists, error: %+v", linkName, err)
}
} else {
linkObjectsToBond = append(linkObjectsToBond, linkObject)
}
}
return linkObjectsToBond, nil
}
func attachLinksToBond(bondLinkObj *netlink.Bond, linkObjectsToBond []netlink.Link, netNsHandle *netlink.Handle) error {
err := util.HandleMacDuplicates(linkObjectsToBond, netNsHandle)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Failed to handle duplicated macs on link slaves, error: %+v", err)
}
bondLinkIndex := bondLinkObj.LinkAttrs.Index
for _, linkObject := range linkObjectsToBond {
err = netNsHandle.LinkSetDown(linkObject)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Failed to set link: %+v DOWN, error: %+v", linkObject.Attrs().Name, err)
}
err = netNsHandle.LinkSetMasterByIndex(linkObject, bondLinkIndex)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Failed to set link: %+v MASTER, master index used: %+v, error: %+v", linkObject.Attrs().Name, bondLinkIndex, err)
}
err = netNsHandle.LinkSetUp(linkObject)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("Failed to set link: %+v UP, error: %+v", linkObject.Attrs().Name, err)
}
}
return nil
}
SR-IOV 在 k8s 中应用
intel官方也给出了SR-IOV技术在容器中使用的开源组件,例如:sriov-cni 和 sriov-device-plugin等.

sriov-device-plugin–>vf 分配
// https://github.com/k8snetworkplumbingwg/sriov-network-device-plugin/blob/d7bd80381b00f5e0818cabcca69edb5f53149bd6/pkg/resources/server.go
func (rs *resourceServer) Allocate(ctx context.Context, rqt *pluginapi.AllocateRequest) (*pluginapi.AllocateResponse, error) {
glog.Infof("Allocate() called with %+v", rqt)
resp := new(pluginapi.AllocateResponse)
for _, container := range rqt.ContainerRequests {
containerResp := new(pluginapi.ContainerAllocateResponse)
envs, err := rs.getEnvs(container.DevicesIDs)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("failed to get environment variables for device IDs %v: %v", container.DevicesIDs, err)
return nil, err
}
if rs.useCdi {
containerResp.Annotations, err = rs.cdi.CreateContainerAnnotations(
container.DevicesIDs, rs.resourceNamePrefix, rs.resourcePool.GetCDIName())
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("can't create container annotation: %s", err)
}
} else {
containerResp.Devices = rs.resourcePool.GetDeviceSpecs(container.DevicesIDs)
containerResp.Mounts = rs.resourcePool.GetMounts(container.DevicesIDs)
}
// 保存分配的信息到文件中
err = rs.resourcePool.StoreDeviceInfoFile(rs.resourceNamePrefix, container.DevicesIDs)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("failed to store device info file for device IDs %v: %v", container.DevicesIDs, err)
return nil, err
}
containerResp.Envs = envs
resp.ContainerResponses = append(resp.ContainerResponses, containerResp)
}
glog.Infof("AllocateResponse send: %+v", resp)
return resp, nil
}
这里 netdevice 作为例子
func (rp *netResourcePool) GetDeviceSpecs(deviceIDs []string) []*pluginapi.DeviceSpec {
glog.Infof("GetDeviceSpecs(): for devices: %v", deviceIDs)
devSpecs := make([]*pluginapi.DeviceSpec, 0)
devicePool := rp.GetDevicePool()
// Add device driver specific and rdma specific devices
for _, id := range deviceIDs {
if dev, ok := devicePool[id]; ok {
netDev := dev.(types.PciNetDevice) // convert generic HostDevice to PciNetDevice
newSpecs := netDev.GetDeviceSpecs()
for _, ds := range newSpecs {
if !rp.DeviceSpecExist(devSpecs, ds) {
devSpecs = append(devSpecs, ds)
}
}
}
}
return devSpecs
}
sriov-cni–>将SR-IOV VF 放入容器Namespace
func cmdAdd(args *skel.CmdArgs) error {
// 解析配置以及参数
// 获取当前的namespace
netns, err := ns.GetNS(args.Netns)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to open netns %q: %v", netns, err)
}
defer netns.Close()
sm := sriov.NewSriovManager()
// 补充原始信息
err = sm.FillOriginalVfInfo(netConf)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to get original vf information: %v", err)
}
defer func() {
if err != nil {
err := netns.Do(func(_ ns.NetNS) error {
_, err := netlink.LinkByName(args.IfName)
return err
})
if err == nil {
_ = sm.ReleaseVF(netConf, args.IfName, netns)
}
// Reset the VF if failure occurs before the netconf is cached
_ = sm.ResetVFConfig(netConf)
}
}()
if err := sm.ApplyVFConfig(netConf); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("SRIOV-CNI failed to configure VF %q", err)
}
result := ¤t.Result{}
result.Interfaces = []*current.Interface{{
Name: args.IfName,
Sandbox: netns.Path(),
}}
if !netConf.DPDKMode {
// 主要将 vf 放入容器 namespace
err = sm.SetupVF(netConf, args.IfName, netns)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to set up pod interface %q from the device %q: %v", args.IfName, netConf.Master, err)
}
}
result.Interfaces[0].Mac = config.GetMacAddressForResult(netConf)
// check if we are able to find MTU for the virtual function
if netConf.MTU != nil {
result.Interfaces[0].Mtu = *netConf.MTU
}
doAnnounce := false
// run the IPAM plugin
if netConf.IPAM.Type != "" {
// 分配 ip
}
// Cache NetConf for CmdDel
logging.Debug("Cache NetConf for CmdDel",
"func", "cmdAdd",
"config.DefaultCNIDir", config.DefaultCNIDir,
"netConf", netConf)
if err = utils.SaveNetConf(args.ContainerID, config.DefaultCNIDir, args.IfName, netConf); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error saving NetConf %q", err)
}
// Mark the pci address as in use.
logging.Debug("Mark the PCI address as in use",
"func", "cmdAdd",
"config.DefaultCNIDir", config.DefaultCNIDir,
"netConf.DeviceID", netConf.DeviceID)
// 记录设备已分配
allocator := utils.NewPCIAllocator(config.DefaultCNIDir)
if err = allocator.SaveAllocatedPCI(netConf.DeviceID, args.Netns); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("error saving the pci allocation for vf pci address %s: %v", netConf.DeviceID, err)
}
if doAnnounce {
// arp 设置
}
return types.PrintResult(result, netConf.CNIVersion)
}
加载配置
func LoadConf(bytes []byte) (*sriovtypes.NetConf, error) {
n := &sriovtypes.NetConf{}
if err := json.Unmarshal(bytes, n); err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("LoadConf(): failed to load netconf: %v", err)
}
// DeviceID takes precedence; if we are given a VF pciaddr then work from there
if n.DeviceID != "" {
// Get rest of the VF information
pfName, vfID, err := getVfInfo(n.DeviceID)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("LoadConf(): failed to get VF information: %q", err)
}
n.VFID = vfID
n.Master = pfName
} else {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("LoadConf(): VF pci addr is required")
}
// Check if the device is already allocated.
// This is to prevent issues where kubelet request to delete a pod and in the same time a new pod using the same
// vf is started. we can have an issue where the cmdDel of the old pod is called AFTER the cmdAdd of the new one
// This will block the new pod creation until the cmdDel is done.
logging.Debug("Check if the device is already allocated",
"func", "LoadConf",
"DefaultCNIDir", DefaultCNIDir,
"n.DeviceID", n.DeviceID)
allocator := utils.NewPCIAllocator(DefaultCNIDir)
isAllocated, err := allocator.IsAllocated(n.DeviceID)
if err != nil {
return n, err
}
if isAllocated { // 如果已经分配
return n, fmt.Errorf("pci address %s is already allocated", n.DeviceID)
}
// Assuming VF is netdev interface; Get interface name(s)
hostIFName, err := utils.GetVFLinkName(n.DeviceID)
if err != nil || hostIFName == "" {
// VF interface not found; check if VF has dpdk driver
hasDpdkDriver, err := utils.HasDpdkDriver(n.DeviceID)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("LoadConf(): failed to detect if VF %s has dpdk driver %q", n.DeviceID, err)
}
n.DPDKMode = hasDpdkDriver
}
if hostIFName != "" {
n.OrigVfState.HostIFName = hostIFName
}
// 参数校验,主要vlan信息,LinkState状态
return n, nil
}
// ApplyVFConfig configure a VF with parameters given in NetConf
func (s *sriovManager) ApplyVFConfig(conf *sriovtypes.NetConf) error {
pfLink, err := s.nLink.LinkByName(conf.Master)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to lookup master %q: %v", conf.Master, err)
}
// 1. Set vlan
if conf.Vlan != nil {
// 如果有vlan的配置项,会继续判断vlanqos的配置,如果有则调用s.nLink.LinkSetVfVlanQos配置,没有则只配置vlan,调用s.nLink.LinkSetVfVlan
if err = s.nLink.LinkSetVfVlanQosProto(pfLink, conf.VFID, *conf.Vlan, *conf.VlanQoS, sriovtypes.VlanProtoInt[*conf.VlanProto]); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to set vf %d vlan configuration - id %d, qos %d and proto %s: %v", conf.VFID, *conf.Vlan, *conf.VlanQoS, *conf.VlanProto, err)
}
}
// 2. Set mac address
if conf.MAC != "" {
// mac配置项
// when we restore the original hardware mac address we may get a device or resource busy. so we introduce retry
if err := utils.SetVFHardwareMAC(s.nLink, conf.Master, conf.VFID, conf.MAC); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to set MAC address to %s: %v", conf.MAC, err)
}
}
// 3. Set min/max tx link rate. 0 means no rate limiting. Support depends on NICs and driver.
// 速率限制
var minTxRate, maxTxRate int
rateConfigured := false
if conf.MinTxRate != nil {
minTxRate = *conf.MinTxRate
rateConfigured = true
}
if conf.MaxTxRate != nil {
maxTxRate = *conf.MaxTxRate
rateConfigured = true
}
if rateConfigured {
if err = s.nLink.LinkSetVfRate(pfLink, conf.VFID, minTxRate, maxTxRate); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to set vf %d min_tx_rate to %d Mbps: max_tx_rate to %d Mbps: %v",
conf.VFID, minTxRate, maxTxRate, err)
}
}
// 4. Set spoofchk flag
if conf.SpoofChk != "" {
spoofChk := false
if conf.SpoofChk == "on" {
spoofChk = true
}
if err = s.nLink.LinkSetVfSpoofchk(pfLink, conf.VFID, spoofChk); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to set vf %d spoofchk flag to %s: %v", conf.VFID, conf.SpoofChk, err)
}
}
// 5. Set trust flag
if conf.Trust != "" {
trust := false
if conf.Trust == "on" {
trust = true
}
if err = s.nLink.LinkSetVfTrust(pfLink, conf.VFID, trust); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to set vf %d trust flag to %s: %v", conf.VFID, conf.Trust, err)
}
}
// 6. Set link state
if conf.LinkState != "" {
var state uint32
switch conf.LinkState {
case "auto":
state = netlink.VF_LINK_STATE_AUTO
case "enable":
state = netlink.VF_LINK_STATE_ENABLE
case "disable":
state = netlink.VF_LINK_STATE_DISABLE
default:
// the value should have been validated earlier, return error if we somehow got here
return fmt.Errorf("unknown link state %s when setting it for vf %d: %v", conf.LinkState, conf.VFID, err)
}
if err = s.nLink.LinkSetVfState(pfLink, conf.VFID, state); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to set vf %d link state to %d: %v", conf.VFID, state, err)
}
}
// Copy the MTU value to a new variable
// and use it as a pointer
pfMtu := pfLink.Attrs().MTU
conf.MTU = &pfMtu
return nil
}
补充 vf 信息
func (s *sriovManager) FillOriginalVfInfo(conf *sriovtypes.NetConf) error {
// 获取网络设备
pfLink, err := s.nLink.LinkByName(conf.Master)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to lookup master %q: %v", conf.Master, err)
}
// Save current the VF state before modifying it
vfState := getVfInfo(pfLink, conf.VFID)
if vfState == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to find vf %d", conf.VFID)
}
conf.OrigVfState.FillFromVfInfo(vfState)
return err
}
func getVfInfo(link netlink.Link, id int) *netlink.VfInfo {
attrs := link.Attrs()
for _, vf := range attrs.Vfs {
if vf.ID == id {
return &vf
}
}
return nil
}
重要工具函数
// https://github.com/k8snetworkplumbingwg/sriov-cni/blob/36e2d17af18803d0a1ced3c0c62a33b321d05a5b/pkg/utils/utils.go
var (
sriovConfigured = "/sriov_numvfs"
// NetDirectory sysfs net directory
NetDirectory = "/sys/class/net"
// SysBusPci is sysfs pci device directory
SysBusPci = "/sys/bus/pci/devices"
// SysV4ArpNotify is the sysfs IPv4 ARP Notify directory
SysV4ArpNotify = "/proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/"
// SysV6NdiscNotify is the sysfs IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Notify directory
SysV6NdiscNotify = "/proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/"
// UserspaceDrivers is a list of driver names that don't have netlink representation for their devices
UserspaceDrivers = []string{"vfio-pci", "uio_pci_generic", "igb_uio"}
)
// 通过 vf pci 反向获取 pf name
func GetPfName(vf string) (string, error) {
pfSymLink := filepath.Join(SysBusPci, vf, "physfn", "net")
_, err := os.Lstat(pfSymLink)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
files, err := os.ReadDir(pfSymLink)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
if len(files) < 1 {
return "", fmt.Errorf("PF network device not found")
}
return strings.TrimSpace(files[0].Name()), nil
}
// 根据 pci 地址及 pf 获取 vf id
func GetVfid(addr string, pfName string) (int, error) {
var id int
vfTotal, err := GetSriovNumVfs(pfName)
if err != nil {
return id, err
}
for vf := 0; vf < vfTotal; vf++ {
vfDir := filepath.Join(NetDirectory, pfName, "device", fmt.Sprintf("virtfn%d", vf))
_, err := os.Lstat(vfDir)
if err != nil {
continue
}
pciinfo, err := os.Readlink(vfDir) // readlink用于显示符号链接的值,即符号链接所指向的实际文件或目录的路径
if err != nil {
continue
}
pciaddr := filepath.Base(pciinfo)
if pciaddr == addr {
return vf, nil
}
}
return id, fmt.Errorf("unable to get VF ID with PF: %s and VF pci address %v", pfName, addr)
}
参考
- https://github.com/k8snetworkplumbingwg/sriov-cni
- https://github.com/k8snetworkplumbingwg/sriov-network-device-plugin
- https://github.com/k8snetworkplumbingwg/bond-cni
- https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/how-to-configure-high-availability-and-network-bonding-on-linux/
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/network/overview-of-single-root-i-o-virtualization--sr-iov-
- https://projectacrn.github.io/latest/tutorials/sriov_virtualization.html
- https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/v4.18/driver-api/uio-howto.html
- SR-IOV 技术及在 Pod 中使用
- SR-IOV vs DPDK
- BONDING_OPTS参数详细说明
- PCI 解释
- Single Root IO Virtualization (SR-IOV)二:SR-IOV 配置
- Linux 内核 Modalias 解析详尽教程
- NVMe协议基础原理介绍
- NVMe存储 全解
- ARM SMMU原理与IOMMU技术